Abstract.
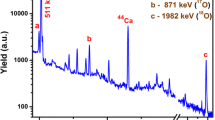
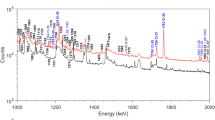
Various K-, L- and M-shell X-ray production cross sections are measured for heavy ion impact on elements in the range Z 2 = 13 to 83. The ion species range from Z 1 = 10 to 36, and ion energies from 1 to 16 MeV are used. Enhanced cross sections are observed when the projectile K- or L- binding energy is similar to the energy of the target K-, L- or M-shell. This effect is used to improve the analysis sensitivity for selected elements. As an example trace analysis of Fe in glass with V, Mn, Co and Ni ions is investigated. Results are compared with proton induced X-ray emission analysis on the same samples. In these samples Fe-Kα X-ray production is similar for irradiation with 3 MeV protons and 14 MeV Ni ions. However the signal to background ratio is four times higher for the irradiation with Ni ions as compared to irradiation with protons. Advantages and drawbacks of heavy ion induced X-ray emission for quantitative analysis compared to proton induced X-ray emission analysis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ecker, K., Weise, HP. & Merkle, K. Trace Analysis by Heavy Ion Induced X-Ray Emission. Mikrochim Acta 133, 313–317 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040070112
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040070112