Summary
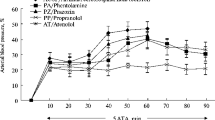
The role of central adrenergic innervation of the brain capillaries is still a matter of discussion. The hypothesis that these nerves control the blood-brain barrier permeability was tested by electrically stimulating the locus coeruleus, the major central adrenergic nucleus, in the anaesthetized rat. Frequencies of 5, 15, and 30 Hz were used. A frequency dependent increase in blood-brain barrier permeability to sodium fluorescein was verified. Prior administration of the α-adrenoceptor antagonist phenoxybenzamine (10 mg/kg i.p., 24 h before electrical stimulation) totally blocked the effect of 15 Hz stimulation. The same dose of pindolol (a β-adrenoceptor antagonist) given 1 h before electrical stimulation potentiated the effect of 5 Hz stimulation. Thus, blood-brain barrier permeability is increased, in a frequency dependent manner, by electrical stimulation of the locus coeruleus. The results obtained with phenoxybenzamine and pindolol suggest an opposite effect of α and β-adrenoceptors on the control of sodium fluorescein transport through the blood-brain barrier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba H, Oishi R, Saeki K (1988) Enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability to sodium fluorescein by stimulation of μ opioid receptors in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 337: 423–428
Bandler R, Carrive P, Zhang SP (1991) Integration of somatic and autonomic reactions within the midbrain periaqueductal gray: viscerotopic, somatotopic and functional organization. Prog Brain Res 87: 269–305
Bolwig TG, Hertz MM, Paulsen OB (1977) The permeability of blood-brain barrier during electrically induced seizures in man. Eur J Clin Invest 7: 87–93
Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Kokfelt T (1968) The effect of imobilization stress on the activity of central monoamine neurons. Life Sci 7: 107–112
Dahlstrom A, Fuxe K (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. 1. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 62 [Suppl 232]: 1–55
Donovick PJ (1974) A metachromatic stain for neural tissue. Stain Technol 49: 49–51
Dóczi T (1993) Volume regulation of the brain tissue — a survey. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 121: 1–8
Edvinsson L, Lindvall O, Nielsen K, Owman C (1973) Are brain vessels innervated by central (non-sympathetic) adrenergic neurons? Brain Res 63: 496–499
Edvinsson L, Owman CH, Siesjo B (1976) Physiological role of cerebrovascular sympathetic nerves in the autorregulation of cerebral blood flow. Brain Res 117: 519–523
Harik SI, Sharma VK, Weatherbae JR, Warren RH, Banergee SP (1980) Adrenergic receptors of cerebral microvessles. Eur J Pharmacol 61: 207–208
Harper CM, McCulloch J (1985) Cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular disease. In: Swash M, Kennard C (eds) Scientific basis of clinical neurology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburg, pp 518–532
Hartman BK (1973) The innervation of cerebral blood vessels by central noradrenergic neurons. In: Usdin E, Snyder SH (eds) Frontiers in catecholamine reasearch. Pergamon, New York, pp 91–96
Johansson BB, Aver LM, Linder LE (1982) Phenothiazine-medited protection of the blood-brain barrier during acute hypertension. Evidence of a modification of the endothelial cell membrane. Stroke 13: 220–225
Kobayashi H, Cazzaniga A, Spano PF, Trabucchi M (1982) Ontogenesis of alpha and beta receptors located on cerebral microvessels. Brain Res 242: 358–360
Korf J, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1973 a) Increased turnover of norepinephrine in the rat cerebral cortex during stress; role of the locus coeruleus. Neuropharmacology 12: 933–938
Korf J, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1973 b) Stimulation and destruction of the locus coeruleus: opposite effects on 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol sulfate levels in the rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 21: 305–310
Korf J, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1973 c) Alterations and endogenous levels of noradrenaline in cerebral cortex following electrical stimulation and acute axotomy of cerebral noradrenergic pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 23: 276–282
Loizou LA (1969) Projections of the locus coeruleus in the albino rat. Brain Res 15: 563–566
Lorenzo AV, Shiarahige JA, Liang M, Barlow CF (1972) Temporary alterations of cerebrovascular permeability during drug induced seizures. Am J Physiol 223: 268–277
