Summary
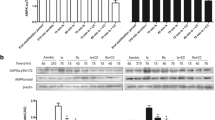
The protein kinase activity in cytosol was similar in control, ischemic, and reperfused hearts; however, a 1.5-fold increase in membrane protein kinase activity was induced by ischemia and reperfusion. The H-7 inhibitable cytosolic protein kinase activity decreased by 40% with 30 min ischemia, while that of membrane fraction increased 1.8-fold. However, the CGS9343B inhibitable protein kinase activity in cytosolic fractions was unaffected by ischemia, while that of membrane increased by about 1.7-fold. These results suggest that myocardial ischemia is associated with enhanced protein kinase C and calmodulin-dependent kinase activities in membrane fraction. Furthermore, the results also suggest a translocation of protein kinase C activity from the cytosol to the membrane. Reperfusion of ischemic myocardium did not result in any further increase of protein kinase C and calmodulin-dependent kinase activities in the membrane. These enhanced protein kinase activities also resulted in an enhanced phosphorylation of endogenous membrane proteins. The creatine kinase released from the heart was increased by both ischemia and reperfusion. Therefore, these results suggest that biochemical cascades of reactions caused by enhanced membrane protein kinase C and calmodulin-dependent kinase activities may contribute to ischemic-reperfusion injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown JH, Buxton IL, Brunton LL (1985) Circ Res 57:532–537
Legssyer A, Poggitoli J, Renard D, Vassort G (1988) J Physiol 401:185–199
Allen IS, Cohen NM, Dhallan RS, Gaa ST, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (1988) Circ Res 62:524–534
Liu J, Casley DG, Nayler WG (1989) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 164:1220–1225
Nishizuka Y (1988) Nature 334:661–665
Corr PB, Shayman JA, Kramer JB, Kipins RJ (1981) J Clin Invest 67:1232–1236
Otani H, Prasad MR, Engelman RM, Otani H, Cordis GA, Das DK (1988) Circ Res 63:930–936
Leatherman GF, Kim D, Smith TW (1987) Am J Physiol 253:H205-H209
Rogers TB, Gaa ST, Massey C, Dosameci A (1991) J Biol Chem 266:4302–4308
Dosameci A, Dhallan RS, Cohen NM, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (1988) Circ Res 62:347–357
Nayler WG, Poole-Wilson PA, Williams A (1979) J Mol Cell Cardiol 117:683–706
Shen AC, Jennings R-B (1972) Am J Pathol 67:441–452
Tani M, Neeley JR (1989) Circ Res 65:1045–1046
Chen K-C, Engler R (1990) In Calcium and the Heart (Langer GA, ed). Raven Press, New York, pp 333–354
Fearon CW, Tashjian AH (1985) J Biol Chem 260:8366–8371
Kraft AS, Anderson WB (1983) Nature 301:621–623
Bell RM (1986) Cell 45:631–632
Vigne P, Breittmayer JP, Duval D, Frelin C, Lazdunski M (1988) J Biol Chem 263:8078–8083
Caroni P, Caragoli E (1981) J Biol Chem 256:9371–9373
Hirota K, Hirota T, Aguilera G, Catt KJ (1985) J Biol Chem 260:3243–3246
Laemmli UK (1970) Nature 227:680–685
Liu X, Prasad MR, Engelman RM, Jones RJ, Das DK (1990) Am J Physiol 259: H1101-H1107
Lamers JM, Weeda E (1984) In: Methods in Studying Cardiac Membranes (Dhalla, NS, ed). CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, Vol. 1, pp 180–199
Hidaka H, Inagaki M, Kawamoto S, Sasakis Y (1984) Biochemistry 23:5036–5041
Norman JA, Ansell GA, Stone LP, Wennogle LP, Wasley JWF (1987) Mol Pharmacol 31:535–540
Prasad MR, Engelman RM, Das DK (1990) Biochem Pharmacol (India) 9:231–240
Presti CF, Scott BT, Jones L (1985) J Biol Chem 260:13879–13889
Das DK, Engelman RM, Prasad MR, Rousou JA, Breyer RH, Jones R, Young H, Cordis G (1989) Biochem Pharmacol 38:465–471
Kim HW, Kim DH, Ikemoto N, Kranias EG (1987) Biochem Biophys Acta 903:333–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, M.R., Jones, R.M. Enhanced membrane protein kinase C activity in myocardial ischemia. Basic Res Cardiol 87, 19–26 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795386
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795386