Abstract
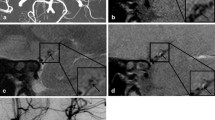
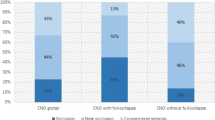
Because the pathogenesis of cerebral ischaemia in internal carotid artery dissection (ICAD) is controversial we studied the topography of cerebral infarction that results from ICAD according to pathophysiology of embolic and haemodynamic stroke. Sixty-four patients with 67 ICADs diagnosed by angiography, Doppler duplex sonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were studied prospectively during the past decade. According to current pathophysiological concepts, cortical territorial infarcts and large subcortical lenticulostriate infarcts revealed by CT or MRI were classified as embolic, while smaller infarcts in the subcortical junctional zone and infarcts in the cortical borderzone between the middle (MCA) and anterior cerebral artery were interpreted as haemodynamic infarcts. Of the 67 dissections 37 (55%) were associated with brain infarcts, of which territorial MCA infarcts of variable size accounted for 60%. These were combined with infarcts of the anterior and posterior cerebral artery in 5%; 8% of the patients had complete MCA infarction. Large lenticulostriate infarcts were present in 11%. Haemodynamic infarcts involved the subcortical junctional zone in 16% but never the anterior cortical borderzone. Although different abnormal Doppler findings indicated haemodynamically significant carotid obstruction in all symptomatic ICADs, only the characteristic high-resistance Doppler signal was significantly associated with the occurrence of brain infarction (in 66%,P < 0.01). The angiographic features of ICAD did not correlate with the incidence or with the topography of cerebral infarction. Patterns of infarction in ICAD indicate a predominantly embolic causation probably due to thrombus formation in the dissected carotid artery in the presence of severe haemodynamic obstruction, as demonstrated by Dopppler sonography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saver JL, Easton JD, Hart RG (1992) Dissections and trauma of cervicocerebral arteries. In: Barnett HIM, Mohr JP, Stein BM, Yatsu FM (eds) Stroke. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 671–688
D'Anglejan-Chatillon J, Ribeiro V, Mas JL, Bousser MG, Laplane D (1990) Dissection de l'artere carotide interne extracranienne. Presse Med 19:661–667
De Bray JM, Dubas F, Joseph PA, Causeret H, Pasquier JP, Emile J (1989) Etude ultrasonique de 22 dissections carotidiennes. Rev Neurol (Paris) 145:702–709
Bogousslavsky J, Despland PA, Regli F (1987) Spontaneous carotid dissection with acute stroke. Arch Neurol 44:137–140
Biller J, Hingtgen, Harold HP, Smoker WRK, Godersky JC, Toffol GJ (1986) Cervicocephalic arterial dissections. A ten-year experience. Arch Neurol 43: 1234–1238
Mokri B (1990) Traumatic and spontaneous extracranial internal carotid artery dissections. J Neurol 237:356–361
Mokri B, Sundt TM, Houser OW, Piepgras DG (1986) Spontaneous dissection of the cervical internal carotid artery. Ann Neurol 19:126–138
Steinke W, Aulich A, Hennerici M (1989) Diagnose und Verlauf von arotisdissektionen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 114:1869–1875
Sturzenegger M (1991) Ultrasound findings in spontaneous carotid artery dissection. Arch Neurol 48:1057–1063
Weiller C, Müllges W, Ringelstein EB, Buell U, Reiche W (1991) Patterns of brain infarction in internal carotid artery dissections. Neurosurg Rev 14: 111–113
Steinke W, Rautenberg W, Schwartz A, Hennerici M (1994) Noninvasive monitoring of internal carotid artery dissection. Stroke 25:998–1005
Hupperts RMM, Lodder J, Wilmink J, Boiten J, Hems-van Raak EPM (1993) Haemodynamic mechanism in small subcortical borderzone infarcts? Cerebrovasc Dis 3:231–235
Weiller C, Ringelstein EB, Reiche W, Buell U (1991) Clinical and hemodynamic aspects of low-flow infarcts. Stroke 22:117–1123
Bogousslavsky J (1991) Topographic patterns of cerebral infarcts. Cerebrovasc Dis 1 [Suppl] 1:61–68
Bogousslavsky J Van Melle G, Regli F (1989) Middle cerebral artery pial territory infarcts: a study of the Lausanne Stroke Registry. Ann Neurol 25:555–560
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F (1986) Unilateral watershed infarcts. Neurology 36:373–377
Ringelstein EB, Zeumer H, Angelou D (1983) The pathogenesis of strokes from internal carotid artery occlusion. Diagnostic and therapeutical implications. Stroke 14:867–875
Weiller C, Ringelstein EB, Reiche W, Buell U, Thron A (1990) The large striatocapsular infarction: a clinical and pathophysiological entity. Arch Neurol 47:1085–1091
Damasio HA (1983) A computed tomographic guide to the identification of cerebral vascular territories. Arch Neurol 40:138–142
Ghika JA, Bogousslavsky J, Regli F (1990) Deep perforators from the carotid system: template of the vascular territories. Arch Neurol 47:1097–1100
Brice JG, Crompton MR (1964) Spontaneous dissecting aneurysms of the cervical internal carotid artery. BMJ 2:790–792
Zwan A van der, Hiilen B (1991) Review of the variability of the territories of the major cerebral arteries. Stroke 22:1078–1084
Zwan A van der, Hillen B, Tulleken CAF, Dujovny M (1993) A quantitative investigation of the variability of the major cerebral arterial territories. Stroke 24:1951–1959
Hennerici M, Steinke W, Rautenberg W (1989) High-resistance Doppler flow pattern in extracranial carotid dissection. Arch Neurol 46:670–672
Lloyd J, Bahnson HT (1971) Bilateral dissecting aneurysms of the internal carotid arteries. Am J Surg 122:549–551
Thapedi IM, Ashenhurst EM, Rozdilsky B (1970) Spontaneous dissecting aneurysm of the internal carotid artery in the neck. Arch Neurol 23:549–554
Anderson RMcD, Schechter MM (1959) A case of spontaneous dissecting aneurysm of the internal carotid artery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 22:195–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinke, W., Schwartz, A. & Hennerici, M. Topography of cerebral infarction associated with carotid artery dissection. J Neurol 243, 323–328 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868406
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868406