Summary
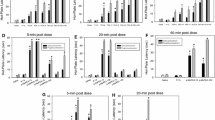
A behavioural test involving potentiation of the effects of an acute injection of β-phenylethylamine (10 mg kg−1 i.p.) was used to assess the time-course of type-B MAO inhibition after administration of (−)deprenyl (5 mg kg−1 i.p.) and of MD 240928 (20 mg kg−1 i.p.) respectively. Potentiation of the effects of β-phenylethylamine was observed 1 h after injection of (−)deprenyl or MD 240928. This effect was still evident 120 h after administration of (−)deprenyl but not 24 h after administration of MD 240928. Comparisons of ex vivo estimates of MAO activity yielded a corresponding time-course for the recovery of this enzyme. The extent of MAO inhibition required for potentiation of the effects of β-phenylethylamine was inferred from a comparison of the behavioural test results and the ex vivo MAO activity observed after (−)deprenyl administration. These comparisons indicate a significant underestimation of MD 240928-induced MAO inhibition using ex vivo measures. This underestimation is interpreted as evidence fordilution effects in the ex vivo assay of MAO inhibition. The potentiation of effects of β-phenylethylamine under the present conditions is proposed as a useful and simple test for effects of reversible type-B MAO inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dostert P, Strolin-Benedetti M, Guffroy C (1983) Different stereoselective inhibition of monoamine oxidase-B by the R- and S-enantiomers of MD 780236. J Pharm Pharmacol 35: 161–165
Dourish CT (1987) The effects of drugs on spontaneous motor activity. In: Greenshaw AJ, Dourish CT (eds) Methods in experimental psychopharmacology. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 153–211
Fowler CJ, Ross SB (1984) Selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A and B-biochemical and pharmacological properties. Med Res Rev 4: 323–358
Green AL (1984) Assessment of the potency of reversible MAO inhibitors in vivo. In: Tipton KF, Dostert P, Strolin-Benedetti M (eds) Monoamine oxidase and disease: prospects for therapy with reversible inhibitors. Academic Press, London, pp 73–81
Green AR, Elhait AS (1980) A new approach to the assessment of the potency of reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors in vivo, and its application to (+)amphetamine, p-methoxyamphetamine and harmaline. Biochem Pharmacol 29: 2781–2789
Maître L, Delini-Stula A, Waldmeier PC (1976) Relations between the degree of monoamine oxidase inhibition and some psychopharmacological responses to monoamine oxidase inhibitors in rats. In: Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) CIBA Foundation Symposium #39 (New Ser): Monoamine oxidase and its inhibition. Elsevier/North Holland Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 247–266
Ortmann R, Schaub M, Feiner A, Lauber J, Christen P, Waldmeier PC (1984) Phenyl-ethylamine-induced stereotypies in the rats: a behavioural test system for assessment of MAO-B inhibitors. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 84: 22–27
Ortmann R, Waldmeier PC, Radeke E, Feiner A, Delini-Stula A (1980) The effects of 5-HT uptake and MAO inhibitors on L-5-hydroxytryptophan-induced excitation in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 311: 185–192
Tipton KF, Fowler CJ, McCrodden JM, Strolin-Benedetti M (1983) The enzyme-activated irreversible inhibition of type B MAO by 3-(4-[(3-chlororphenyl)methoxy]phenyl)-5-[(methylamino)methyl]-2-oxazolidinone methane sulphonate (compound MD 780236) and the enzyme-catalysed oxidation of this compound as competing reactions. Biochem J 209: 235–242
Tipton KF, Strolin-Benedetti M, McCrodden J, Boucher T, Fowler CJ (1984) The inhibition of rat liver monoamine oxidase-B by the enantiomers of MD 780236. In: Tipton KF, Dostert P, Strolin-Benedetti M (eds) Monoamine oxidase and disease: prospects for therapy with reversible inhibitors. Academic Press, London, pp 155–163
Waldmeier PC, Feiner AE, Lauber J (1984) Reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors: relation between effects on enzymatic activity measured ex vivo and on amine activity. In: Tipton KF, Dostert P, Strolin-Benedetti M (eds) Monoamine oxidase and disease: prospects for therapy with reversible inhibitors. Academic Press, London, pp 108–116
Yu PH, Boulton AA (1979) Activation of platelet monoamine oxidase by plasma in humans. Life Sci 25: 31–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turkish, S., Yu, P.H. & Greenshaw, A.J. Monoamine oxidase-B inhibition: a comparison of in vivo and ex vivo measures of reversible effects. J. Neural Transmission 74, 141–148 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244780
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244780