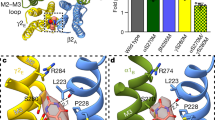
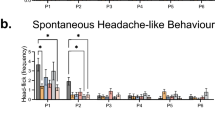
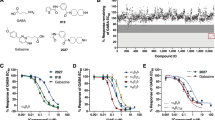
Abstract
ALTHOUGH benzodiazepines are widely used in routine medical practice their mechanism of action remains controversial1,2. Several authors have suggested that the action of benzodiazepines is to potentiate GABA-ergic processes in the central nervous system3–5. In addition, a number of studies have shown the effect of benzodiazepines to be antagonised by γ-amino-butyric acid (GABA) antagonists6,7. But, Steiner and Felix8 and Gähwiler9 have adopted the opposite view and reported that in the cerebellum and Deiters nucleus benzodiazepines antagonise the inhibitory action of GABA. On the other hand, Dray and Straughan6 have shown microiontophoretic applications of benzodiazepines to be inhibitory on the spontaneous and glutamate activity of neurones of the brain stem and were unable to confirm that benzodiazepines antagonise the action of GABA. Curtis et al.10 were also unable to confirm the results of Steiner and Felix8 on the neurones of the cerebellum and spinal cord. In the recent paper by Squires and Braestrup11 a direct interaction of benzodiazepines with GABA-receptors has been discarded. We have investigated the interaction between chlordiazepoxide (Librium) and GABA by observing the effects of simultaneous microiontophoretic application of both agents on the spontaneous and glutamate-evoked firing of single neurones of sensorimotor cortex of the rabbit and here we report that the actions of the two are synergistic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haefely, W., Pieri, L., Pole, P. & Schaffner, R. Nature 263, 173–174 (1976).
Steiner, F. A. & Felix, D. Nature 263, 174 (1976).
Costa, E., Guidotti, A., Mao, C. C. & Suria, A. Life Sci. 17, 167–186 (1975).
Haefely, W. et al. in Mechanism of Action of Benzodiazepines (eds Costa, E. & Greengard, P.) 131–151 (Raven, New York, 1975).
Zakusov, V. V. et al. Archs int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 214, 188–205 (1975).
Dray, A. & Straughan, D. W. J. Pharm. Pharmac. 28, 314–315 (1976).
Ostrovskaya, R. U. & Molodavkin, G. M. Bull. exp. Biol. Med. U.S.S.R. 82, 1073–1076 (1976).
Steiner, F. A. & Felix, D. Nature 260, 346–347 (1976).
Gähwiler, B. H. Brain Res. 107, 176–179 (1976).
Curtis, D. R., Lodge, D., Johnston, G. A. R. & Brand, S. J. Brain Res. 118, 344–347 (1976).
Squires, R. F. & Braestrup, C. Nature 266, 732–734 (1976).
Kozhechkin, S. N., Ostrovskaya, R. U. Bull. exp. Biol. Med. U.S.S.R. 82, 1448–1450 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOZHECHKIN, S., OSTROVSKAYA, R. Are benzodiazepines GABA antagonists?. Nature 269, 72–73 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/269072a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/269072a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.