Summary
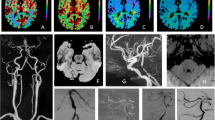
In the past 5 years we have investigated 29 patients with symptomatic basilar artery stenoses (14 cases) and occlusions (14) and a patent primitive trigeminal artery with thin-calibered basilar and vertebral arteries (1) using directional continuous-wave Doppler sonography of the vertebral arteries. A total of 19 patients survived, and 17 of them were clinically and sonographically reexamined after 40.4 ± 15.8 months (mean ± SD). Among the 8 patients with basilar stenoses, 6 — with no further transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) in the interval — exhibited an increase in the summed modified Pourcelot indices (relative end-diastolic flow velocities) of the vertebrals by 0.18 ± 0.16; the other 2 showed a decrease by 0.26 each, in 1 case temporally related to a TIA, in the 2nd case without further clinical deterioration. In the 8 survivors with basilar occlusions, 5 remained — by sonographic criteria — unchanged with summed modified Pourcelot indices of the vertebrals of 0.00, while 3 patients exhibited a slight increase in the summed modified Pourcelot indices of 0.13 ± 0.03. While the difference between the outcome of subsets of patients treated with regimens of 30,000–40,000 units heparin/day or phenprocoumon and less radical drugs were statistically not significant, the former regimen appeared clinically more efficacious in preventing further deterioration in approximately two-thirds of the patients affected. Due to the potential recurrence of neurological symptoms, a treatment period with phenprocoumon of 6 months after discharge from hospital appears justified. Due to these therapeutic efforts, approximately half of the patients initially affected survived with no or only a mild neurological deficit. Directional continuous-wave Doppler sonography is, in our opinion, a reliable technique for examining the short- and long-term changes in peripheral vascular resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biedert S, Betz H, Reuther R (1986) Die Doppler-sonographische Diagnose von Basilarisstenosen und -obliterationen. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 235:221–230
Büdingen HJ, Reutern GM von, Freund HJ (1982) Doppler-Sonographie der extracraniellen Hirnarterien. Thieme, Stuttgart
Caplan LR (1979) Occlusion of the vertebral or basilar artery. Follow-up analysis of some patients with benign outcome. Stroke 10:277–282
Caplan LR (1981) Vertebrobasilar disease. Time for a new strategy. Stroke 12:111–114
Fields WS, Ratinov G, Weibel J, Campos RJ (1966) Survival following basilar artery occlusion. Arch Neurol 15:463–471
Kubik CS, Adams RD (1946) Occlusion of the basilar artery: A clinical and pathological study. Brain 69:73–121
Marshall J (1964) Natural history of transient ischemic cerebrovascular attacks. Quart J Med 33:309–324
Meyer JS, Sheehan S, Bauer RB (1960) An arteriographic study of cerebrovascular disease in man. I. Stenosis and occlusion of the vertebral-basilar arterial system. Arch Neurol 2:27–45
Reutern GM von, Büdingen HJ, Freund HJ (1976) Doppler-sonographische Diagnostik von Stenosen und Verschlüssen der Vertebralarterien und des Subclavian-Steal-Syndroms. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 222:209–222
Ringelstein EB, Zeumer H (1982) The role of continuous-wave Doppler sonography in the diagnosis and management of basilar and vertebral artery occlusions, with special reference to its application during local fibrinolysis. J Neurol 228:161–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herm Prof. Dr. H. Gänshirt anläßlich seiner Emeritierung in Dankbarkeit gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biedert, S., Schulz, U., Betz, H. et al. Basilar artery disease —Clinical outcome and doppler sonographical follow-up. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 237, 91–100 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382372
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382372