Menzies SA, Betz AL, Hoff JT (1993) Contributions of ions and albumin to the formation and resolution of ischemic brain edema. J Neurosurg 78: 257–266
Mraovitch S, Iadecola C, Ruggiero DA, Reis DJ (1985) Widespread reductions in cerebral blood flow and metabolism elicited by electrical stimulation of the parabrachial nucleus in rat. Brain Res 341: 283–296
Mraovitch S, Kumada M, Reis DJ (1982) Role of the nucleus parabrachialis in cardiovascular regulation in cat. BrainRes 232: 57–75
Nag S (1984) Cerebral endothelial surface change in hypertension. Acta Neuropath (Berl) 63: 276–281
Nag S (1986) Cerebral endothelial plasma membrane alterations in acute hypertension. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70: 38–43
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd Ed. Academic Press, Sydney
Petito CK, Shaefer JA, Plum F (1977) Ultrastructural characteristics of brain and blood-brain barrier in experimental seizures. Brain Res 127: 251–267
Preskorn SH, Hartman BK, Irwin GH, Hughes CW (1982) Role of central adrenergic system in mediating amitriptyline induced alterations in mammalian blood-brain barrier in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 223: 388–395
Quagliarello VJ, Long WJ, Scheld WM (1986) Morphologic alterations of the blood-brain barrier with experimental meningitis in the rat. Temporal sequence and the role of encapsulation. J Clin Invest 77: 1084–1095
Raichle ME, Eichling JO, Grubb RL, Hartman BK (1976) Central noradrenergic regulation of brain microcirculation. In: Pappius HM, Feindel WM (eds) Dynamics of brain edema. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 11–17
Raichle ME, Hartman BK, Eichling JO, Sharpe LG (1975) Central noradrenergic regulation of cerebral flow and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72: 3726–3730
Rapoport S, Thompson H (1975) Opening of the blood-brain barrier by a pulse of hidrostatic pressure. Biophys J 15: 326 a
Rennels ML, Nelson E (1975) Capillary innervation in mammalian central nervous system: an electron microscopic demonstration. Am J Anat 144: 233–241
Sarmento A, Albino-Teixeira A, Azevedo I (1988) Increase in blood-brain barrier permeability due to amitriptyline is accompanied by augmented pinocytosis in cerebral capillaries. Br J Pharmacol 96: 838 (Abstract)
Sarmento A, Albino-Teixeira A, Azevedo I (1990) Amitriptyline induced morphologic alterations of the rat blood-brain barrier. Eur J Pharmacol 176: 69–74
Sarmento A, Borges N, Azevedo I (1991) Adrenergic influences on the control of blood-brain barrier permeability. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343: 633–637
Skinho JE, Paulson OB (1969) Carbon dioxide and cerebral circulatory control. Arch Neurol 20: 249–252
Swanson LW, Connelly MA, Hartman BK (1977) Ultrastructural evidence for central monoaminergic innervation of blood vessels in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Brain Res 136: 166–173
Thierry AM, Javoy F, Glowinski F, Kety SS (1968) Effects of the stress on the metabolism of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in the central nervous system of the rat. Modification of norepinephrine turnover. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 163: 163–171
Tunkel AR, Sheld WM (1989) Alterations of blood-brain barrier in bacterial meningitis: in vivo and in vitro models. Ped Inf Dis J 8: 911–913
Tunkel AR, Wispelwey B, Sheld WM (1990) Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of meningitis. Inf Dis Clin North Am 4: 555–581
Ungerstedt U (1971) Mapping of the central dopamine, nor-adrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine pathways. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 367: 1–30
Westergaard EV, Deurs B, Bronsted HE (1977) Increased vesicular transfer of horseradish peroxidase across cerebral endothelium evoked by active hypertension. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37: 141–152
Xu BN, Yabuki A, Mishima H, Miyazaki M, Maeda M, Ishii S (1993) Pathophysiology of brain swelling after acute experimental brain compression and decompression. Neurosurgery 32: 289–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Instituto Nacional de Investigação Científica (INIC FmP1).
Nuno Borges is a PhD student with a grant from Junta Nacional de Investigação Científica e Tecnológica (JNICT).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarmento, A., Borges, N. & Lima, D. Influence of electrical stimulation of locus coeruleus on the rat blood-brain barrier permeability to sodium fluorescein. Acta neurochir 127, 215–219 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808769
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808769