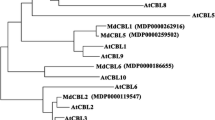
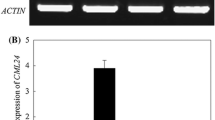
Abstract
Profilins are actin-binding proteins in eukaryotes which participate in the phosphoinositide pathway via binding to PIP2. Using polyclonal rabbit sera raised against plant profilins, the occurrence of several profilin isoforms is demonstrated in two-dimensionally analyzed tobacco pollen extracts. The cDNAs coding for two novel tobacco profilin isoforms (ntPro2, ntPro3) were isolated from a pollen cDNA library by antibody screening. When the cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences of the two isoforms were compared with a previously isolated tobacco pollen profilin cl)NA (ntPro1), significant differences were noted in the non-coding regions, whereas the coding sequences, in particular the functional domains, showed little variation. The cDNAs coding for the three tobacco profilin isoforms were expressed inEscherichia coli and shown to bind comparably to different anti-profilin antisera. The high degree of similarity among the different tobacco pollen profilin isoforms points to functional equivalence. Assuming that the presence of profilin is indispensable to the control of the large amounts of actin present in pollen, the occurrence of different profilin isoforms in pollen is interpreted to represent a protective mechanism against loss of profilin functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almo SC, Pollard TD, Way M, Lattman EE (1994) Purification, characterization and crystallization ofAcanthamoeba profilin expressed inEscherichia coli. J Mol Biol 236: 950–952
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Drobak BK, Watkins PAC, Valenta R, Dove SK, Lloyd CW, Staiger CJ (1994) Inhibition of plant plasma membrane phosphoinositide phospholipase C by the actin-binding protein profilin. Plant J 6: 389–400
Fedorov AA, Pollard TD, Almo SC (1994) Purification, characterization and crystallization of human platelet profilin expressed inEscherichia coli. J Mol Biol 241: 480–482
Finkel T, Theriot JA, Dise KR, Tomaselli GF, Goldschmidt-Clermont (1994) Dynamic actin structures stabilized by profilin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 1510–1514
Fling SP, Gregerson DS (1986) Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity Tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem 155: 83–88
Giehl K, Valenta R, Rothkegel M, Ronsiek M, Mannherz HG, Jockusch B (1994) Interaction of plant profilin with mammalian actin. Eur J Biochem 226: 681–689
Grote M, Swoboda I, Meagher RB, Valenta R (1995) Localization of profilin- and actin-like immunoreactivity in in vitro-germinated tobacco pollen tubes by electron microscopy after special water-free fixation techniques. Sex Plant Reprod 8: 180–186
Haarer BK, Lillie SH, Adams AEM, Magdolen V, Bandlow W, Brown SS (1990) Purification of profilin fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae and analysis of profilin-deficient cells. J Cell Biol 110:105–114
Haugwitz M, Noegel AA, Rieger D, Lottspeich F, Schleicher M (1991)Dictyostelium discoideum contains two profilin isoforms that differ in structure and function. J Cell Sci 100: 481–489
Haugwitz M, Noegel AA, Karakesioglou J, Schleicher M (1994) Dictyostelium amoebae that lack G-actin-sequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and development. Cell 79: 303–314
Honore B, Madsen P, Andersen AH, Leffers H (1993) Cloning and expression of a novel human profilin variant, profilin II. FEBS Lett 330: 151–155
Jarolim E, Rumpold H, Endler AT, Ebner H, Scheiner O, Kraft D, Scheiner O (1989) IgE and IgG antibodies of patients with allergy to birch as tools to define the allergen profile ofBetula verrucosa. Allergy 44: 385–395
Magdolen V, Drubin DG, Mages G, Bandlow W (1993) High levels of profilin suppress the lethality caused by overproduction of actin in yeast cells. FEBS Lett 316: 41–47
