Abstract
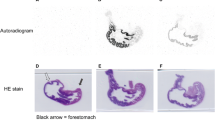
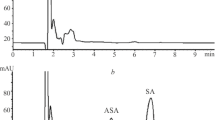
The distribution of three radioactively labelled salicylate derivatives with low ulcerogenic activity was compared with that of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and salicylic acid using whole body autoradiography and liquid scintillation counting techniques in rats. The methyl ester of ASA (AME) was distributed in vivo very similarly to that observed with ASA and salicylic acid. AME is rapidly demethylated following absorption from the stomach and is subsequently converted to ASA and salicylate. Salicylate is the main metabolite produced from both AME and ASA, which specifically accumulates in inflamed tissues.
The 3-methyl-and 6-methyl-substituted salicylic acids are not as rapidly absorbed as either ASA or salicylic acid and do not pass readily into the brain or bone marrow.
These results show that the methyl (ester) group of AME (which adequately protects the gastric mucosa from damage caused by ASA itself) does not impair the quantity of pharmacologically active form of drug (salicylate and ASA) generated in vivo. However, insertion of the methyl group at the 3- and 6-position of salicylic acid markedly affects both absorption, distribution and pharmaco-activity of these acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.W. Whitehouse, K.D. Rainsford, I.G. Young, N.G. Ardlie andK. Brune,Alternatives to Aspirin Derived from Biological Sources, in:Aspirin and Related Drugs: Their Actions and Uses (Eds. K.D. Rainsford, K. Brune and M.W. Whitehouse; Agents and Actions, Suppl.1 Birkhäuser Basel 1977), pp. 43–57.
K.D. Rainsford andM.W. Whitehouse,Gastric Irritancy of Aspirin and its Congeners: Anti-Inflammatory Activity Without this Side-Effect, J. Pharm. Pharmac.28, 83–86 (1976).
J. Hannah, W.V. Rule, J. Jones, A.R. Matzuk, K.W. Kelly, B.E. Witzel, W.J. Holtz, R.A. Houser, T.Y. Shen, L.H. Sarett, V.J. Lotti, E.A. Risley, C.G. van Arman andC.A. Winter,Novel Analgesic-Anti-Inflammatory Salicylates, J. Med. chem.21, 1093–1100 (1978).
E.M. Glenn, B.J. Bowman andN.A. Rohloff,Anomalous Biological Effects of Salicylates and Prostaglandins, Agents and Actions9, 257–264 (1979).
K.D. Rainsford,The Biochemical Pathology of Aspirin Induced Gastric Damage, Agents and Actions5, 326–344 (1975).
M.W. Whitehouse andK.D. Rainsford,Side-Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Are they Essential or can they be Circumvented?, in:Inflammation Mechanisms and their Impact on Therapy (Eds. I.L. Bonta, J. Thompson and K. Brune; Agents and Actions, Suppl. 3, Birkhäuser, Basel 1977), pp. 171–187.
K. D. Rainsford,Structure-Activity Relationships of Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs 1. Gastric Ulcerogenic Activity, Agents and Actions8, 587–605 (1978).
T.D. Lightbody andJ. Reid,Ortho-Cresotinate and Diabetes mellitus, Br. med. J.ii, 1704–1707 (1960).
A.J. Cummings andB.K. Martin,A Kinetic Study of the Elimination of 3-Methyl Salicylic Acid and its Acetyl Derivative in Man, Br. J. Pharmac.25, 470–480 (1965).
P.K. Seth andK.K. Tangeri,Biochemical Effects of some Newer Salicylic Acid Congeners, J. Pharm. Pharmac.18, 831–833 (1966).
H. Sievertsson, J.L.G. Nilsson andL. Paalzow,The Analgesic Properties of Methylsalicylic Acids, Acta Pharm. Suecica7, 289–292 (1970).
K.N. Von Kaulla andG. Ens,On Structure-Related Properties of Synthetic Organic Clot-Dissolving (Thrombolytic) Compounds, Biochem. Pharmac.16, 1023–1034 (1967).
W.L. Stafford,The Binding by Bovine Plasma and Plasma Fractions of Salicylic Acid and Some of its 3-Alkyl Analogues, Biochem. Pharmac.11, 685–692 (1962).
