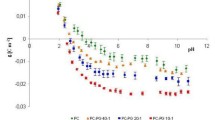
Summary
Furosemide-binding proteins were isolated from cholate-solubilized membranes of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells by affinity chromatography, using furosemide as ligand. Solubilized proteins retarded by the affinity material were eluted by furosemide. In reducing and denaturing gels, the major proteins eluted by furosemide were 100 and 45 kDa. In nonreducing, nondenaturing gels, homodimers of both polypeptides were found, whereas no oligomeric proteins containing both polypeptides were seen. It is concluded that the furosemide gel binds two distinct dimeric proteins. The isolated proteins were reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles and the K+ transport activity of these vesicles was assayed by measurement of86Rb+ uptake against a large opposing K+ gradient. The reconstituted system was found to contain a K+ transporting protein, which is sensitive to Ba2+ like the K+ channel previously demonstrated to be activated in intact cells after cell swelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.C. 1983. Sulfonamide diuretics.In: Diuretics. E.J. Cragoe, editor. pp. 119–200. John Wiley, New York
Aull, F. 1982. Specific drug sensitive transport pathways for chloride and potassium ions in steady-state Ehrlich mouse ascites tumor cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 688:740–746
Aull, F., Nachbar, M.S., Oppenheim, J.D. 1977. Chloride self exchange in Ehrlich ascites cells. Inhibition by furosemide and 4-acetamido-4′-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 471:341–347
Brazy, P.C., Gunn, R.B. 1976. Purosemide inhibition of chloride transport in human red blood cells.J. Gen. Physiol. 68:583–599
Cherksey, B.D., Hoffmann, E.K., Jessen, F. Zeuthen, T. 1987. The K+ and Cl− channel protein from Ehrlich ascites tumour cells under reducing and oxidizing conditions.J. Physiol. (London) 390:223P
Cherksey, B.D., Zeuthen, T. 1987. A membrane protein with a K+ and Cl− channel.Acta Physiol. Scand. 129:137–138
Cherksey, B.D., Zeuthen, T. 1988. H-bumetanide binding to the purified putative co-transporter protein.Acta Physiol. Scand. 133:267–268
Chipperfield, A.R. 1980. An effect of chloride on (Na+K) co-transport in human red blood cells.Nature (London) 286:281–282
Chipperfield, A.R. 1986. The (Na+-K+-Cl−) co-transport system.Clin. Sci. 71:465–476
Dunham, P.B., Ellory, J.C. 1981. Passive potassium transport in low potassium sheep red cells: Dependence upon cell volume and chloride.J. Physiol. (London) 318:511–530
Dunham, P.B., Stewart, G.W., Ellory, J.C. 1980. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:1711–1715
Ellory, J.C., Dunham, P.B., Logue, P.J., Stewart, G.W. 1982. Anion-dependent cation transport in erythrocytes.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London (B) 299:483–495
Ellory, J.C., Hall, A.C., Stewart, G.W. 1985. Volume-sensitive cation fluxes in mammalian red cells.Mol. Physiol. 8:235–246
Feit, P.W., Hoffmann, E.K., Schiødt, M., Kristensen, P., Jessen, F., Dunham, P.B. 1988. Purification of proteins of the Na/Cl cotransporter from membranes of Ehrlich ascites cells using a bumetanide-sepharose affinity column.J. Membrane Biol. 103:135–147
Frizzell, R.A., Field, M., Schultz, S.G. 1979. Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues.Am. J. Physiol. 236:F1-F8
Garty, H., Rudy, B., Karlish, S.J.D. 1983. A simple and sensitive procedure for measuring isotope fluxes through ion-specific channels in heterogenous populations of membrane vesicles.J. Biol. Chem. 258:13094–13099
Geck, P., Heinz, E. 1986. The Na-K-2Cl cotransport system.J. Membrane Biol. 91:91–105
Geck, P., Pietrzyk, C., Burckhardt, B.-C., Pfeiffer, B., Heinz, E. 1980. Electrically silent contransport of Na+, K+ and Cl− in Ehrlich cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600:432–447
Görg, A., Postel, W., Weser, J., Schiwaro, H.W.; Boesken, W.H. 1985. Horizontal SDS electrophoresis in ultrathin poregradient gels for the analysis of urinary proteins.Science Tools 32:5–9
Greger, R. 1985. Ion transport mechanisms in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron.Physiol. Rev. 65:760–797
Haas, M., Forbush, B., III. 1987. Na, K, Cl-cotransport system: Characterization by bumetanide binding and photolabeling.Kidney Int. 32 (Suppl. 23):S134-S140
Haas, M., McManus, T.J. 1985. Effect of norepinephrine on swelling-induced potassium transport in duck red cells. Evidence against a volume-regulatory decrease under physiological conditions.J. Gen. Physiol. 85:649–667
Helenius, A., Simons, K. 1972. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 247:3656–3661
Hoffmann, E.K., Lambert, I.H., Simonsen, L.O. 1986a. Separate, Ca2+-activated K+ and Cl− transport pathways in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells.J. Membrane Biol. 91:227–244
