Summary
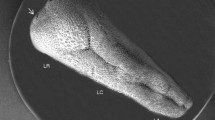
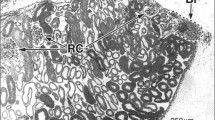
The nine-banded armadillo possesses a salivary bladder which is a dilated portion of the main duct of the submandibular gland at its origin. The wall of the bladder is composed of an epithelium, a submucosa and a thick coat of skeletal muscle. The ultrastructure of the epithelium reveals that it is complex and consists of three cell types: 1) principal cells, 2) light cells, and 3) basal cells. The general organization of the epithelium suggests that it is a transporting type of epithelium such as that found in the amphibian and reptilian urinary bladders and the mammalian gall bladder. The submucosa is composed primarily of densely-packed collagen fibers. The skeletal muscle is very vascular and richly innervated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chevalier, J., Ripoche, P., Pisam, M., Bourguet, J., Hugon, J.S.: A time course study of water permeability and morphological alterations induced by mucosal hyperosmolarity in frog urinary bladder. Cell Tiss. Res. 154, 345–356 (1974)
Choi, J.K.: The fine structure of the urinary bladder of the toad, Bufo marinus. J. Cell Biol. 16, 53–72 (1963)
Claude, P., Goodenough, D.A.: Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from “tight” and “leaky” epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 58, 390–400 (1973)
Diamond, J.M., Bessert, W.H.: Standing gradient osmotic flow. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2061–2083 (1967)
DiBona, D.R., Civan, M.M., Leaf, A.: The cellular specificity of the effect of vasopressin on toad urinary bladder. J. Membr. Biol. 1, 79–91 (1969)
Fahrenholz, C.: In: Handbuch der vergleichenden Anatomie der Wirbeltiere (eds.: Bolk, L., Göppert, E., Kallius, E., Lubosch, W.), Bd. III, S. 176–177. Berlin-Wien: Urban & Schwarzenberg 1937
Ferguson, D.R., Heap, P.F.: The morphology of the toad urinary bladder: A stereoscopic and transmission electron microscopical study. Z. Zellforsch. 109, 297–305 (1970)
Friend, D.S., Gilula, N.B.: Variations in tight and gap junctions in mammalian tissues. J. Cell Biol. 53, 758–776 (1972)
Frömter, E., Diamond, J.M.: Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nature (Lond.) New Biol. 235, 9–13 (1972)
Karnovsky, M.J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 27, 137A-138A (1965)
Kaye, G.I., Wheeler, H.O., Whitlock, R.T., Lane, N.: Fluid transport in the rabbit gallbladder. A combined physiological and electron microscope study. J. Cell Biol. 30, 237–268 (1966)
Mollenhauer, H.H.: Plastic embedding mixtures for use in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 39, 111–114 (1964)
Padykula, H.A., Gauthier, G.F.: In: Exploratory concepts in muscular dystrophy and related disorders (ed.: Milhorat, J.), p. 117. Amsterdam: Excerpta Med. Found. 1967
Pak Poy, R.F.K., Bentley, P.J.: Fine structure of the epithelial cells of the toad urinary bladder. Exp. Cell Res. 20, 235–237 (1960)
Peachey, L.D., Rasmussen, H.: Structure of the toad's urinary bladder as related to its physiology. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 101, 529–553 (1961)
Pearse, A.G.E.: In: Histochemistry: Theoretical and applied, vol. I, p. 659. Boston: Little, Brown and Co. 1968
Pouchet, M.G.: Des conditions anatomiques de la fonction salivaire sousmaxillaire chez les édentés. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 66, 670 (1868)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Rosen, S.: The turtle bladder. I. Morphological studies under varying conditions of fixation. Exp. molec. Path. 12, 286–296 (1970a)
Rosen, S.: Localization of carbonic anhydrase activity in transporting urinary epithelia. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 668–670 (1970b)
Shackleford, J.M.: The salivary glands and salivary bladder of the nine-banded armadillo. Anat. Rec. 145, 513–519 (1963)
Shackleford, J.M., Wilborn, W.H.: Structural and histochemical diversity in mammalian salivary glands. Ala. J. med. Sci. 5, 180–203 (1968)
Staehelin, L.A.: Structure and function of intercellular junctions. Int. Rev. Cytol. 39, 191–283 (1974)
Strum, J.M., Danon, D.: Comparative ultrastructural analysis of two tortoise bladders, Testudo graeca and Geochelone carbonaria. Anat. Rec. 184, 97–110 (1976)
Takada, M.: Fenestrated capillaries seen in most organs of the digestive system. Nagoya med. J. 15, 29–30 (1969)
Takada, M.: Fenestrated venules of the large salivary glands. Anat. Rec. 166, 605–610 (1970)
Tormey, J. McD., Diamond, J.M.: The ultrastructural route of fluid transport in rabbit gallbladder. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2031–2060 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported in part by a research grant from U.S.P.H.S. (GRS 5-S01-RR-05705)
The authors wish to acknowledge the technical assistance of Elizabeth Underwood
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruby, J.R., Raworth Allen, E. Ultrastructure of the salivary bladder of the nine-banded armadillo. Cell Tissue Res. 169, 383–394 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219609
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219609