Abstract
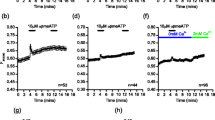
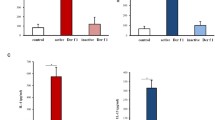
Pepstatin A, a pentapeptide isolated from cultures of actinomycetes, induced histamine secretion from human basophils in the concentration range of 3×10−7 to 10−4 M. The characteristics of this reaction were similar to those of f-met-peptide-induced histamine release: pepstatin A-induced release required Ca2+ and the release reaction was complete within 2 min at 22 or 37°C, but did not occur at 4°C. Release by both pepstatin a and f-met-peptide was reversibly inhibited by two non-releasing analogs of f-met-peptide, CBZ-Phe-Met and BOC-Met-Leu-Phe, Further, there was complete cross-desensitization between pepstatin A and f-met-peptide, while cells desensitized to pepstatin A released normally with anti-IgE and vice versa. A variety of pharmacological agents had similar effects on both pepstatin A and f-met-peptide-induced release (e.g., no enhancement with D2O; marked enhancement with cytochalasin B). We suggest that pepstatin A induces histamine release from human basophils by activating a cell surface receptor(s), also activated by the synthetic tripeptide f-met-peptide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Anti-IgE:
-
rabbit anti-Fc∈
- BOC-Met-Leu-Phe:
-
N-t-BOC-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine
- CBZ-Phe-Met:
-
carbobenzoxy-phenylalanylmethionine
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetertraacetic acid
- f-met-peptide:
-
formyl-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine
- PIPES:
-
piperazine-N,N′-bis(2-ethanesulphonic acid)
- P:
-
25 mM PIPES buffer, 110 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH 7.4
- PC:
-
PIPES buffer containing 2.0 mM CaCl2.
References
S.K. Ackerman andS.D. Douglas,Pepstatin A — a human leukocyte chemoattractant, Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol.14, 244–250 (1979).
E. Gillespie andL.M. Lichtenstein,Histamine release from human leukocytes: studies with deuterium oxide, colchicine and cytochalasin B, J. clin. Invest.51, 2941–2947 (1972).
O. Kawanami, F. Basset, R. Barrios, J.G. Lacronique, V.J. Ferrans andR.G. Crystal,Hypersensitive pneumonitis in man. Light- and electron-microscopic studies of 18 lung biopsies, Am. J. Path.110, 275–289 (1983).
G. Marone, A.K. Kagey-Sobotka andL.M. Lichtenstein,Effects of arachidonic acid and its metabolites on antigen-induced histamine release from human basophils in vitro, J. Immun.123, 1669–1677 (1979).
G. Marone, S. Poto, R. Petracca, M. Triggiani, E. de Lutio di Castelguidone andM. Condorelli,Activation of human basophils by staphylococcal protein A. 1. The role of cyclic AMP, arachidonic acid metabolites, microtubules and microfilaments, Clin. exp. Immunol.50, 661–668 (1982).
G. Marone, M. Columbo, S. Poto andM. Condorelli,Inhibition of histamine release from human basophils in vitro by calmodulin antagonists, Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol.28, 334–340 (1983).
G. Marone, G. Ambrosio, D. Bonaduce, A. Genovese, M. Triggiani andM. Condorelli,Inhibition of IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils and mast cells by fenoterol, Int. Archs Allergy appl. Immun.74, 356–361 (1984).
R.D. Nelson, S.K. Ackerman, V.D. Fiegel, M.P. Bauman andS.D. Douglas,Cytotaxin receptors of neutrophils: evidence that F-methionyl peptides and pepstatin share a common receptor, Infect. Immun.26, 996–999 (1979).
J.T. O'Flaherty, H.J. Showell, D.L. Kreutzer, P.A. Ward andE.L. Becker,Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro neutrophil responses to chemotactic factors by a competitive antagonist, J. Immun.120, 1326–1332 (1978).
R. Patterson, M. Roberts, R.C. Roberts, D.A. Emanuel andJ.N. Fink,Antibodies of different immunoglobulin classes against antigens causing famer's lung, Am. Rev. resp. Dis.114, 315–324 (1976).
M. Schmitt, R.G. Painter, A.J. Jesaitis, K. Preissner, L.A. Sklar andC.G. Cochrane,Photoaffinity labeling of the N-formyl peptide receptor binding site of intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A label suitable for following the fate of the receptorligand complex. J. biol. Chem.258, 649–654 (1983).
R.P. Siraganian andW.A. Hook,Mechanism of histamine release by formyl methonine-containing peptides, J. Immun.119, 2078–2083 (1977).
R.J. Smith, B.J. Bowman andS.S. Iden,Pepstatin A-induced degranulation and superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils, Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol.22, 83–93 (1982).
H. Umezawa, T. Aoyagi, H. Morishima, M. Matsuzaki, M. Hamada andT. Takeuchi,Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by actinomycetes, J. Antibiotics23, 259–262 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marone, G., Columbo, M., Soppelsa, L. et al. Histamine release from human basophils by pepstatin A. Agents and Actions 16, 306–309 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01982863
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01982863