Abstract
The results of a study on serum HAI and neutralizing antibodies induced in mice, by whole influenza virus vaccines containing A/Brazil/11/78 (H1N1), A/Bangkok/1/79 (H1N2) and B/Singapore/222/79 viruses are reported.
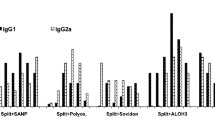
According to the GMT of HAI, the antigenic potency of the three vaccine strains appear to be different. The A/Brazil/1.1/78 antigen induced the lowest HAI antibody responses and the A/Bangkok/1/79 antigen the greatest. This behaviour, with a few exceptions, was noted regardless of the HA amount (0.08 μg 0.4 μg, 2 μg) of each strain present in the vaccine, the number of doses (one or two), or the kind of preparation (monovalent or trivalent). The data obtained with the neutralization test with vaccines with medium HA content are concordant with previous findings.
On the basis of the ratios of the GMT of the neutralizing antibodies to the GMT of the HAI antibodies, it was concluded that the HAI antibodies to A/Bangkok/1/79 antigen possess, on the whole, a neutralizing activity that is higher than that found for the HAI antibodies to A/Brazil/11/78 and B,/Singapore/222/79 strains. For the latter strains, the neutralizing activity increased after the second dose.
The observation of the different degrees of antigenicity of the three vaccine strains suggests That, with currently used inactivated influenza virus vaccines containing equivalent amounts of all- three antigens, the dosage should be taken into consideration when the vaccines are used for subjects lacking in previous exposure to vaccine strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DowdleW.R., LavesW.G., GalphinI.C., DownieJ.C. (1976): Antigenic relations-hips among influenza virus A neuraminidase (N2) antigens by immunodiffusion and post infection neutralization test. -J. Clin. Microbiol., 3, 233–238.
DowdleW.R., KendalA.P., NobleG.R. (1979): Influenza viruses. In: Diagnostic procedures for viral, rickettsial and chlamydial infections. LenDette E.M., Schmidt N.J. (ed), 585–609, Washington, Am. Pub. Hlth Ass..
EnnisF.A., MaynesR.E., BarryD.W., ManischewitzJ.E., DunlapR.C., VerbonitzM.W., BozemanF.M., SchildG.C. (1977): Correlation of laboratory studies with clinical responses to A/New Jersey influenza vaccines. - J. Infect. Dis., 136 (Suppl.), S397-S406
HinzJ., GruschkanH., MaulerR., HennessenW. (1973): Antigenic potency of influenza virus, virions and subunits. - Symp. Series Immunobiol. Standard., 20, 85–91.
KilbourneF.D. (1976): Comparative efficacy of neuraminidase-specific and conventional influenza virus vaccines in induction of antibody to neuraminidase in humans. - J. Infect. Dis., 134, 384–394.
LaMontagneJ.R., NobleG.R., QuinnanG.V., CourlinG.T., BlackwelderW.C., SmithJ.I., EnnisF.A., BozemanF.M. (1983): Summary of clinical trials of inactivated influenza vaccine-1978. - Rev. Infect. Dis., 5, 723–736.
MaulerR., HinzJ., GruschkanH., HennessenW. (1973): Potency testing of influenza virus vaccines.- Symp. Series Immunobiol. Standard., 20, 119–124.
MaynerR.E., BlackburnR.J., BarryD.W. (1977): Quantitation of influenza vaccine hemagglutinin by immunoelectrophoresis. - Dev. Biol. Standard., 39, 169–178.
McLarenC., VerbonitzM.W., DanielS., GrubbsG.E., EnnisF.A. (1977): Effect of priming infection on serologic response to whole and subunit influenza virus vaccines in animals. - J. Infect. Dis., 136 (Suppl.), S706-S711.
