Summary
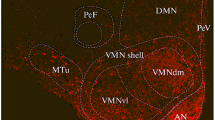
Using a highly sensitive antibody to somatostatin, its hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic distribution in the rat was re-examined by light microscopic immunohistochemistry (PAP-method). The scattered somatostatin-producing perikarya occur in multiple layers within the subependymal neuropil surrounding the third ventricle. They supply with short-distance projections the following hypothalamic nuclei: 1) preoptic nuclei (especially their suprachiasmatic and medial components), 2) the peripheral zones of the suprachiasmatic nuclei, 3) the ventromedial and 4) arcuate nuclei, and 5) the ventral premammillary nuclei. Furthermore, the following long-distance projections have been observed: In a rostral direction (A1) rostral of the anterior commissure to the lamina terminalis, (A2) to the OVLT, (A3) to the olfactory tubercle, and (A4) rostrally and caudally by-passing the anterior commissure to the dorsal part of the stria terminalis.
More caudally, at the retrochiasmatic level an ascending dorso-lateral projection joins the ventral amygdalo-hypothalamic pathway in a reciprocal manner (B1). In addition, a descending ventrolateral tract projects to the optic tract bending dorsal to it in different directions: (C1) medial to the median eminence, (C2) lateral to the corticomedial amygdala, and (C3) caudal for additional support of the arcuate and ventral premammillary nuclei.
The principal tract of somatostatin-containing fibers descends in the subependymal neuropil to the median eminence (D).
The results are discussed with reference to a possible participation of the somatostatin fiber system in the afferent branch of the circuit connecting the hypothalamus with the amygdala via the stria terminalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajika, K., Hökfelt, T.: Projections to the median eminence and the arcuate nucleus with special reference to monoamine systems: Effects of lesions. Cell Tissue Res. 158, 15–35 (1975)
Brazeau, P., Martin, J.B.: unpublished results, cited by Martin, J.B., 1976
Brownstein, M., Arimura, A., Sato, H., Schally, A.V., Kizer, J.S.: The regional distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain. Endocrinol. 96, 1456–1462 (1975)
Carson, K.A., Nemeroff, Ch.B., Rone, M.S., Youngblood, W.W., Prange, A.J., Hanker, J.S., Kizer, J.S.: Biochemical and histochemical evidence for the existence of a tuberoinfundibular cholinergic pathway in the rat. Brain Res. 129, 169–173 (1977)
Conrad, C.D., Stumpf, W.E.: Endocrine-optic pathways to the hypothalamus. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 15–29 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Dhariwal, A.P.S., Krulich, L., McCann, S.M.: Purification of growth hormone inhibiting factor (GIF) from sheep hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinol. 4, 282–288 (1969)
Döcke, F., Moldenhauer, U.: Influence of the mediocortical amygdala on PMSG (serum gonadotropin) -induced ovulation in immature female rats. Endokrinol. 70, 19–26 (1977)
Döcke, F., Rohde, W., Moldenhauer, U., Dörner, G.: Maturation of the oestrogen-dependent LH-stimulating activity of the mediocortical amygdala in female rats. Endokrinol. 69, 262–265 (1977)
Epelbaum, J., Willoughby, J.O., Brazeau, P., Martin, J.B.: Effects of brain lesions and hypothalamic deafferentation on somatostatin distribution in the rat brain. Endocrinol. 101, 1495–1502 (1977)
Findlay, A.L.R.: Hypothalamic inputs: methods and five examples. In: Progress in Brain Res., Vol. 38. Topics in neuroendocrinology, pp. 163–191 (J. Ariëns Kappers, J.P. Schadé, eds.). Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier Publ. Comp. 1972
Flerkó, B.: Oestrogen-sensitive neurons and their role in the control of ovulation. In: Neuroendocrine regulation of fertility. Int. Symp. Simla, 1974, pp. 114–123 (T.C. Anand Kumar ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1976
Halász, B.: Neural control of pituitary function. In: Progress in Brain Res., Vol. 38. Topics in neuroendocrinology, pp. 97–118 (J.A. Ariëns Kappers, J.P. Schadé, eds.). Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier Publ. Comp. 1972
Halász, B., Köves, K., Réthelyi, M., Bodoky, M., Koritsánszky, S.: Recent data on neuronal connections between nervous structures involved in the control of the adenohypophysis. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 9–14 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Heimer, L.: Olfactory projections to the diencephalon. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 30–39 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-Munchen-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Kawakami, M., Kimura, F., Konda, N.: Role of the forebrain structures in the regulation of gonadotropin secretion. In: Neuroendocrine regulation of fertility. Int. Symp. Simla, 1974, pp. 101–113 (T.C. Anand Kumar, ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1976
Krisch, B.: Morphological equivalent of the bifunctional role of somatostatin. Cell Tissue Res. 179, 211–224 (1977)
Krulich, L., Dhariwal, A.P.S., McCann, S.M.: The effect of growth hormone releasing and inhibiting factors on synthesis and release of growth hormone in vitro in the rat. (Abstract) Excerpta Med. Found. Int. Congr. 244, 32 (1967)
Krulich, L., Dhariwal, A.P.S., McCann, S.M.: Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of purified hypothalamic extracts on growth hormone release from rat pituitary in vitro. Endocrinol. 83, 783–790 (1968)
Leonardelli, J., Poulain, P.: About a ventral LHRH preoptico-amygdaloid pathway in the guinea pig. Brain Res. 124, 538–543 (1977)
Martin, J.B.: Plasma growth hormone (GH) response to hypothalamic or extrahypothalamic electrical stimulation. Endocrinol. 91, 107–115 (1972)
