Abstract
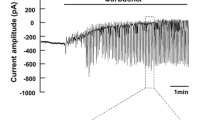
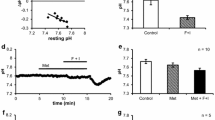
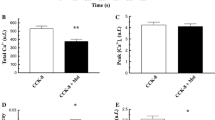
The cellular regulation mechanism of Na-K-Cl cotransport was studied in dispersed acinar cells of the guinea pig nasal gland by a microfluorimetric imaging method using the Na+-sensitive dye sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate. Addition of 1 μm acetylcholine (ACh) induced an immediate increase in intracellular Na+ concentration ([Na+]i) by 36.7±9.9 mm, which was almost completely abolished by the addition of atropine. The increased [Na+]i after cholinergic stimulation was due to the external Cl−-dependent cotransport system (about 80% of the total Na+ influx) and the dimethyl amiloride-sensitive Na+-H+ exchange system (of about 20%). The ACh-induced increase in [Na+]i was dependent on extracellular Ca2+ and was prevented by pretreatment with 8-(N, N-diethylamino)octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate or O-O′-bis(2-aminophenyl)ethyleneglycol-N, N, N′, N′-tetraacetic acid tetraacetoxymethyl ester. Addition of 1μm ionomycin mimicked the ACh-induced increase in [Na+]i which was dependent on external Cl−. Moreover, both a calmodulin antagonist trifluoperazine and a myosin light chain kinase inhibitor ML-7 reduced the ACh-induced response in [Na+]i. However, the following treatment did not affect the basal [Na+]i nor the ACh-induced increase in [Na+]i: (i) addition of dibutyryl cAMP, 8-Br-cGMP, or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, (ii) pretreatment of protein kinase inhibitors, H-89, H-8, H-7 or chelerythrine, (iii) prevention of cytosolic Cl− efflux by the addition of diphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid or, (iv) prevention of cytosolic K+ efflux by the addition of charybdotoxin. The present results suggest that the ACh-induced increase in [Na+]i, mainly responsible for activation of Na-K-Cl cotransport, is mediated by a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baraniuk, J.N., Lundgren, J.D., Okayama, M., Mullol, J., Merida, M., Shelhamen, J.H., Kaliner, M.A. 1990. Vasoactive intestinal peptide in human nasal mucosa. J. Clin. Invest. 86:825–831
Berridge, M.J., Irvine, R.F. 1984. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 312:315–321
Breitwieser, G.E., Altamirano, A.A., Russell, J.M. 1990. Osmotic stimulation of Na+-K+-Cl− cotransport in squid giant axon is [Cl−]i dependent. Am. J. Physiol. 258:C749-C753
Brock, T.A., Brugnara, C., Canessa, M., Gimbrone, M.A. Jr. 1986. Bradykinin and vasopressin stimulate Na+-K+-Cl− cotransport in cultured endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 250:C888-C895
Chijiwa, T., Mishima, A., Hagiwara, M., Sano, M., Hayashi, K., Inoue, T., Naito, K., Toshioka, T., Hidaka, H. 1990. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinoline sulfonamide (H89), of PC12D phenochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265:5467–5272
Chiou, C.Y., Malagodi, M.H. 1975. Studies on the mechanism of action of a new Ca2+ antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride in smooth and skeletal muscles. Br. J. Pharmacol. 53:279–285
Crook, R.B., von Brauchitsch, D.K., Polansky, J.R. 1992. Potassium transport in nonpigmented epithelial cells of ocular ciliary body: inhibition of a Na+, K+, Cl− cotransporter by protein kinase C. J. Cell Physiol. 153:214–220
DeJonge, H.R., Vaandrager, A.B., O'Grady, S.M., Field, M. 1985. A 50-kDa protein in flounder intestine brush borders (BB) is phosphorylated by cGMP and Ca-CaM kinases and is specifically dephosphorylated by a cAMP-activated phosphatase. Fed. Proc. 45:4281
Frömter, E., Diamond, J.M. 1972. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nature 235:9–13
Gawin, A.Z., Emery, B.F., Baraniuk, J.N., Kaliner, M.A. 1991. Nasal glandular secretory response to cholinergic stimulation in humans and guinea pig. J. Appl. Physiol. 71:2460–2468
Geck, P., Heinz, E. 1986. The Na-K-2Cl cotransport system. J. Membrane Biol. 91:97–105
Haas, M. 1989. Properties and diversity of (Na-K-Cl) cotransporters. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 51:443–457
Haas, M., McBrayer, D.G. 1994. Na-K-Cl cotransport in nystatintreated tracheal cell: regulation by isoproterenol, apical UTP, and [Cl]i. Am. J. Physiol. 266:C1440-C1452
Hagiwara, M., Inagaki, M., Hidaka, H. 1987. Specific binding of a novel compound, N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesufonamide (H-8) to the active site of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 31:523–528
Harootunian, A.T., Kao, J.P.Y., Eckert, B.K., Tsien, R.Y. 1989. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cytosolic free Na+ in individual fibroblasts and lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 264:19458–19467
Herbert, J.M., Augereau, J.M., Gleye, J., Maffrand, J.P. 1990. Chelerythrine is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 172:993–999
Ikeda, K., Ishigaki, M., Sunose, H., Wu, D., Takasaka, T. 1995a. Intracellular Ca2+ response induced by acetylcholine in the submucosal nasal gland acinar cells in guinea pigs. Am. J. Physiol. 268:L361-L367
Ikeda, K., Ishigaki, M., Wu, D., Sunose, H., Takasaka, T. 1995b. Na+ transport processes in isolated guinea pig nasal gland acinar cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 163:204–209
