Summary
Morphometric analysis by light microscopy of p-phenylene-diamine stained semithin sections of axolotl tail muscle revealed differences in the cross-sectional area of the fibres and in the number of mitochondria and of lipid inclusions per fibre, and indicated the presence of three distinct types of fibres. The tripartition was found to be statistically highly significant.
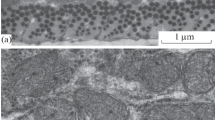
Representative fibres from each group established by light microscopic morphometry were subjected to an ultrastructural morphometric analysis. The volume content of mitochondria amounted to 9.8% of the fibre volume for red, 4.0% for intermediate and 0.8% for white fibres. The myofibrils composed 60%, 70% and 83% in the same fibres. The volume of the sarcotubular system (t-tubuli and sarcoplasmic reticulum) was 2.5% in red, 4.5% in intermediate and 11.7% in white fibres. The three fibre types also demonstrated differences in myofibrillar cross-striation pattern and number of triads. The reliability of the light microscopic morphometry was tested by correlation with EM montages of the representative fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bone, Q.: On the function of the two types of myotomal muscle in elasmobranch fish. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 46, 321–349 (1966)
Brunst, V.V.: The axolotl (Siredon mexicanum). II. Morphology and Pathology. Lab. Invest. 4, 429–449 (1955)
Burke, R.E., Levine, D.N., Tsairis, P., Zajac, F.E.: Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 723–748 (1973)
Dubowitz, V., Pearse, A.G.E.: A comparative histochemical study of oxidative enzymes and phosphorylase activity in skeletal muscle. Histochemie 2, 105–117 (1960)
Flood, P.R.: Structure of the segmental trunk muscle in the amphioxus. With notes on the course and “endings” of the so-called ventral root fibres. Z. Zellforsch. 84, 389–416 (1968)
Flood, P.R.: The skeletal muscle fibre types of Myxine glutinosa L. related to those of other chordates. In: Myxine glutinosa Symposium. Acta Regia Societatis Scientiarum et Litterarum Gothoburgensis. Zoologica 8, 17–21 (1973)
Flood, P.R., Storm Mathisen, J.: A third type of muscle fiber in the parietal muscle of the atlantic hagfish, Myxine glutinosa. Z. Zellforsch. 58, 638–640 (1962)
Francis, L.T.B.: The anatomy of the salamander. Oxford: Carendon Press 1934
Gilev, V.P.: Electron microscope examination of skeletal muscle of the axolotl. Usp. sovrem. Biol. 41, 97–102 (1956)
Hay, E.: The fine structure of differentiating muscle in the salamander tail. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 6–34 (1965)
Jasper, D.: Body muscles of the lamprey. Some structural features of the T-system and sarcolemma. J. Cell Biol. 32, 219–227 (1967)
Kilarski, W.: The fine structure of striated muscle in teleosts. Z. Zellforsch. 79, 562–580 (1970)
Korneliussen, H.: Identification of muscle fiber types in “semithin” sections stained with p-phenylene-diamine. Histochemie 32, 95–98 (1972)
Korneliussen, H., Nicolaysen, K.: Ultrastructure of four types of striated muscle fibres in the Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa L.). Z. Zellforsch. 143, 273–290 (1973)
Lie, H.R.: A quantitative identification of three muscle fiber types in the body muscle of Lampe t ra Fluviatilis and their relation to blood capillaries. Cell Tiss. Res. 134, 109–119 (1974)
Nag, A.G.: Ultrastructure and adenosine triphosphate activity of red and white muscle fibers of the caudal region of a fish, Salmo gairdneri. J. Cell Biol. 55, 42–57 (1972)
Page, S.G.: A comparison of the fine structure of frog slow and twich muscle fibers. J. Cell Biol. 26, 477–497 (1965)
Patterson, S., Goldspink, G.: The fine structure of red and white myotomal muscle fibers of the coalfish (Gadus virens). Z. Zellforsch. 133, 463–474 (1972)
Porter, K.R., Palade, G.E.: Studies on endoplasmic reticulum. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 269–300 (1957)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead nitrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Samaha, F.J., Lloyd, G., Albers, R.W.: Phenotypic differences between the actomyosin ATPase of the three fiber types of mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol. 26, 120–125 (1970)
Sherkov, H.K.: Morpho-physiological characterization of peripheral motor apparatus in Salamandra salamandra. Zur. evol. biochem. fiziol. 6, 467–469 (1970)
Totland, G. K.: Histological and histochemical studies of segmental muscle in the axolotl Ambystoma mexicanum Shaw (Amphibia: Urodela). Norw. J. Zool. 24, 79–90 (1976)
Voss, H.: Das histologische Bild der Axolotlmuskulatur, insbesondere die quergestreiften Ringbinden der Muskelfasern. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 28, 161–184 (1932)
Waterman, R.E.: Development of the lateral musculature in the teleost, Brachydanio rerio. A fine structural study. Amer. J. Anat. 125, 457–494 (1969)
Watson, M.L.W.: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 475–478 (1958)
Weibel, E.R.: Stereological techniques for electron microscopic morphometry. In: Principles and Techniques of electron microscopy. Vol. III (M.A. Hayat, ed.). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Comp. 1973
Weibel, E.R., Elias, H.: Quantitative methods in morphology. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1967
Willemse, J.J.: Arrangements of connective tissue fibres and muscle fibres in the tail musculature of adult newts. Z. Morph. Tiere 77, 255–269 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author would like to express his thanks to Dr. Per R. Flood for his critical revision of the manuscript. I also wish to thank Mrs. Siri Nome Eikhom for advice on the statistical analysis, and Norwegian Research Council for Science and Humanities for financial support
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Totland, G.K. Three muscle fibre types in the axial muscle of axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum Shaw) A quantitative lightand electron microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res. 168, 65–78 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219724
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219724