Abstract
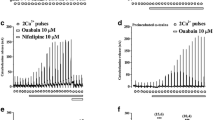
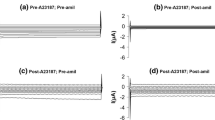
Activation of Ca2+ and cAMP-dependent Cl− conductances by extracellular ATP was studied using the whole-cell patch clamp technique. Immediately after addition of extracellular ATP (10 μm), activation of wholecell Cl− current exhibiting delayed inactivation and activation kinetics at hyperpolarizing and depolarizing voltages, respectively, was observed. After prolonged activation, the kinetic characteristics of the ATP-induced Cl− current became time- and voltage-independent. When applied to the later phase of the ATP-activated whole-cell current, the disulfonic acid stilbene DIDS (200 μm) could only inhibit 64% of the current while diphenylamine-dicarboxylic acid (DPC, 1 mm) completely inhibited it. Inclusion of a peptide inhibitor for protein kinase A (PKI, 10 nm) in the pipette solution blocked ATP-induced time- and voltage-independent current activation but did not affect the delayed activating and inactivating current activation but did not affect the delayed activating and inactivating current which could be totally blocked by DIDS. Anion selectivity sequence was determined in the presence of either PKI or DIDS and found to be significantly different. Increased pipette EGTA (10 mm) or treatment of the cells with trifluoperazine (40 μm), an inhibitor of calmodulin, suppressed both types of ATP-induced Cl− currents. No current activation by ATP was observed when cells were dialyzed with the IP3 receptor blocker, heparin (10 ng/ml). These results suggest that extracellular ATP activates IP3-linked Ca2+-dependent regulatory pathway, which in turn activates cAMP-dependent pathway, leading to activation of both Ca2+ and cAMP-dependent Cl− conductances in epididymal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M.P., Welsh, M.J. 1991. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:6003–6007
Chan, H.C., Golstein, J., Nelson, D.J. 1992. Alternate pathways for chloride conductance activation in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C1273-C1283
Chan, H.C., Zhou, W.L., Fu, W.O., Ko, W.H., Wong, P.Y.D. 1995. Different regulatory pathways involved in ATP-stimulated chloride secretion in rat epididymal epithelium. J. Cell Physiol (in press)
Cheng, H.C., Kemp, B.E., Pearson, R.B., Smith, A.J., Misconi, L., Van Patten, S.M., Walsh, D.A. 1986. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 261:989–992
Cliff, W.H., Frizzell, R.A. 1990. Separate Cl− conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl−-secreting epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4956–4960
Cuthbert, A.W., Wong, P.Y.D. 1986. Electrogenic anion secretion in cultured rat epididymal epithelium. J. Physiol. 378:335–345
Dho, S., Stewart, K., Foskett, J.K. 1992. Purinergic receptor activation of Cl− secretion in T84 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C67-C74
Dubyak, G.R., El-Moatassim, C. 1993. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am. J. Physiol. 265:C577-C606
Fedan, J.S., Belt, J.J., Yuan, L.X., Frazer, D.G. 1993. Contractile effects of nucleotides in guinea pig isolated perfused trachea: involvement of respiratory epithelium, prostanoids and Na+ and Cl− channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 264:210–216
Flezar, M., Heisler, S. 1993. P2-purinergic receptors in human breast tumor cells: coupling of intracellular calcium signaling to anion secretion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 265:1499–1510
Fuller, C.M., Benos, D.J. 1992. CFTR Am. J. Physiol. 263:C267-C286
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current from cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Huang, S.J., Fu, W.O., Chung, Y.W., Zhou, T.S., Wong, P.Y.D. 1993. Properties of cAMP-dependent and Ca2+-dependent whole-cell Cl− conductances in the rat epididymal cells. Am. J. Physiol. 264:C794-C802
Leung, A.Y.H., Tai, H.L., Wong, P.Y.D. 1993. ATP stimulates Ca2+ release from a rapidly exchanging pool in cultured rat epididymal cells. Am. J. Physiol. 264:C1388-C1394
Massom, L., Lee, H., Jarrett, H.W. 1990. Trifluoperazine binding to porcine brain calmodulin and skeletal muscle troponin C. Biochemistry 29:671–681
Nilsson, T., Zwiller, J., Boynton, A.L., Berggren, P.O. 1988. Heparin inhibits IP3-induced Ca2+ release in permeabilized pancreatic β-cells. FEBS Lett. 229:211–214
O'Neil, K.T., DeGrado, W.F. 1990. How calmodulin binds its targets: sequence independent recognition of amphophilic α-helices. TIBS 15:59–64
Seamon, K.B., Padgett, W., Daly, J.W. 1981. Forskolin: Unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membrane and intact cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:3363–3367
Stutts, M.J., Chinet, T.C., Mason, S.J., Fullton, J.M., Clarke, L.L., Boucher, R.C. 1992. Regulation of Cl− channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by extracellular ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1621–1625
Tang, W.J., Krupinski, J., Gilman, A.G. 1991. Expression and characterization of calmodulin-activated (Type I) adenylylcyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 266:8595–8603
Wagner, J.A., Cozens, A.L., Schulman, H., Gruenert, D.C., Stryer, L., Gardner, P. 1991. Activation of chloride channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Nature 349:793–796
Wong, P.Y.D. 1988a. Control of anion and fluid secretion by apical P2-purinoceptors in the rat epididymis. Br. J. Pharmacol 95:1315–1321
Wong, P.Y.D. 1988b. Mechanism of adrenergic stimulation of anion secretion in cultured rat epididymal epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 254:F121-F133
Wong, P.Y.D. 1990. Electrolyte and fluid transport in the epididymis. In: Epithelial Secretion of Water and Electrolytes. J. Young and P. Wong, editors, pp. 333–347. Springer-Verlag, New York
Wong, P.Y.D., Huang, S.J. 1990. Secretory agonists stimulate a rise in intracellular cyclic AMP but not Ca2+ and inositol phosphates in cultured rat epididymal epithelium. Exp. Physiol. 75:321–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Mr. W.O. Fu for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Croucher Foundation, the University and Polytechnic Grants Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, H.C., Zhou, W.L. & Wong, P.Y.D. Extracellular ATP activates both Ca2+- and cAMP-dependent Cl− conductances in rat epididymal cells. J. Membarin Biol. 147, 185–193 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233546
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233546