Abstract
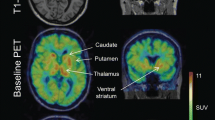
Regional cerebral glucose metabolism (rCMRGlc) and dopamine D2 receptor binding were measured in a 31-year-old, severely affected, untreated patient with Wilson's disease of 3 years' duration using positron emission tomography and18F-deoxyglucose and18F-methylspiperone ([18F]MSP), respectively. There was a severe reduction of striatal and extrastriatal rCMRGlc as well as of striatal [18F]MSP accumulation rate. After 1 year of treatment withd-penicillamine, striatal and extrastriatal rCMRGlc and striatal [18F]MSP accumulation rate reached almost normal levels. It is hypothesized that recovery of motor functions due to copper trapping therapy was associated with an increase in basal ganglia activity and a re-expression or upregulation of dopamine D2 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horoupian DS, Sternlieb I, Scheinberg IH (1988) Neuropathological findings in penicillamine-treated patients with Wilson's disease. Clin Neuropathol 7:62–67
Scheinberg IH, Sternlieb I (1984) Wilson's disease. In: Smith LH (ed) Major problems in internal medicine, vol 23. Saunders, Philadelphia
Walshe JM, Gibbs KR (1987) Brain copper in Wilson's disease. Lancet II:1030
Hawkins RA, Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME (1987) Wilson's disease studied with FDG and PET. Neurology 37:1707–1711
De Volder A, Sindic CJ, Goffinet AM (1988) Effect ofd-penicillamine treatment on brain metabolism in Wilson's disease: a case study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:947–949
Kuwert T, Hefter H, Scholz D, Milz M, Weiss P, Arendt G, Herzog H, Loken M, Hennerici M, Feinendegen LE (1992) Regional cerebral glucose consumption measured by positron emission tomography in patients with Wilson's disease. Eur J Nucl Med 19:96–101
Baron JC, Mazière B, Loc'h C et al (1986) Loss of striatal [76Br]bromospiperone binding sites demonstrated by positron emission tomography in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:131–136
Pascual J, Berciano J, Grijalba B, Olmo E del, Gonzales AM, Figols J, Pazos A (1992) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in progressive supranuclear palsy: an autoradiographic study. Ann Neurol 32:703–707
Brooks DJ, Ibanez V, Playford ED, Sawle GV, Leigh PN, Kocen RS, Harding AE, Marsden CD (1991) Presynaptic and postsynaptic striatal dopaminergic function in neuroacanthocytosis: a positron emission tomographic study. Ann Neurol 30:166–171
Brooks DJ, Ibanez V, Sawle GV, Playford ED, Quinn N, Mathias CJ, Lees AJ, Marsden CD, Bannister R, Frackowiak RSJ (1992) Striatal D2 receptor status in patients with Parkinson's disease, striatonigral degeneration, and progressive supranuclear palsy, measured with11C-raclopride and positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 31:184–192
Nagatsu T, Kato T, Nagatsu I, et al (1979) Catecholamine-related enzymes in the brain of patients with parkinsonism and Wilson's disease. In: Poirer LJ, Sourkes TL, Bedard PJ (eds) Advances in neurology, vol 24. Raven Press, New York, pp 283–292
Nyberg P, Gottfries CTG, Homgreen G, Perrson S, Roos BE, Winblad B (1982) Advanced catecholaminergic disturbances in the brain in a case of Wilson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand 65:71–75
Walshe JM (1956) Penicillamine: a new oral therapy for Wilson's disease. Am J Med 21:487–495
Walshe JM (1982) Treatment of Wilson's disease with trientine (triethylene tetramine) dihydrochloride. Lancet I:643–647
Walshe JM (1983) Wilson's disease: genetics and biochemistry — their relevance to therapy (Hudson memorial lecture). J Inherited Metab Dis 6 [Suppl 1]:51–58
Hefter H, Arendt G, Stremmel W, Freund H-J (1993) Motor impairment in Wilson's disease. I. Slowness of voluntary limb movements. Acta Neurol Scand 87:133–147
Rota Kops E, Herzog H, Schmid A, Holte S, Feinendegen LE (1990) Performance characteristics of an eightring whole body PET scanner. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:437–445
Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G (1986) Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]fluoro2-deoxy-d-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med 27:235–238
Huang S-C, Phelps ME, Hoffman EJ, Sideris K, Selin CJ, Kuhl DE (1980) Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am Physiol Soc E69–E82
Phelps ME, Huang SC, Hoffman EJ, Selin C, Sokoloff L, Kuhl DE (1979) Tomographic measurement of local cerebral glucose metabolic rate in humans with [F-18]2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose: validation of method. Ann Neurol 6:371–388
Reivich M, Alavi A, Wolf A, Fowler J, Russel J, Arnett C, MacGregor RR, Shine C-Y, Atkins H, Anand A, Dann R, Greenberg JH (1985) Glucose metabolic rate kinetic model parameter determination in humans: the lumped constants and rate constants for [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose and [11C]deoxyglucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:179–192
Greitz T, Bohm C, Holte S, Eriksson L (1991) A computerized brain atlas: construction, anatomical content, and some applications. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:26–38
Hamacher K, Nebeling B, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G (1991) [18F]Methylspiper-one: direct n.c.a. nucleophilic [18F]fluorination of N-methyl-4-nitrospiperone for remote controlled routine production of n.c.a. [18F]MSP. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm 30:353–354
