Summary
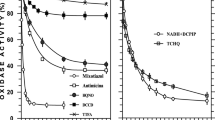
Ferrochelatase in membrane preparations fromAzospirillum brasilense displayed an activity of 2.17 μmol protoheme formed · h−1 · mg protein−1 which is 10-fold greater than previous reports for other bacteria. This ferrochelatase showed an apparentK m of 20.9 μM for Fe2+, a pH optimum of 6.0–6.5, and stimulation by oleic or stearic acids. Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ inhibited the incorporation of Fe2+ into protoporphyrin IX while Ni2 and Mg2+ had no effect on protoheme synthesis. Activity with Fe2+ and mesoporphyrin IX was less than with protoporphyrin IX but deuteroporphyrin IX produced the highest rate of protoheme synthesis. The membrane fraction containing ferrochelatase activity was found to insert Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ and Co2+ enzymatically into protoporphyrin IX to produce metalloporphyrins. Cu2+ incorporation into protoporphyrin IX proceeded at a rate greater than with Fe2+ and theK m for Cu2+ was 21.9 μM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugany H, Flohe L, Weser U (1971) Kinetics of metal chelatase from rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett 13:92–94
Dailey HA (1977) Purification and characterization of membrane bound ferrochelatase fromSpirillum itersonii. J Bacteriol 132:302–307
Dailey HA (1982) Purification and characterization of membrane bound ferrochelatase fromRhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem 257:14714–14718
Dailey HA, Lascelles J (1974) Ferrochelatase activity in wild type and mutant strains ofSpirillum itersonii. Arch Biochem Biophys 160:523–529
Falk JE (1964) Porphyrins and metalloporphyrins. Elsevier Publishing Co., Amsterdam
Goldin BR, Little HN (1969) Metalloporphyrin chelatase from barley. Biochim Biophys Acta 171:321–332
Gornall GG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Jacobs NJ, Jacobs JM (1976) Nitrate, fumarate, and oxygen as electron acceptors for a late step in microbial heme synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 449:1–9
Jones MS, Jones OTG (1970) Ferrochelatase ofRhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J 119:453–462
Jones MS, Jones OTG (1969) The structural organization of haem synthesis in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J 113:507–514
Kassner RJ, Walchak DH (1973) Heme formation from Fe(II) and porphyrin in the absence of ferrochelatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 304:294–303
Labbe RF, Hubbard N (1961) Metal specificity of the ironprotoporphyrin chelating enzyme from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 52:130–135
Porra RJ, Jones OTG (1963) Studies on ferrochelatase 1. Assay and properties of ferrochelatase from a pig liver mitochondrial extract. Biochem J 87:181–185
Porra RJ, Ross BD (1965) Heme synthase and cobalt porphyrin synthase in various micro-organisms. Biochem J 94:557–562
Porra RT, Vitolos K, Labbe RF, Newton NA (1967) Studies on ferrochelatase. The effects of thiols and other factors on the determination of activity. Biochem J 104:321–327
Riethmueller G, Tuppy H (1964) Hämsynthetase (Ferrochelatase) inSaccharomyces cerevisiae nach aerobem und anaerobe) Wachstum. Biochem Z 340:413–420
Sawada H, Takeshita M, Sugita Y, Yoneyama Y (1969) Effect of lipid on protoheme ferro-lyase. Biochim Biophys Acta 178:145–155
Shagam JY, Barton LL, Reed WP, Chiovetti R (1988) Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled lectin analysis of the surface of the nitrogen-fixing bacteriumAzospirillum brasilense by flow cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1831–1837
Taketani S, Tokunaga R (1981) Rat liver ferrochelatase. Purification, properties and stimulation by fatty acids. J Biol Chem 256:12748–12753
Wagner GS, Tephly TR (1975) A possible role of copper in the regulation of heme biosynthesis through ferrochelatase. Adv Exp Med Biol 58:343–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Price, M.J., Saiz, B.L. & Barton, L.L. Ferrochelatase activity inAzospirillum brasilense with reference to the influence of metal cations. Biol Metals 2, 31–35 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116198
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116198