Ikeda, K., Saito, Y., Nishiyama, A., Takasaka, T. 1991. Effects of pH on intracellular calcium level in isolated cochlear outer hair cells of guinea pig. Am. J. Physiol. 261:C231-C236
Ikeda, K., Saito, Y., Nishiyama, A., Takasaka, T. 1992a. Intracellular pH regulation in isolated cochlear outer hair cell of the guinea-pig. J. Physiol. 447:327–348
Ikeda, K., Saito, Y., Nishiyama, A., Takasaka, T. 1992b. Na+-Ca2+ exchange in the isolated outer hair cells of the guinea-pig studied by fluorescence image microscopy. Pfluegers Arch. 420:493–499
Kawamoto, S., Hidaka, H. 1984. 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) is a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C in rabbit platelet. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 125:258–264
Lytle, C., Forbush, B. III. 1992. The Na-K-Cl cotransport protein of shark rectal gland. II. regulation by direct phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 267:25438–25443
Manganel, M., Turner, R.J. 1989. Agonist-induced activation of Na+/ H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells. J. Membrane Biol. 111:191–198
Nauntofte, B. 1992. Regulation of electrolyte and fluid secretion in salivary acinar cells. Am. J. Physiol. 263:G823-G837
Nishizuka, Y. 1984. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 308:693–698
O'Donnell, M.E. 1991. Endothelial cell sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Evidence of regulation by Ca+ and protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 266:11559–11566
O'Donnell, M.E., Owen, N.E. 1986. Atrial natriuretic factor stimulates Na/K/Cl cotransport in vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:6132–6136
O'Grady, S.M., Palfrey, H.C., Field, M. 1987. Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues. Am. J. Physiol. 253:C177-C192
Okada, M., Saito, Y., Sawada, E., Nishiyama, A. 1991. Microfluorimetric imaging study of the mechanism of activation of the Na+/H+ antiport by muscarinic agonist in rat mandibular acinar cells. Pfluegers Arch. 419:338–348.
Owen, N.E., Ridge, K.M. 1989. Mechanism of angiotensin II stimulation of Na-K-Cl cotransport of vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 257:C629-C636
Paris, S., Pouyssegur, J. 1986. Growth factors activate the bumetanide-sensitive Na/K/Cl cotransport in hamster fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 261:6177–6183
Paulais, M., Turner, R.J. 1992. Activation of the Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter in rat parotid acinar cells by aluminum fluoride and phosphatase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 267:21558–21563
Petersen, O.H. 1992. Stimulus-secretion coupling: Cytoplasmic calcium signals and the control of ion channels in exocrine acinar cells. J. Physiol. 448:1–51
Petersen, O.H., Maruyama, Y. 1984. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature 307:693–696
Saitoh, M., Ishikawa, T., Matsushima, S., Naka, M., Hidaka, H. 1987. Selective inhibition of catalytic activity of smooth mescle myosin light chain kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 262:7796–7801
Smith, J.B., Smith, L. 1987. Na+/K+/Cl− cotransport in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: Stimulation by angiotensin II and calcium ionophores, inhibition by cyclic AMP and calmodulin antagonists. J. Membrane Biol. 99:51–63
Sunose, H., Zhang, W., Ishigaki, M., Katori, Y., Suzuki, M., Ikeda, K., Takasaka, T., Saito, Y., Nishiyama, A. 1994. Isolation of acini from nasal glands of the guinea-pig. Acta Physiol. Scand. 151:377–384
Tokumitsu, H., Chijiwa, T., Hagiwara, M., Mizutani, A., Terasawa, M., Hidaka, H. 1990. KN-62, 1-[N,O-bis(1,5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-Nmethyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazine, a specific inhibitor of Ca2+/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 265:4315–4320
Torchia, J., Lytle, C., Pon, D.J., Forbush, B. III, Sen, A,K. 1992. The Na-K-Cl cotransporter of avian salt gland. Phosphorylation in response to cAMP-dependent and calcium-dependent secretagogues. J. Biol. Chem. 267:25444–25450
Wittner, M., DiStefano, A., Wangemann, P., Delarge, J., Liegeois, J.F., Greger, R. 1987. Analogues of torasemide-structure function relationship-experiments in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle of rabbit nephron. Pfluegers Arch. 408:54–64
Wu, D., Sunose, H., Ikeda, K., Ishigaki, M., Takasaka, T. 1994. Ionic currents induced by acethylcholine in isolated acinar cells of the guinea pig nasal gland. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 202:307–313
Zhang, G.H., Gragoe, E.J. Jr., Melvin, J.E. 1992. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in rat sublingual mucous acini at rest and during muscarinic stimulation. J. Membrane Biol. 129:311–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are grateful to Ms. Michiko Yokoyama for her assistance in the preparations of this manuscript. This work was supported by Grant-In-Aid 05807156 and 06807131 to K. Ikeda.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, K., Wu, D. & Takasaka, T. Cellular mechanisms in activation of Na-K-Cl cotransport in nasal gland acinar cells of guinea pigs. J. Membarin Biol. 146, 307–314 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233950
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233950