Abstract
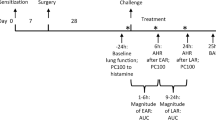
The aim of the present study was to examine the role of neuropeptides, especially substance P (SP) and neurokinin A (NKA), in toluene diisocyanate (TDI)-induced airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to acetylcholine aerosols. Thirty parts per billion of TDI in air administered over 4 hours caused a significant increase in the airway constrictive response to acetylcholine (ACH) aerosols in rabbits (ΔRI: 245 ± 30%, p < 0.005) without altering basic values of respiratory, cardiovascular or blood gas parameters. Inhalation of the aerosolized neuropeptides SP and NKA resulted in a similar increase in airway responsiveness (AR) to ACH as exposure to 30 ppb TDI. To determine whether neuropeptides contribute to TDI-induced AHR, we studied their effects after systemic treatment with capsaicin as well as after infusion of specific synthetic antagonists for SP and NK2 (NKA) receptors. CAPS treatment performed on 4 consecutive days as well as antagonists' infusion only moderately (p > 0.05) decreased airway responses to ACH. CAPS application prevented the TDI-induced increase in AR to ACH in all rabbits. The increase in airway resistance to ACH did not significantly change after TDI exposure (98 ± 22% of the control response before TDI, p > 0.05). Simultaneous infusion of specific synthetic SP and NK2 receptor antagonists also abolished the TDI-induced increase in airway responses to ACH in all animals investigated (P > 0.05). The results of this study demonstrate that neuropeptides, especially the tachykinins SP and NKA, are important mediators in TDI-induced AHR in rabbits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Takeda N, Irifune M, Ogino S, Kalubi B, Imamura I, Fuhini H, Wada H, Matsunaga T (1992) Effects of capsaicin desensitization on nasal allergy like symptoms and histaminrelease in the nose induced by Toluene Diisocyanate in guinea pigs. Acta Otolaryngol 112:7803–7809
Abraham WM, Ahmed A, Cortes A, Soler M, Farmer SG, Baugh LE, Harbeson SL (1991) Airway effects of inhaled bradykinin, substance P, and neurokinin A in sheep. J Allergy Clin Immunol 87:557–564
Barnes PJ, Baraniuk JN, Belvisi MG (1991) Neuropeptides in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:1187–1198 and 1391–1399
Bartlett MS (1937) Properties of sufficiency and statistical tests. (1937) Proc Roy Soc 160:268–282
Carstairs J, Barnes PJ (1986) Autoradiographic mapping of substance P receptors in lung. Eur J Pharmacol 127:295
Casale TB (1991) Neuropeptides and the lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol 88:1
Cheung D, Bel E, Den Hartigh J, Dijkman J, Sterk P (1992) The effect of inhaled neutral endopeptidase inhibitor thiorphan on airway responsiveness to neurokinin A in normal humans in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis 145:1275–1280
Dharmarajan V, Rando R (1980) Critical evaluation of continuous monitors for toluene diisocyanate. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 41:12–18
Erdbs EG, Skidgel RA (1989) Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and related regulators of peptide hormones. FASEB J 3:145–151
Gordon T, Sheppard D, McDonald D, Scypinski, Distefano S (1985) Airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation induced by toluene diisocyanate in then guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:1106–1112
Ishikawa J, Ichinose M, Nakajima N, Takahashi T, Yamauchi H, Miura M, Shirato K (1994) Potassium channel opener, YM 934, inhibits neurogenic plasma leakage in guinea pig airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 150:1379–1383
Karol MH (1988) The development of animal models for TDI a3sthma. Bull Eur Pathophysiol Respir 23:571–576
Lai YL (1991) Role of the axon reflex in capsaicin-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs. Respir Physiol 83:35–46
Laufer R, Wormser U, Friedman Z, Gilon CH, Chorev M, Selinger Z (1985) Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7444–7448
Link RF, Wallace DL (1950) On the ratio of two ranges. Ann Math Statist 21:112–116
Lotz M, Vaughan JH, Carson DA (1988) Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science 241:1218
Lundberg JM, Hökfeld T, Martling CR, Saria A, Cuello C (1984) Substance P immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res 235:251–261
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Ballati L, Lecci A, Manzini S, Patacchini R, Renzetti AA, Rovero P, Quartara L, Giachetti A (1991) In vivo evidence for tachykininergic transmission using a new NK-2 receptor selective antagonist MEN 10,376. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:1172–1178
Mapp CE, Boniotti A, Papi A, Chitano P, Fabbri LM, Ciaccia A (1992) The products of the reactions between toluene diisocyanate and water contract isolated guinea pig bronchi. Eur J Pharmacol 228:103–106
Mapp CE, Graf PD, Boniotti A, Nadel JA (1991) Toluene diisocyanate contracts guinea pig bronchial smooth muscle by activating capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:1082
Marek W, Baur X, Ulmer WT (1993) Immediate allergic and nonallergic reactivity of the airways in ascaris skin-sensitive sheep. Respiration 60:264–272
Marek W, Potthast J, Marczynski B, Baur X (1995) Toluene diisocyanate induction of airway hyperresponsiveness at the threshold limit value (10 ppb) in rabbits. Lung (in press)
Martling CR (1987) Sensory nerves containing tachykinins and CGRP in the lower airways. Functional implications for bronchoconstriction, vasodilatation and protein extravasion. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 563:1–57
Matsuda H, Kawakita K, Kiso Y, Nakano T, Kitamura Y (1989) Substance P induces granulocyte infiltration through degranulation of mast cells. J Immunol 142:927
Nilsson G, Alving K, Ahlstedt S (1991) Effects on immune responses in rats after neuromanipuladon with capsaicin. Int J Immunopharmacol 13:21–26
Omini C, Brunelli G, Hernandez A, Daffonchio L (1989) Bradykinin and substance P potentiate acetylcholine-induced bronchospasm in guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol 163:195–197
Phillipou S, Potthast J, Marek W (1993) Ultrastructural study of rabbit lung tissue subsequent to capsaicin treatment over several days. Respiration 60:232–236
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Dion S, D'Orleans-Juste P (1989) Receptors for substance P and related neurokinins. Pharmacol 38:1
Sheppard D, Thompson JE, Scypinski Dusser D, Nadel JA, Borson DB (1988) Toluene diisocyanate increases airway responsiveness to substance P and decreases airway neutral endopeptidase. J Clin Invest 81:1111–1115
Solway J, Leff AR (1991) Sensory neuropeptides and airway function. J Appl Physiol 71:2077–2087
Stretten CD, Belvisi MG, Barnes PJ (1990) Sensory nerve depletion potentiates inhibitory NANC nerves in guinea pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol 184:333–337
Tamura G, Sakai K, Taniguchi Y (1989) Neurokinin A-induced bronchial hyperresponsiveness to metacholine in Japanese monkeys. Tohuko J Exp Med 159:69–73
Thompson JE, Scypinski LA, Gordon T, Sheppard D (1987) Tachykinins mediate the acute increase in airway responsiveness caused by toluene diisocyanate in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis 136:43–49
Tissot M, Pradelles P, Giroud JP (1988) Substance P like levels in inflammatory exudates. Inflammation 12:25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: Dr. rer. nat. Wolfgang Marek
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marek, W., Potthast, J.J.W., Marczynski, B. et al. Role of substance P and neurokinin A in toluene diisocyanate-induced increased airway responsiveness in rabbits. Lung 174, 83–97 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177703
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177703