Hoffmann, E.K., Schiødt, M., Dunham, P.B. 1986b. The number of chloride-cation cotransport sites on Ehrlich ascites cells measured with [3H]bumetanide.Am. J. Physiol. 250:C688-C693
Hoffmann, E.K., Simonsen, L.O. 1989. Membrane mechanisms in volume and pH regulation in vertebrate cells.Physiol. Rev. (in press)
Hoffmann, E.K., Simonsen, L.O., Lambert, I.H. 1984. Volume-induced increase of K+ and Cl− permeabilities in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Role of internal Ca2+.J. Membrane Biol. 78:211–222
Hoffmann, E.K., Simonsen, L.O., Sjøhlm, C. 1979. Membrane potential, chloride exchange, and chloride conductance in Ehrlich mouse ascites tumour cells.J. Physiol. (London) 296:61–84
Hoffmann, E.K., Sjøhlm, C., Simonsen, L.O. 1983. Na+, Cl− co-transport in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells activated during volume regulation (regulatory volume increase).J. Membrane Biol. 76:269–280
Jessen, F., Sjøholm, C., Hoffmann, E.K. 1986. Identification of the anion exchange protein of Ehrlich cells: A kinetic analysis of the inhibitory effects of 4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid (DIDS) and labeling of membrane proteins with3H-DIDS.J. Membrane Biol. 92:195–205
Kagawa, Y. 1972. Reconstitution of oxidative phosphorylation.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 265:297–338
Kinne, R.K.H., Kinne-Saffran, E., Schoelermann, B., Schuetz, H., Doell, G. 1987. Functional molecular size of rabbit kidney Na, K, Cl cotransporter.Kidney Int. 31:171
Klaerke, D.A., Petersen, J., Jørgensen, P.L. 1987. Purification of Ca2+-activated K+ channel protein on calmodulin affinity columns after detergent solubilization of luminal membranes from outer renal medulla.FEBS Lett 216:211–216
Kramhøft, B., Lambert, I.H., Hoffmann, E.K., Jørgensen, F. 1986. Activation of Cl-dependent K transport in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells.Am. J. Physiol. 251:C369-C379
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (London) 227:680–685
Lambert, I.H., Simonsen, L.O., Hoffmann, E.K. 1984. Volume regulation in Ehrlich ascites tumour cells: pH sensitivity of the regulatory volume decrease, and role of the Ca2+-dependent K+ channel.Acta Physiol. Scand. 120:46A
Lauf, P.K. 1985a. On the relationship between volume- and thiol-stimulated K+ Cl− fluxes in red cell membranes.Mol. Physiol. 8:215–234
Lauf, P.K. 1985b. K+:Cl− cotransport: Sulfhydryls, divalent cations, and the mechanism of volume activation in a red cell.J. Membrane Biol. 88:1–13
Lauf, P.K., McManus, T.J., Haas, M., Forbush, B., III., Duhm, J., Flatman, P.W., Saier, M.H., Jr., Russel, J.M. 1987. Physiology and biophysics of chloride and cation cotransport across cell membranes.Fed. Proc. 46:2377–2394
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275
McManus, T.J., Haas, M., Starke, L.C., Lytle, C.Y. 1985. The duck red cell model of volume-sensitive chloride-dependent cation transport:In: Membrane Transport Driven by Ion Gradients. G. Semenza and R. Kinne, editors.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 456:183–186
McManus, T.J., Schmidt, W.F., III. 1978. Ion and co-ion transport in avian red cells.In: Membrane Transport Processes. J.F. Hoffmann, editor. Vol. 1, pp. 79–106. Raven, New York
O'Grady, S.M., Palfrey, H.C., Field, M. 1987. Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues.Am. J. Physiol. 253:C177-C192
Peterson, G.L. 1977. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable.Anal. Biochem. 83:346–356
Rodbard, D., Kapadia, G., Chramback, A. 1971. Pore gradient electrophoresis.Anal. Biochem. 40:135–157
Schubert, D., Boss, K., Dorst, H.-J., Flossdorf, J., Pappert, G. 1983. The nature of the stable noncovalent dimers of band 3 protein from erythrocyte membranes in solutions of Triton X-100.FEBS Lett. 163:81–84
Steck, T.L. 1972. Cross-linking the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane.J. Mol. Biol. 66:295–305
Tzagoloff, A., Penefsky, H.S. 1971. Extraction and purification of lipoprotein complexes from membranes.In: Methods in Enzymology, W.B. Jakoby, editor. Vol. 22, pp, 219–230. Academic, New York and London
Warnock, D.G., Greger, R., Dunham, P.B., Benjamin, M.A., Frizzell, R.A., Field, M., Spring, K.R., Ives, H.E., Aronson, P.S., Seifter, J. 1984. Ion transport processes in apical membranes of epithelia.Fed. Proc. 43:2473–2487
Zeuthen, T., Andersen, P.M., Eskesen, K.E., Cherksey, B.D. 1988. Characterization of a purified co-transporting protein.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 90:687–691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jessen, F., Cherksey, B.D., Zeuthen, T. et al. Isolation and reconstitution of furosemide-binding proteins from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J. Membrain Biol. 108, 139–151 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871025
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871025