Martin, J.B.: Brain regulation of growth hormone secretion. In: Frontiers in neuroendocrinology, Vol. 4, pp. 129–268 (L. Martini, W.F. Ganong, eds.). New York: Raven Press 1976
Moore, R.Y., Lenn, N.J.: A retinohypothalamic projection in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 146, 1–14 (1972)
Moore, R.Y., Karapas, F., Lenn, N.J.: A retinohypothalamic projection in the rat. Anat. Rec. 169, 382–383 (1971)
Moss, R.L.: Unit responses in preoptic and arcuate neurons related to anterior pituitary function. In: Frontiers in neuroendocrinol, Vol. 4, pp. 95–128 (L. Martini, W.F. Ganong, eds.). New York: Raven Press 1976
Murphy, J.T., Renaud, L.: Mechanisms of inhibition in the ventro-medial nucleus of the hypothalamus. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 85–102 (1969)
Oksche, A.: The neuroanatomical basis of comparative neuroendocrinology. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 29, 225–239 (1976)
Oksche, A.: Pattern of neuroendocrine cell complexes (subunits) in hypothalamic nuclei: neurobiological and phylogenetic concepts. In: Neurosecretion and neuroendocrine activity — evolution, structure and function, pp. 64–71 (W. Bargmann, A. Oksche, A. Polenov, B. Scharrer, eds.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Oksche, A., Farner, D.S.: Neurohistological studies of the hypothalamo-hypophysial system of Zonotrichia leucophrys gambelii (Aves, Passeriformes). With special attention to its role in the control of reproduction. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 48 (4), 1–136 (1974)
Olmos, J.S. De, Ingram, W.R.: The projection field of the stria terminalis in the rat brain. An experimental study. J. Comp. Neurol. 146, 303–334 (1972)
Pfaff, D.W.: The neuroanatomy of sex hormone receptors in the vertebrate brain. In: Neuroendocrine regulation of fertility. Int. Symp. Simla, 1974, pp. 30–45 (T.C. Anand Kumar, ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1976
Renaud, L.P., Brazeau, P., Martin, J.B.: Depressant action of TRH, LH-RH and somatostatin on the activity of central neurons. Nature 225, 233–235 (1975)
Sar, M., Stumpf, W.E.: Distribution of androgen-concentrating neurons in the rat brain. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 120–133 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Sofroniew, M.V., Weindl, A.: Extrahypothalamic neurophysin-containing perikarya, fiber pathway and fiber clusters in the end brain. Endocrinol. 102, 334–337 (1978)
Stumpf, W.E.: Uptake of estrogens in the amygdala-preoptic-hypothalamic-hypophyseal-gonadal complex. J. Anat. 111, 476 (1972)
Stumpf, W.E.: The brain: an endocrine gland and hormone target. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 2–8 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Stumpf, W.E.: The anatomical substrate of neuroendocrine regulation as defined by autoradiography with 3H-estradiol, 3H-testosterone, 3H-dihydrotestosterone and 3H-progesterone. In: Neuroendo-crine regulation of fertility. Int. Symp. Simla, 1974, pp. 46–56 (T.C. Anand Kumar, ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: 1976
Stumpf, W.E., Sar, M.: Hormone-architecture of the mouse brain with 3H-estradiol. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 82–103 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Stumpf, W.E., Sar, M., Keefer, D.A.: Atlas of estrogen target cells in rat brain. In: Anatomical neuroendocrinology, pp. 104–119 (W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant, eds.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1975
Taleisnik, S.: Sites concerned with inhibition of gonadotropin secretion. In: Neuroendocrine regulation of fertility. Int. Symp. Simla, 1974, pp. 92–100 (T.C. Anand Kumar, ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: Karger 1976
Tannenbaum, G.S., Martin, J.B.: Evidence for an endogenous ultradian rhythm governing growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinol. 98, 562–570 (1976)
Vandesande, F., Dierickx, K.: Identification of the vasopressin producing and of the oxytocin producing neurons in the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory system in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 164, 153–162 (1975)
Velasco, M.E., Taleisnik, S.: Release of gonadotropins induced by amygdaloid stimulation in the rat. Endocrinol. 84, 132–139 (1969)
Weindl, A., Sofroniew, M.V.: Psychotropic effects of hypothalamic hormones. Immunohistochemical identification of extrahypophyseal connections of neuroendocrine neurons. Arzneim. Forsch. (Drug Res.) 26, 1191–1194 (1976a)
Weindl, A., Sofroniew, M.V.: Demonstration of extrahypothalamic peptide reacting neurons. A morphologic contribution to the investigation of psychotropic effects of neurohormones. Pharmacopsych. 9, 226–234 (1976b)
Wenisch, H., Hartwig, H.-G.: Karyometrische Untersuchungen am Nucleus suprachiasmaticus geblendeter Ratten. Z. Zellforsch. 143, 143–147 (1973)
Willoughby, J.O., Martin, J.B.: Pulsatile growth hormone secretion: inhibitory role of the medial preoptic area. Brain Res. 148, 240–244 (1978a)
Willoughby, J.O., Martin, J.B.: The suprachiasmatic nucleus synchronizes growth hormone secretory rhythms with the light-dark cycle. Brain Res. 151, 413–417 (1978b)
Willoughby, J.O., Terra, L.C., Brazeau, P., Martin, J.B.: Pulsatile growth hormone, prolactin and thyrotropin secretion in rats with hypothalamic deafferentation. Brain Res. 127, 137–152 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant Nr. Kr. 569/2) and Stiftung Volkswagenwerk.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krisch, B. Hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic distribution of somatostatin-immunoreactive elements in the rat brain. Cell Tissue Res. 195, 499–513 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233892
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233892