Abstract
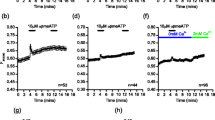
We have previously shown that physiological concentrations of zinc (≃7×10−6 M) inhibit the release of histamine from human basophil leukocytes (Maroneet al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 217: 292, 1981). In these experiments we compared the effect of zinc chloride on the release of chemical mediators from human basophils and mast cells isolated from human lung. Preincubation (5 min, 37°C) of human basophils and lung mast cells with zinc chloride (10−6–3×10−5 M) caused dose-related inhibition of histamine and peptide leukotriene C4 (LTC4) release induced by anti-IgE. Increase Ca2+ concentrations (0.3 to 6 mM) in the extracellular medium completely reversed the inhibitory effect of zinc on anti-IgE-mediated histamine secretion. Zinc chloride was a competitive antagonist of the action of Ca2+ in histamine secretion induced by anti-IgE with a dissociation constant (Kd) of about 10−5 M in both the basophil and mast cell systems. Thus physiological concentrations of zinc inhibit the release of histamine from human basophils and lung mast cells, presumably by blocking Ca2+ uptake induced by anti-IgE activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Jarom, T.A. Hall andA. Polliack,Electron microscopic X-ray microanalysis of normal and leukemic human lymphocytes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA73, 3690–3694 (1976).
A.M. Angyal andG.T. Archer,The zinc content of rat mast cells, Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci.46, 119–121 (1968).
B. Högberg andB. Uvnäs,Further observations on the disruption of rat mesentery mast cells caused by compound 48/80, antigen-antibody reaction, lecithinase A and decylamine, Acta Physiol. Scand.48, 133–145 (1960).
G. Marone, S.R. Findlay andL.M. Lichtenstein,Modulation of histamine release from human basophils in vitro by physiological concentrations of zinc, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.217, 292–298 (1981).
S. Hammarström, Leukotrienes. InAdvances in Clinical Immunology. The Role of Chemical Mediators in Pulmonary and Cardiac Diseases, pp. 77–90 (EdsM. Condorelli, G. Marone andL.M. Lichtenstein). O.I.C. Medical Press, Florence 1984.
R.P. Schleimer, D.W. MacGlashan, Jr., S.P. Peters, K.A. Knauer, E.S. Schulman, G.K. Adams, III, A. Kagey-Sobotka andL.M. Lichtenstein,In vivo and in vitro studies of human anaphylaxis. InAdvances in Clinical Immunology. The Role of Chemical Mediators in Pulmonary and Cardiac Diseases, pp. 65–76 (EdsM. Condorelli,G. Marone andL.M. Lichtenstein). O.I.C. Medical Press, Florence 1984.
D.W. MacGlashan, Jr., R.P. Schleimer, S.P. Peters, E.S. Schulman, G.K. Adams, III, H.H. Newball andL.M. Lichtenstein,Generation of leukotrienes by purified human lung mast cells, J. Clin. Invest.70, 747–751 (1982).
D.W. MacGlashan, Jr. andL.M. Lichtenstein,Dimeric IgE may not represent the unit signal for the release of all mediators in human basophils (abstr.), Fed. Proc.43, 1663 (1984).
G. Marone,The role of basophils and mast cells in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases, Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol.76 (suppl. 1), 70–82 (1985).
G. Marone, S. Vigorita, C. Antonelli, G. Torella, A. Genovese andM. Condorelli,Evidence for an adenosine A 2/R a receptor on human basophils, Life Sci.36, 339–345 (1985).
E.S. Schulman, D.W. MacGlashan, Jr., S.P. Peters, R.P. Schleimer, H.H. Newball andL.M. Lichtenstein,Human lung mast cells: purification and characterization, J. Immun.129, 2662–2667 (1982).
E.C. Hayes, D.L. Lombardo, Y. Girard, A.L. Maycock, J. Rokach, A.S. Rosenthal, R.N. Young, R.W. Egan andH.J. Zweerink,Measuring leukotrienes of Slow Reacting Substance of Anaphylaxis: development of a specific radioimmunoassay, J. Immun.131, 429–433 (1983).
R.J. Tallarida, A. Cowan andM.W. Adler,pA 2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism, Life Sci.25, 637–644 (1979).
M.D. Stevens, W.F. Mac Kenzie andV.D. Anand,A simplified method for determination of zinc in whole blood, plasma, and erithrocytes by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, Biochem. Med.18, 158–163 (1977).
M. Chvapil, P.L. Weldy, L. Stankova, D.S. Clark andC.F. Zukoski,Inhibitory effect of zinc ions on platelet aggregation and serotonin release reaction, Life Sci.16, 561–572 (1975).
M. Chvapil, L. Stankova, C. Zukoski, IV andC. Zukoski III,Inhibition of some functions of polymorphonuclear leukocytes by in vitro zinc, J. Lab. Clin. Med.89, 135–146 (1977).
K.M.K. Rao, S.A. Schwartz andR.A. Good,Age-dependent effects of zinc on the transformation response of human lymphocytes to mitogens, Cell. Immunol.42, 270–278 (1979).
M.D.P. Boyle, J.J. Langone andT. Borsos,Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. IV. Effect of metal salts, J. Immun.122, 1209–1213 (1979).
E.F. Gordon, R.C. Gordon andD.B. Passal,Zinc metabolism: basic, clinical, and behavioral aspects, J. Pediatr.99, 341–349 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marone, G., Columbo, M., de Paulis, A. et al. Physiological concentrations of zinc inhibit the release of histamine from human basophils and lung mast cells. Agents and Actions 18, 103–106 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01987995
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01987995