Abstract
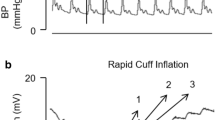
A noninvasive method for estimating the mean capillary pressure Pcap and the pre-and postcapillary resistance ratio Rv/Ra in human fingers is described. Volume change in a finger segment was detected with a transmittance-type infra-red photoelectric plethysmograph during a gradual and linear increase in occluding cuff pressure. There was an inflection point in the volume curve which would be produced by the difference in the compliance between the arterial and venous vascular bed in the segment. This transitional point was assumed to represent the complete compression of the venous vascular bed at the cuff pressure level. Thus Pcap was defined as the cuff pressure corresponding to the inflection point. Rv/Ra was calculated from the Pcap, the venous pressure Pv and the mean arterial pressure Pam. The latter two pressures, Pv and Pam, were also indirectly and simultaneously measured by the compression pressure of another cuff and by our new type of volume oscillation method, respectively. The values of Pcap and Rv/Ra were in good agreement with those reported by other investigators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eichna, L. W. andBordley, J. III (1942) Capillary blood pressure in man. Direct measurements in the digits of normal and hypertensive subjects during vasoconstriction and vasodilatation variously induced.J. Clin. Invest.,21, 711–729.
Fahr, G. andErshler, I. (1941) Studies of the factors concerned in edema formation. II. The hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries during edema formation in right heart failure.Ann. Internal Med.,15, 798–810.
Fronek, A. (1971) Isoconductometric estimation of effective capillary pressure in isolated hindlimb.Am. J. Physiol.,220, 1005–1008.
Granger, D. N., Perry, M. A., Kvietys, P. R. andTaylor, A. E. (1983) A new method for estimating intestinal capillary pressure.,244, G341-G344.
Hakim, T. S., Michel, R. P. andChang, H. K. (1982) Partitioning of pulmonary vascular resistance in dogs by arterial and venous occlusion.J. Appl. Physiol.,52, 710–715.
Holloway, H., Perry, M., Downey, J., Parker, J. andTaylor, A. (1983) Estimation of effective pulmonary capillary pressure in intact lungs.J. Appl. Physiol.,54, 846–851.
Johnson, P. C. (1965) Effect of venous pressure on mean capillary pressure and vascular resistance in the intestine.Circ. Res.,16, 294–300.
Landis, E. M. (1926) The capillary pressure in frog mesentery as determined by micro-injection methods.Am. J. Physiol.,75, 548–570.
Landis, E. M. (1930) Micro-injection studies of capillary blood pressure in human skin.Heart,15, 209–228.
Landis, E. M. andPappenheimer, J. R. (1963) Exchange of substances through the capillary walls. InHandbook of physiology.Hamilton, W. F. andDow, P. (Eds), Am. Physiol. Soc., 961–1034.
Levick, J. R. andMichel, C. C. (1978) The effects of position and skin temperature on the capillary pressures in the fingers and toes.J. Physiol.,274, 97–109.
MacLeod, M. (1960) Systemic capillary pressure, in acute glomerulonephritis estimated by direct micropuncture.Clin. Sci.,19, 27–33.
Mahler, F., Muheim, M. H., Intaglietta, M., Bollinger, A. andAnliker, M. (1979) Blood pressure fluctuations in human nailfold capillaries.Am. J. Physiol.,236, H888-H893.
Pappenheimer, J. R. andSoto-Rivera, A. (1948) Effective osmotic pressure of the plasma proteins and other quantities associated with the capillary circulation in the hindlimbs of cats and dogs.,152, 471–491.
Penaz, J. (1973) Photoelectric measurement of blood pressure, volume and flow in the finger. Dig. 10th Int. Conf. Med. & Biol. Eng., Dresden, Session 7 Haemodynamics I, No. 7-2, 104.
Rappaport, M. B., Bloch, E. H. andIrvin, J. W. (1959) A manometer for measuring dynamic pressures in the microvascular system.J. Appl. Physiol.,14, 651–655.
Renkin, E. M. (1984) Control of microcirculation and bloodtissue exchange. InHandbook of physiology.Renkin, E. M., Michel, C. C. andGeiger, S. R. (Eds.), Am. Physiol. Soc., 627–687.
Roy, C. S. andBrown, J. G. (1880) The blood-pressure and its variations in the arterioles, capillaries and smaller veins.J. Physiol.,2, 323–359.
Shimazu, H., Fukuoka, M., Hayashi, S., Seki, K., Ito, H., Yamakoshi, K. andTogawa, T. (1985) Noninvasive measurement of pressure/volume characteristics in human limb veins by electrical admittance plethysmography.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,23, 38–42.
Von Kries, N. (1875) Ueber den Druck in den Blutcapillaren der menschlichen Haut.Arbeiten Physiol., Anstalt Leipzig,10, 69–80.
Wiederhielm, C. A., Woodbury, J. W., Kirk, S. andRushmer, R. F. (1964) Pulsatile pressures in the microcirculation of frog's mesentery.Am. J. Physiol.,207, 173–176.
Yamakoshi, K., Shimazu, H. andTogawa, T. (1979) Indirect measurement of instantaneous arterial blood pressure in the rat.Am. J. Physiol.,237, H632-H637.
Yamakoshi, K., Shimazu, H. andTogawa, T. (1980) Indirect measurement of instantaneous arterial blood pressure in the human finger by the vascular unloading technique.IEEE Trans.,BME-27, 150–155.
Yamakoshi, K., Shimazu, H., Shibata, M. andKamiya, A. (1982a) New oscillometric method for indirect measurement of systolic and mean arterial pressure in the human finger. Part 1: model experiment.Med. & Biol. eng. & Comput.,20, 307–313.
Yamakoshi, K., Shimazu, H., Shibata, M. andKamiya, A. (1982b) New oscillometric method for indirect measurement of systelic and mean orterial pressure in the human finger. Part 2: correlation study,20, 314–318.
Zweifach, B. W. (1956) Rat mesoappendix procedure for bioassay of humoral substances acting on peripheral blood vessels.Ergeb. Anat. Entwicklngsgesch.,35, 175–186.
Zweifach, B. W. (1974) Quantitative studies of microcirculatory structure and function. II. Direct measurement of capillary pressure in splanchinic mesenteric vessels.Circ. Res.,34, 858–867.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimazu, H., Ito, H. & Yamakoshi, K. Noninvasive method for estimating the mean capillary pressure and pre- and postcapillary resistance ratio in human fingers. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 24, 585–590 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446260
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446260