Summary
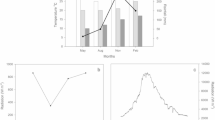
This study describes the phenology of sporophytes of the fern Dryopteris filix-mas in relation to whole plant development. Sterile and fertile potted sporophytes were set out at an exposed site and the seasonal development of the fronds was measured from the commencement of unfolding, through the phase of increasing length, up to discoloration. The physiological activity of the fronds was determined by measuring photosynthetic gas exchange. The fronds of sterile sporophytes unfolded in April, about a week earlier than those of fertile plants, but the colour had already begun to turn in September and their life span was 1–2 months shorter. However, between mid-June and the end of August the sterile sporophytes put out several sets of new fronds: these overwintered without changing color and were still photosynthetically active in the following spring. All types of fronds were fully expanded 1–2 months from the beginning of unfolding and, with a natural supply of CO2, had similar maximum net photosynthetic rates of 8–9 μmol/m2 · s. The decline in photosynthetic performance began before symptoms of senescence were visible and was due to decreased efficiency of the mesophyll. It is concluded that the phenology of D. filix-mas changes with transition from the sterile to the fertile phase. Whereas fertile sporophytes are genuinely summergreen, the sterile sporophytes with their summer fronds remain green throughout the winter and should therefore be termed semi-evergreen. The formation of overwintering summer shoots clearly extends the period of photosynthetic productivity of sterile sporophytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer H (1978) Photosynthesis of ivy leaves (Hedera helix) after heat stress I. CO2-gas exchange and diffusion resistances. Physiol Plant 44:400–406
Bauer H, Bauer U (1980) Photosynthesis in leaves of the juvenile and adult phase of ivy (Hedera helix) Physiol Plant 49:366–372
Caemmerer S von, Farquhar GD (1981) Some relationship between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153:376–387
Čatský J, Tichá I (1982) Photosynthetic characteristics during ontogenesis of leaves 6. Intracellular conductance and its components. Photosynthetica 16, 253–284
Dostál J, Reichstein T, Fraser-Jenkins CR, Kramer KU (1984) Pteridophyta. In: Conert HJ, Hamann U, Schultze-Motel W, Wagenitz G (eds) Illustrierte Flora von Mitteleuropa Vol I/1. 3rd edition. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin, Hamburg, pp 137–142
Hollinger DY (1987) Photosynthesis and stomatal conductance patterns of two fern species from different forest understoreys. J Ecol 75:925–935
Kozlowski TT (1971) Growth and development of trees. Vol I. Academic Press, New York
Landgren CR (1987) Overwintering strategies of Vermont (US) wintergreen and evergreen ferns in the northern hardwood forest. Abstracts of the XIV International Botanical Congress, Berlin (No 6-37-3) p 386
Larcher W (1984) Ökologie der Pflanzen auf physiologischer Grundlage. 4th ed. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart
Ludlow CJ, Wolf FT (1975) Photosynthesis and respiration rates of ferns. Amer Fern J 65:43–48
MacKinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–322
Nobel PS, Calkin HW, Gibson AC (1984) Influences of PAR, temperature and water vapor concentration on gas exchange by ferns. Physiol Plant 62:527–534
Sato T (1982) Phenology and wintering capacity of sporophytes and gametophytes of ferns native to northern Japan. Oecologia 55:53–61
Sato T (1983) Determination of the developmental age of sporophytes of some summer-green ferns in Hokkaido, Japan. Jap J Ecol 33:161–167
Sato T (1987) A quantitative estimation of sporophyte development in Dryopteris filix-mas (L.) Schott, determined from the overwintering phenology in the leaf. Flora 179:99–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, H., Gallmetzer, C. & Sato, T. Phenology and photosynthetic activity in sterile and fertile sporophytes of Dryopteris filix-mas (L.) Schott. Oecologia 86, 159–162 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317526
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317526