Abstract
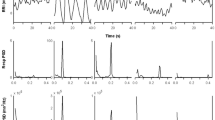
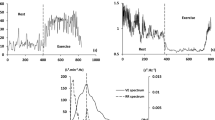
The respiratory effects on impedance-determined cardiac indices ((dZ/dt)min, stroke volume (SV), the Heather index (HI) and the O-wave) were measured at 100 kHz on ten normal males in the supine and sitting positions. The respiration was synchronised to 1/5th of the heart rate using voluntary cardiorespiratory synchronisation (VCRS). Digital filtering was used to eliminate breathing artefacts in the impedance signals, SV, (dZ/dt)min and HI were statistically higher during inspiration than expiration. Ensemble-averaging of (dZ/dt) signals using the R spike of the ECG as reference will lose beat-to-beat information and statistically reduce (dZ/dt)min because of the variation of RZ intervals during respiration Zo increased with inspiration and decreased in expiration delayed by one heart beat. The ratio of the O-wave height to (dZ/dt)min changed by 48 per cent from the beginning of inspiration to the end of expiration. Based on the timing and direction of the changes, the data imply that the traditional band impedance measurement is more closely related to the right heart event than to that of the left heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almasi, J. J. andSchmitt, O. H. (1974) Basic technology of voluntary cardiorespiratory synchronization in electrocardiology.IEEE Trans.,BME-21, (4), 264–273.
Almasi, J. J. andSchmitt, O. H. (1970) Systematic and random variation of ECG electrode system impedence.Ann. NY Acad. Sci.,170, 509.
Denniston, J. C., Maher, J. T., Reeves, J. T., Cruz, J. C., Cymerman, A. andGrover, R. F. (1976) Measurement of cardiac output by electrical impedance at rest and during exercise.J. Appl. Physiol.,40, 91–95.
Doerr, B. M., Miles, D. S. andFrey, M. A. B. (1981) Influence of respiration on stroke volume determined by impedance cardiography.Aviat. Space Environ. Med.,52, (7), 394–398.
Donovan, K. D., Dobb, G. J., Woods, W. P. andHockings, B. E. (1986) Comparisons of transthoracic electrical impedance and thermodilution methods for measuring cardiac output.Critical Care Med.,14, 1038–1044.
Ferrigno, M., Hickey, D. D., Liner, M. H. andLundgren, C. E. G. (1986) Cardiac performance in humans during breath holding.J. Appl. Physiol.,60, 1871–1877.
Geddes, L. E. andBaker, L. E. (1972) Thoracic impedance changes following saline injection into right and left ventricles.J. Appl. Physiol.,33, 278–281.
Hill, R. V., Jasen, J. C. andFling, J. L. (1967) Electrical impedance plethysmography: a critical analysis.J. Appl. Physiol.,22, 161–168.
Hubbard, W. N., Fish, D. R. andMcBrien, D. J. (1986) The use of impedance cardiography in heart failure.Int. J. Cardiol.,12, 71–79.
Kubicek, W. G., Karnegis, J. N., Patterson, R. P., Witsoe, D. A. andMattson, R. H. (1966) Development and evaluation of an impedance cardiac output system.Aerospace Med.,37, 1208–1212.
Kubicek, W. G., Kottke, F. J., Ramos, M. U., Patterson, R. P., Witsoe, D. A., LaBree, J. W., Remole, W., Layman, T. E., Shoening, H. andGaramella, J. T. (1974) The Minnesota impedance cardiograph—theory and applications.Biomed. Eng.,9, 410–416.
Lababidi, Z., Ehmke, D. A., Durnin, R. E., Leaverton, P. E. andLauer, R. M. (1970) The first derivative thoracic impedance cardiogram.Circulation,XLI, 651–658.
Miyamoto, Y., Tamura, T. andMikami, T. (1981) Automatic determination of cardiac output using an impedance plethysmography.Biotelem. Patient Monit.,8, 189–203.
Mohapatra, S. N. (1981)Noninvasive cardiovascular monitoring by electrical impedance techniques. Pitman Medical, London.
Muzi, M., Ebert, T. J., Tristani, F. E., Jeutter, D. C., Barney, J. A. andSmith, J. J. (1985) Determination of cardiac output using ensemble-averaged impedance cardiograms.J. Appl. Physiol.,58, 200–205.
Patterson, R. P., Kubicek, W. G., Kinnen, E., Witsoe, D. A. andNoren, G. (1964) Development of an electrical impedance plethysmography system to monitor cardiac output. Proc. of the First Ann. Rocky Mountain Bioeng. Symp., 56–71.
Patterson, R. P. (1978) The use of signal averaging of the electrical impedance signal to determine cardiac timing information during uninterrupted exercise. Proc. of the 13th Ann. Meeting of AAMI, Arlington, Virginia, USA, 206.
Patterson, R. P. (1989) Fundamentals of impedance cardiography.IEEE Eng. in Med. and Biol.,8, (1), 35–38.
Penny, B. (1986) Theory and cardiac applications of electrical impedance measurements.CRC Critical Reviews in Biomed. Eng.,13, 227–281.
Permutt, S. andWise, R. A. (1986) Mechanical interaction of respiration and circulation. InHandbook of Physiology.Fishman, A. (Ed.) American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, USA, 647–659.
Quesnay, M. C. D., Stoute, G. J. andHughson, R. L. (1987) Cardiac output in exercise by impedance cardiography during breath holding and normal breathing.J. Appl. Physiol.,62, 101–107.
Ramos, M. U. (1977) An abnormal early diastolic impedance waveform: A predictor of poor prognosis in the cardiac patient?Am. Heart J.,94 (3), 274–281.
Raza, S. B., Patterson, R. P. andWang, L. (1989) Removal of respiratory artifacts. Presented at 11th Int. Conf. of IEEE in Med. and Biol., Seattle, WA, USA.
Ruskin, J., Bache, R. J., Rembert, J. C. andGreenfield, J. C. (1973) Pressure-flow studies in man: Effect of respiration on left ventricular volume.CirculationXLVIII, 79–85.
Smith, J. J., Muzi, M., Barney, J. A., Ceschi, J., Hayes, J. andEbert, T. (1989) Impedance-derived cardiac indices in supine and upright exercise.Annals of Biomed. Eng.,17, 507–515.
Sokolow, M. andMcIlroy, M. B. (1986)Clinical cardiology. Lange Medical Publications, Los Altos, California, USA.
Thompson, F. D. andJoekes, A. M. (1981)Thoracic impedance. Cardiodynamic assessment: validation in clinical use. St. Peter's Hospital. Geigy Pharmaceutical, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Patterson, R.P. & Raza, S.B. Respiratory effects on cardiac related impedance indices measured under voluntary cardio-respiratory synchronisation (VCRS). Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 29, 505–510 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442322