Abstract
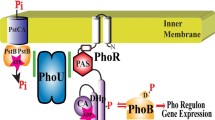
Complementation between mutants impaired in inorganic phosphate (Pi) transport via the phosphate-specific transport (PST) system was studied. For that purpose the transport of Pi via the alternative Pi transport (PIT) system was bioenergetically arrested. Complementation was found betweenpstB andphoT mutations, whereas each of these mutations failed to complement with aphoS mutation. The data obtained confirm previous studies in which the inducibility of alkaline phosphatase was used to determine complementation and indicated a polar effect of thephoS mutation onpstB andphoT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Amemura, M., Shinagawa, H., Makino, K., Otsuji, N., Nakata, A. 1982. Cloning and complementation tests with alkaline phosphatase regulatory genes (phoS andphoT) ofEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology152:692–701.
Bachmann, B. 1983. Linkage map ofEscherichia coli K12, edition 7. Microbiological Reviews47:180–230.
Cox, G. B., Rosenberg, H., Downie, J. A., Silver, S. 1981. Genetic analysis of mutants affecting the Pst inorganic phosphate transport system. Journal of Bacteriology148:1–9.
Echols, H., Garen, A., Garen, S., Torriani, A. 1961. Genetic control of repression of alkaline phosphatase inE. coli. Journal of Molecular Biology3:425–438.
Garen, A., Otsuji, N. 1964. Isolation of a protein specified by a regulator gene. Journal of Molecular Biology8:841–852.
Gerdes, R. G., Rosenberg, H. 1974. The relationship between the phosphate-binding protein and a regulator gene product fromEscherichia coli. Biochimicha et Biophysica Acta351:77–86.
Iwakura, M., Shimura, Y., Tsuda, K. (1982). Isolation of DNA fragment containingphoS gene ofEscherichia coli. Journal of Biochemistry92:615–622.
Kaczorowski, G. J., Robertson, D. E., Kaback, H. R. 1979. Mechanism of lactose transduction in membrane vesicles fromEscherichia coli. II. Effect of imposed ΔΨ, ΔpH, and\(\Delta \mu _{H^ + } \). Biochemistry18:3697–3704.
Levitz, R., Bittan, R., Yagil, E. 1981. Complementation tests between alkaline phosphatase constitutive mutants (phoS andphoT) inEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology145:1432–1435.
Lin, E. C. C., Koch, J. P., Chused, T. M., Jorgensen, S. E. 1962. Utilization ofL-α-glycerophosphate byEscherichia coli without hydrolysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America48:2145–2150.
Lowry O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry193:265–275.
Miller, J. H. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Rosenberg, H., Gerdes, R. G., Chegwidden, K. 1977. Two systems for the uptake of phosphate inEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology131:505–511.
Rosenberg, H., Gerdes, R. G., Harold, F. M. 1979. Energy coupling to the transport of inorganic phosphate inEscherichia coli K-12. Biochemical Journal178:133–137.
Shaw K. J., Berg, C. M. 1979.Escherichia coli K12 auxotrophs induced by insertion of the transposable element Tn5. Genetics92:741–747.
Sprague, G. F., Bell, R. M., Cronan, Jr., J. E. 1975. A mutant ofEscherichia coli auxotrophic for organic phosphates: evidence for two defects in inorganic phosphate transport. Molecular and General Genetics143:71–77.
Torriani, A. 1966. Alkaline phosphatase ofE. coli pp. 224–235. In: Cantoni, G. L., Davis, D. R. (eds.), Procedures in nucleic acid research. New York: Harper and Row.
Willsky, G. R., Bennet, R. L., Malamy, M. H. 1973. Inorganic phosphate transport inEscherichia coli: involvement of two genes which play a role in alkaline phosphatase regulation. Journal of Bacteriology113:529–539.
Willsky, G. R., Malamy, M. H. 1976 Control of the synthesis of alkaline phosphatase and the phosphate-binding protein inEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology127:595–609.
Yagil, E., Silberstein, N., Gerdes, R. G. 1976. Coregulation of the phosphate-binding protein and alkaline phosphatase inEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology127:656–659.
Zuckier, G., Torriani, A. 1981. Genetic and physiological tests of three phosphate-specific transport mutants ofEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology145:1249–1256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brucker, R., Levitz, R., Yagil, E. et al. Complementation tests between mutations in the phosphatespecific transport region ofEscherichia coli . Current Microbiology 10, 303–307 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577145
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577145