Summary
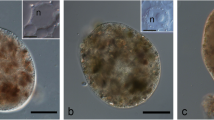
Basic proteins ofBlastocystis hominis were detected by the ammoniacal silver and ethanolic phosphotungstic acid techniques using electron microscopy. The central vacuole showed many silver grains when treated with ammoniacal silver and an increased electron density when treated with phosphotungstic acid. The intensity of positive reactions correlated with the electron density of the central vacuole, because cells having an electron-lucent central vacuole showed no silver grain deposits. Since it is known that the concentration of electron-dense materials in the central vacuole increases during log phase of growth, and then decreases in stationary phase, this organelle must accumulate basic proteins during cell growth.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benchimol M, Elias CA, De Souza W (1982)Tiitrichomonas foetus: ultrastructural localization of basic proteins and carbohydrates. Exp Parasital 54: 135–144
Boreham PFL, Stenzel DJ (1993)Blastocystis in humans and animals: morphology, biology, and epizootiology. Adv Parasitol 32: 1–70
Brumpt E (1912)Blastocystis hominis n. sp. et formes voisines. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 5: 725–730
Gordon M, Bensch KG (1968) Cytochemical differentiation of the guinea pig sperm flagellum with phosphotungstic acid. J Ultrastruct Res 24: 33–50
MacRae EK, Meetz GD (1970) Electron microscopy of the ammoniacal silver reaction for histones in the erythropoietic cells of the chick. J Cell Biol 45: 235–245
Nakamura Y, Hashimoto T, Yoshikawa H, Kamaishi T, Nakamura F, Okamoto K, Hasegawa M (1996) Phylogenetic position ofBlastocystis hominis that contains cytochrome-free mitochondria, inferred from the protein phytogeny of elongation factor lα. Mol Biochem Parasitol 77: 241–245
Silberman JD, Sogin ML, Leipe DD (1996) Human parasite finds taxonomic home. Nature 380: 398
Souto-Padron T, De Souza W (1978) Ultrastructural localization of basic proteins inTrypanosoma cruzi. J Histochem Cytochem 26: 349–358
Stenzel DJ, Dunn LA, Boreham PFL (1989) Endocytosis in cultures ofBlastocystis hominis. Int J Parasitol 19: 787–791
Yoshikawa H, Hayakawa A (1996) Morphological changes in the central vacuole ofBlastocystis hominis during in vitro culture. Protoplasma 194: 63–68
—, Kuwayama N, Enose Y (1995a) Histochemical detection of carbohydrates ofBlastocystis hominis. J Euk Microbiol 42: 70–74
—, Satoh J, Enose Y (1995b) Light and electron microscopic localization of lipids inBlastocystis hominis. J Electron Microsc 44: 100–103
Zierdt CH (1991)Blastocystis hominis: past and future. Clin Microbiol Rev 4: 61–79
—, Donnolley CT, Muller J, Constantopoulos G (1988) Biochemical and ultrastructural study ofBlastocystis hominis. J Clin Microbiol 26: 965–970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshikawa, H., Oishi, K. Ultrastructural localization of basic proteins ofBlastocystis hominis . Protoplasma 200, 31–34 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280732
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280732