Mittermann I, Swoboda I, Pierson E, Eller N, Kraft D, Valenta R, Heberle-Bors E (1995) Molecular cloning and characterization of profilin from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): increased profilin expression during pollen maturation. Plant Mol Biol 27: 137–146
Pollard TD, Rimm DL (1991) Analysis of cDNA clones forAcanthamoeba profilin-I and profilin-II shows end to end homology with vertebrate profilins and a small family of profilin genes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 20: 169–177
Ree R van, Voitenko V, Leeuwen WA van, Aalberse R (1992) Profilin is a cross- reactive allergen in pollen and vegetable foods. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 98: 97–104
Rihs HP, Rozynek P, May-Taube K, Welticke B, Baur X (1994) Polymerase chain reaction based cDNA cloning of wheat profilin: a potential plant allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 105: 190–194
Rothkegel M, Mayboroda O, Rohde M, Wucherpfennig C, Valenta R, Jockusch BM (1996) Plant and animal profilins are functionally equivalent and stabilize microfilaments in living animal cells. J Cell Sci (in press)
Ruhlandt G, Lange U, Grolig F (1994) Profilins purified from higher plants bind to actin from cardiac muscle and to actin from a green alga. Plant Cell Physiol 35: 849–854
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Schutt CE, Myslik JC, Rozycki MD, Goonesekere NCW, Lindberg U (1993) The structure of crystalline profilin-β-actin. Nature 365:810–816
Short JM, Fernandez JM, Sorge JA, Huse WD (1988) λ ZAP: a bacteriphage λ expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucl Acids Res 16: 7583–7600
Staiger CJ, Goodbody KC, Hussey PJ, Valenta R, Drobak BK, Lloyd CW (1993) The profilin multigene family of maize: differential expression of three isoforms. Plant J 4: 631–641
Staiger CJ, Yuan M, Valenta R, Shaw PJ, Warn RM, Lloyd CW (1994) Microinjected profilin affects cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells by rapidly depolymerizing actin microfilaments. Curr Biol 4: 215–219
Tilney LG, Inoue S (1982) Acrosomal reaction ofThyone sperm. II. The kinetics and possible mechanism of acrosomal process elongation. J Cell Biol 93: 820–827
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfers of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 4350–4354
Valenta R, Duchene M, Pettenburger K, Sillaber C, Valent P, Bettelheim P, Breitenbach M, Rumpold H, Kraft D, Scheiner O (1991) Identification of profilin as a novel pollen allergen: IgE autoreactivity in sensitized individuals. Science 253: 557–560
Valenta R, Duchene M, Ebner C, Valent P, Sillaber C, Deviller P, Ferreira F, Tejkl M, Edelmann H, Kraft D, Scheiner O (1992) Profilins constitute a novel family of functional plant pan-allergens. J Exp Med 175: 377–385
Valenta R, Ferreira F, Grote M, Swoboda I, Vrtala S, Duchene M, Deviller P, Meagher RB, McKinney E, Heberle-Bors E, Kraft D, Scheiner O (1993) Identification of profilin as an actin binding protein in higher plants. J Biol Chem 268: 22777–22781
Valenta R, Ball T, Vrtala S, Duchene M, Kraft D, Scheiner O (1994) cDNA cloning and expression of timothy grass (Phleum pratense) pollen profilin inEscherichia coli: comparison with birch pollen profilin. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 199:106–118
Vallier P, Dechamp C, Valenta R, Vial O, Deviller P (1992) Purification and characterization of an allergen from celery immunochemically related to an allergen present in several other plant species. Identification as a profilin. Clin Exp Allergy 22: 774–782
Witke W, Sharpe AH, Kwiatkowsky DJ (1993) Profilin deficient mice are not viable. Mol Biol Cell 4: 149a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittermann, I., Heiss, S., Kraft, D. et al. Molecular characterization of profilin isoforms from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) pollen. Sexual Plant Reprod 9, 133–139 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221392