Abstract
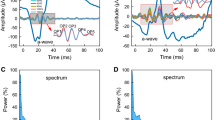
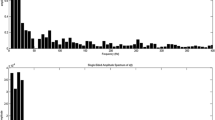
The dark-adapted and light-adaped electroretinograms of 13 subjects with 23 normal eyes were analyzed by means of Fourier spectrum. The oscillatory potentials in the time domain were filtered out from the electroretinogram after a corresponding bandpass was given in the frequency domain. The coefficient of variation of total power, dominant power and dominant frequency of the isolated oscillatory potentials in the frequency domain, summed amplitudes and area of the isolated oscillatory potentials, each amplitude and implicit time of the first four major oscillatory potential wavelets in the time domain were compared. The implicit time showed the smallest coefficient of variation; summed amplitudes of OP1 to OP4 showed smaller coefficients of variation than those of the area, the amplitude of each oscillatory potential wavelet, dominant frequency and dominant and total power. The coefficient of variation of these measurement parameters in light-adapted electroretinograms was smaller than those in dark-adapted electroretinograms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CV:
-
coefficient of variation
- OP:
-
oscillatory potential
References
Brunette JR, Desrochers R. Oscillatory potentials. A clinical study in diabetics. Can J Opthalmol 1970; 5: 373–80.
Simonsen SE. ERG in juvenile diabetics. A prognostic study. In: Goldberg M, Fine SL, eds. Symposium on the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Washington, DC: US Public Health Service (Publ No. 1980) 1969; 681–89.
Speros P, Price J. Oscillatory potentials, history, techniques and potential use in the evaluation of disturbances of retinal circulation. Surv Ophthalmol 1981; 25: 237–52.
Bresnick G, Korth K, Groo A, Palta M. Electroretinographic oscillatory potentials predict progression of diabetic retinopathy. Preliminary report. Arch Ophthalmol 1984; 102: 1307–11.
Bresnick G, Palta M. Oscillatory potential amplitudes. Relation to severity of diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 1987; 105: 929–933.
Usami E. Studies on oscillatory potentials in the cases of occlusion of the retinal artery and thrombosis of the retinal vein. Jpn J Opthalmol Suppl 1966; 10: 113–9.
Algvere P. Clinical studies on the oscillatory potentials of the human electroretinogram with special reference to the scotopic b-wave. Acta Ophthalmol 1968; 46: 993–1023.
Algvere P, Wachmeister L, Westbeck S. On the oscillatory potentials of the human electroretinogram in light and dark adaptation. Acta Ophthalmol 1972; 50: 739–759.
Hennekes R, Deschner, R. Alteration of oscillatory potentials in diabetics induced by photocoagulation of the retina. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Opthalmol 1984; 221: 230–3.
Tsuchida Y, et al. Isolation of faster components in the electrooretinogram and visually evoked response in man. Am J Ophthalmol 1973; 75: 846.
Kothe AC, Lovasik JV, Couplands SG. Variability in clinically measured photopic oscillatory potentials. Doc Ophthalmol 1989; 71: 381–95.
Vallabhan G, Kristiansen S, Price J, Young RSL. Effect of adaptation and wavelength on the power spectrum of human oscillatory potentials. Doc Ophthalmol 1988; 69: 145–51.
Stodmeister R. The spectral sensitivity functions of human ERG wavelengths. Ophthalmic Res 1973; 5:21–30.
Van der Torren K. Groeneweg G, Van Lith G. Measuring oscillatory potentials. Fourier analysis. Doc Ophthalmol 1988; 69: 153–59.
Yonemura D, Kawasaki K. New approaches to ophthalmic electrodiagnosis by retinal oscillatory potential. Doc Ophthalmol 1979; 48: 163–222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XX., Yuan, N. Measurement of the oscillatory potentials of the electroretinogram in the domains of frequency and time. Doc Ophthalmol 76, 65–71 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140499
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140499