Abstract
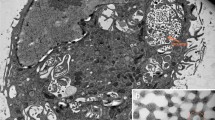
SEM images of rat peritoneal mast cells showed that microtubule-like filament seemed to penetrate the granules and project several branches just beneath the granular surface. Each granule appeared to be a cluster of microgranules. TEM observations frequently revealed microtubules connecting the granule surface to the subplasmalemmal network or to the adjacent granule surface and on some occasions, microtubules also appeared to penetrate the granule membranes. Moreover, TEM revealed that individual granules seemed to consist of a mass of microgranules, each 10–15 nm in diameter; freeze-fracture images showed similar configurations. These findings suggest that the microtubule-like filamentous structures in mast cells play a role corresponding to that of the open canalicular system in platelets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. S. C. Orr, D. E. Hall and A. C. Allison,Role of contractile microfilaments in the release of histamine from mast cells. Nature236, 350–351 (1972).
E. Gillespie, R. J. Levine and S. E. Malawista,Histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells: inhibition by colchicine and potentiation by deuterium oxide. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.164, 158–165 (1972).
K. Tasaka and M. Mio,Microfilament-associated degranulation of sensitized guinea-pig lung mast cells. Agents and Actions27, 79–82 (1989).
E. H. Nielsen and H. Jahn,Cytoskeletal studies on Lowicryl K4M embedded and Affi-Gel 731 attached rat peritoneal mast cells. Virchows Arch.45, 313–323 (1984).
K. Tasaka, M. Akagi, K. Miyoshi and M. Mio,Role of microfilaments in the exocytosis of rat peritoneal mast cells. Int. Archs. Allergy Appl. Immunol.87, 213–221 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tasaka, K., Akagi, M., Mio, M. et al. The existence of filaments connecting the granules and the cell membrane in rat peritoneal mast cells. Agents and Actions 33, 48–52 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993124
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993124