K. Brune, H. Gubler andA. Schweitzer,Autoradiographic Methods for the Evaluation of Ulcerogenic Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Pharmac, Ther.5, 199–207 (1979).
K. Brune, K.D. Rainsford andA. Schweitzer,Biodistribution of Mild Analgesics., Br. J. Clin. Pharmac. (1980) (in press).
G.A. Bruno andJ.E. Christian,Correction of Quenching Associated with Liquid Scintillation Counting, Anal. Chem.33, 650–651 (1961).
D.W. Yesair andC.B. Coutinho,Method for Extraction and Separation of Drugs and Metabolites from Biological Tissue, Biochem. Pharmac.19, 1569–1578 (1970).
C.H. Morris, J.E. Christian, R.R. Landolt andW.G. Hansen,Metabolism of Aspirin in Rumen and Corpus Tissues of Rat Stomach During the First Four Minutes After Administration, J. Pharm. Sci.62, 1017–1018 (1973).
O. Baine G.F. Adamson, J.W. Barton, J.L. Fitch, D.R. Swayampati andH. Jerskey,A Study of the Kolbe-Schmitt Reaction. II. The Carbonation of Phenols, J. org. Chem.19, 510 (1954).
A.J. Birch, R.A. Massey-Westropp andC.J. Moyle,Studies in Relation to Biosynthesis VII, 2-Hydroxy-6-methyl Benzoic Acid in Penicillium griseofolyum. Aust. J. Chem.8, 539–544 (1955).
C. Davidson,Salicylate Metabolism in Man, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.179, 249–268 (1971).
K.D. Rainford, A. Schweitzer andK. Brune,Autoradiographic and Biochemical Observations on the Distribution of New Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (submitted for publication).
K.F. Tempero, V.J. Cirillo andS.L. Steelman,Diflunisal: A Review of Pharmakokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties, Drug Interactions, and Special Tolerability Studies in Humans. Br. J. clin. Pharmac.4, 315–365 (1977).
P.M. Brooks andW.W. Buchanan, in:Current Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eds. W.B. Buchanan and W.C. Dick; Churchill, Edinburgh (1976), p. 33.
R.A. Scherrer,Aryl- and Heteroarylcarboxylic Acids, in:Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Chemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 1 (Eds R.A. Scherrer and M.W. Whitehouse; Academic Press, New York 1974), pp. 45–89.
R. Kumar andJ.D. Billimora Gastric Ulceration and the Content of Salicylate in Plasma in Rats after Administration of 14 C-Labelled Aspirin and its Synthetic Triglyceride, 1,3-Dipalmitoyl-2(2′-acetoxy-(14 C) carboxyl benzoyl)glycerol J. Pharm. Pharmac.30, 754–758 (1978).
M.H. Sherlock, U.S. Patent 3,644,424 (to Shering Corp.), cited in Ref. [25], pp. 45–89 (1974).
B. Chiego,Analgesic Salicylic Acid Derivatives, German Patent 2,037,017, Chem., Abst.76, 24921 (1972).
E.T. Burrows andJ.M. Johnson,Anti-Inflammatory Salicylic Acid Derivatives, British Patent 1,220,447 (to John Wyeth & Bro. Ltd.), Chem. Abstr.75, 35462 (1971).
D.V. Parke The Biochemistry of Foreign Compounds (Pergamon Press, London 1968).
J. Renson, H. Weissbach andS. Udenfriend,On the Mechanism of Oxidative Clearage of Aryl-Alkyl Ethers by Liver Microsomes Molec. Pharmac.1, 145–148 (1965).
K.D. Rainsford andM.W. Whitehouse,Anti-Inflammatory/ Anti-Pyretic Salicylic Acid Esters with Low Gastric Ulcerogenic Activity, Agents and Actions10, 451–456 (1980).
A.G. Ramsey, H.C. Elliott andA.M. Haynes,The Effect of Methyl Acetyl Salicylate on Renal Tubular Ionic Reabsorption, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol Med.132, 307–313 (1969).
D.P.R.L. Giudicelli andH. Najer,O-Acetyl Salicylic Acid Esters (to Synthélabo S.A.) Ger. Offen, 2,320,945, Chem. Abstr.80, 26976 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rainsford, K.D., Schweitzer, A., Green, P. et al. Bio-distribution in rats of some salicylates with low gastric ulcerogenicity. Agents and Actions 10, 457–464 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01968047
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01968047