McLarenC., WilliamsM.S., BozemanF.M., MaynerR.E., GrubbsG.E., BarthlowW.E., StatonE., EnnisF.A. (1978): Comparative antigenicity and immuno genicity of 1976 influenza virus vaccines: results of mouse protection experiments. - J. Biol. Stand., 6, 315–330.
MurphyB.R., RennelsM.B., DouglasR.G., BettsR.F., CouchR.B., CateT.R., ChanockR.M., KendalA.P., MaassabH.F., SuwanagoolS., SotmanS.B., CisnerosL.A., AnthonyW.C., NalinD.R., LevineM.M. (1980): Evaluation of influenza A/Hong Kong/123'77 (H1N1) ts-lA 2 and cold-adapted recombinant viruses in seronegative adult volunteers.- Infect. Immun., 29, 348–355.
OxfordJ.S., SchildG.C., WoodJ.M., NewmanR.W., SeagroattV. (1977): The assay of influenza virus structural antigens in vaccines by rocket immunoelectrophoresis.- Dev. Biol. Standard., 39, 201–208.
ProfetaM.L., BigatelloA., VacchiniV., BramatiL., FerranteP. (1979): Confronto try vaccini antinfluenzali inattivati contenenti sub-unity e preparazioni a virioni interi: studio della reattogenicità e del potere immunizzante in bambini ed adulti. -Boll. Ist. Scroter, Milan., 58, 457–4714.
ProfetaM.L., NardiG. (1983): Attività neutralizzante ed inihente l'emoaaglutinazione degli anticorpi sierici dopo infezione naturale e dopo vaccinazione con to stipite di virus influenzale A/USSR/90/77 (H1N1). - Boll. Ist. Sieroter. Milan. 62, 130–136.
SchildG.C., WoodJ.M., NewmanR.W. (1975): A single radial-diffusion technique for the assay of influenza hemagglutinin antigen. - Bull. W.H.O., 52, 223–231.
TannockG.A., WarkM.C., SmithL.E., SutherlandM.M. (1981): A clearance test in mice using non-adapted viruses to determine the immunogenicity of influenza strains. - Arch. Virol., 70, 91–101.
TannockG.A., PaulJ.A., BarryR.D. (1984): Relative immunogenicity of the cold-adapted influenza virus A Ann Arbor 6/60 (A/AA/6/60-ca), recombinants of A/AA/6,′60-ca, and parental strains with similar surface antigens. - Infect. Immun., 43, 457–462.
TobitaK., SugiuraA., EnomotoC., FuruyameM. (1985): Plaque assay and primary isolation of influenza A virus in an established line of canine kidney cells (MDCK) in the presence of trypsin. -Med. Microbiol. Immunol., 162. 9–14.
TyrrelD.A.J., SmithJ.W.G. (1979): Vaccination against influenza A. - Brit. Med. Bull., 35, 77–85.
VirelizierJ.L. (1975): Host defense against influenza virus: the role of anti-hem agglutinin antibody.- J. Immunol., 115, 434–439.
WrightP.E., OkabaN., McKeeH.F., MaassabH.F., KarzonD.T. (1982): Cold-adapted influenza A recombinant vaccines in seronegative young children.- J.Infect. Dis., 146, 71–79.
WrightP.F., CherryJ.D., FoyH.M., GlezenW., HallB., McIntoshK., MoritoA.S., ParrottR.H., PortnayB., TaberL.H. (1983): Antigenicity and reactogenicity of influenza A/USSR/77 virus vaccine in children. A multicentered evaluation of dosage and safety. - Rev. Infect. Dis., 5, 758–764.
YodenS., KidaH., YanagawaR. (1985): Is bivalent binding of monoclonal antibodies to different antigenic areas on the hemagglutinin of influenza virus required for neutralization of viral infectivity?- Arch. Virol., 85, 209–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Profeta, M.L., Ruggeri, M. Relative antigenicity in mice of H1N1, H3N2 and B strains present in inactivated influenza virus vaccines. Eur J Epidemiol 3, 61–66 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145074
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145074