Summary
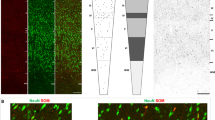
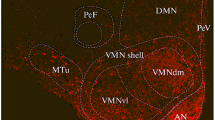
By use of the indirect immunofluorescence technique a small group of large somatostatin-positive neurons is described in the subependymal area of the anterior paraventricular thalamus of the male rat. Retrograde-tracing experiments suggest that they project to areas outside the blood-brain barrier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett-Clarke C, Romagnano MA, Joseph SA (1980) Distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain: telencephalon and diencephalon. Brain Res 188:473–486
Bentivoglio M, Kuypers HGJM, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Loewe H, Dann O (1980) Two new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers which are transported over long distances. Neurosci Lett 18:25–30
Brazeau P, Vale W, Burgus R, Ling N, Butcher M, Rivier J, Guillcmin R (1973) Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science 179:77–79
Elde R, Hökfelt T (1978) Distribution of hypothalamic hormones and other peptides in the brain. In: Ganong WF, Martini L (eds) Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Vol 5. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–33
Finley JCW, Maderdrut JL, Roger LJ, Petrusz P (1981) The immunocytochemical localization of somatostatin-containing neurons in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 6:2173–2192
Hökfelt T, Skagerberg G, Skirboll L, Björklund A (1983) Combination of retrograde tracing and neurotransmitter histochemistry. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy. Vol 1: Methods in Chemical Neuroanatomy. Elsevier Science Publ, Amsterdam, pp 228–285
Hökfelt T, Dalsgaard C-J, Meister B, Everitt BJ (1985) Tracing of afferents to the median eminence using combined immunohistochemistry and intravenous administration of fluorescent compounds. Neurosci Lett Suppl 22:565
Johansson O, Hökfelt T, Elde RP (1984) Immunohistochemical distribution of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the adult rat. Neuroscience 13:265–339
Krisch B (1978) Hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic distribution of somatostatin-immunoreactive elements in the rat brain. Cell Tissue Res 195:499–513
Krulich L, Dhariwal APS, McCann SM (1968) Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of purified hypothalamic extracts on growth hormone release from rat pituitary in vitro. Endocrinology 83:783–790
Paxinos G, Watson C (s) (1982) The brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Pease PC (1962) Buffered formaldehyde as a killing agent and primary fixative for electron microscopy. Anat Res 142:342
Vincent SR, McIntosh CHS, Buchanan AMJ, Brown JC (1985) Central somatostatin systems revealed with monoclonal antibodies. J Comp Neurol 238:169–187
Zamboni L, de Martino C (1967) Buffered picric acid formaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 148A:35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceccatelli, S., Meister, B., Hökfelt, T. et al. Immunohistochemical evidence for a magnocellular somatostatin cell group in the anterior paraventricular thalamus of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 246, 683–685 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215212
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215212