Patlak CS, Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD (1983) Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple time uptake data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:1–7
Arnett CD, Shine C-Y, Wolf AP, et al (1985) Comparison of three 18F-labeled butyrophenone neuroleptic drugs in the baboon using positron emission tomography. J Neurochem 44:835–844
Arnett CD, Wolf AP, Shine C-Y, Fowler JS, MacGregor RR, Christman DR, Smith MR (1986) Improved delineation of human dopamine receptors using [18F]-N-Methylspiroperidol and PET. J Nucl Med 27:1878–1882
Wienhard K, Coenen HH, Pawlik G, Rudolf J, Laufer P, Jovkar S, Stöcklin G, Heiss W-D (1990) PET studies of dopamine receptor distribution using (18F)fluoroethylspiperone: findings in disorders related to the dopaminergic system. J Neural Transm 81:195–213
Williams FIB, Walshe JM (1981) Wilson's disease: an analysis of the cranial computerized tomography appearances found in 60 patients and the changes in response to treatment with chelating agents. Brain 104:735–752
Starosta-Rubinstein S, Young AB, Kluin K, Hill G, Aisen AM, Gabrielsen T, Brewer GJ (1987) Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease. Correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol 44:365–370
Lingam S, Wilson J, Nazer H, Mowat AP (1987) Neurological abnormalities in Wilson's disease are reversible. Neuropediatrics 18:11–12
Meyer B-U, Britton TC, Benecke R (1991) Wilson's disease: normalisation of cortically evoked motor responses with treatment. J Neurol 238:327–330
Linne T, Agatz I, Saaf J, Wáhlund LO (1990) Cerebral abnormalities in Wilson's disease as evaluated by ultralow-field magnetic resonance imaging and computerized image processing. Magn Reson Imaging 8:819–824
Ikeda K, Sakata C, Nemoto H, Yokoi F, Sunohara N, Iio M (1991) Clinicoradiological correlation of Wilson's disease by magnetic resonance imaging, computed and positron emission tomography. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 31:147–153
Prayer L, Wimberger D, Kramer J, Grimm G, Oder W, Imhof H (1990) Cranial MRI in Wilson's disease. Neuroradiology 32:211–214
Lockwood AH, Yap EWH, Rhoades HM, Wong W-H (1991) Altered cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in patients with liver disease and minimal encephalopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:331–336
Thuomas KÅ, Aquilonius SM, Bergström K, Westermark K (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Wilson's disease. Neuroradiology 35:134–141
Brugieres P, Combes C, Ricolfi F, Degos JD, Poirier J, Gaston A (1992) Atypical MR presentation of Wilson disease: a possible consequence of paramagnetic effect of copper? Neuroradiology 34:222–224
Snow BJ, Bhatt M, Martin WRW, Li D, Calne DB (1991) The nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway in Wilson's disease studied with positron emission tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:12–17
Oertel WH, Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Kraft E, Trenkwalder C, Scherer J, Weinzierl M, Vogl T, Kirsch CM (1992) Decrease of D2 receptors indicated by 1231-iodobenzamide single-photon emission computed tomography relates to neurological deficit in treated Wilson's disease. Ann Neurol 32:743–748
Schlang G, Kleinschmidt A, Hefter H, Kuwert T, Nebeling B, Stöcklin G, Seitz RJ (1993) Dopamine D2-receptor distribution and cerebral glucose metabolism in Wilson's disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13 [Suppl 1]:S389
Wong DF, Wagner HN, Dannals RF, Links JM, Frost JJ, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Rosenbaum AE, Gjedde A, Douglass KH, Petronis JD, Folstein MF, Toung JKT, Burns HD, Kuhar MJ (1984) Effects of age on dopamine and serotonin receptors measured by positron tomography in the living human brain. Science 226:1393–1396
Maura G, Giardi A, Raiteri M (1988) Release-regulating D-2 dopamine receptors are located on striatal glutamatergic nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:680–684
Gerfen CR (1992) The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization in the basal ganglia. Ann Rev Neurosci 15:285–320
Leenders KL, Aquilonius SM, Bergström K, et al (1988) Unilateral MPTP lesion in a rhesus monkey: effects on the striatal dopaminergic system measured in vivo with PET using various novel tracers. Brain Res 445:61–67
Savasta M, Dubois A, Benavides J, Scatton B (1988) Different plasticity changes in D1 and D2 receptors in the rat striatal subregions following impairment of dopaminergic transmission. Neurosci Lett 85:119
Weihmuller FB, Bruno JP, Neff NH, Hadjiconstantinou M (1990) Dopamine receptor plasticity following MPTP-induced nigrostriatal lesions in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol 180:369–372
Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V, Popilskis S, Kostic V, Levivier M, Fahn S, Cadet JL (1991) Unilateral MPTP-induced parkinsonism in monkeys. A quantitative autoradiographic study of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors and reuptake sites. Neurochirurgie 37:377–382
Walshe JM (1988) Diagnosis and treatment of presymptomatic Wilson's disease. Lancet II:435–437
Brewer GJ, Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan V (1992) Wilson disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 71:139–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlaug, G., Hefter, H., Nebeling, B. et al. Dopamine D2 receptor binding and cerebral glucose metabolism recover afterd-penicillamine-therapy in Wilson's disease. J Neurol 241, 577–584 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00920620
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00920620