Abstract
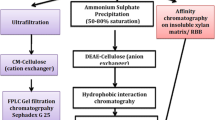
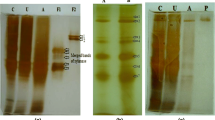
β-1,4-Xylanase, produced extracellularly by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MIR 32, was isolated directly from the culture broth by adsorption on a cation exchanger, Amberlite IRC-50, in fluidized bed with a low degree of expansion. The enzyme was eluted from the adsorbent by increase in pH, with a recovery of 82.3% and purification of 5.3 fold. About 99.99% of the colony forming units, 82% of the contaminating neutral protease activity, and 100% of the reducing sugars present in the crude feedstock were removed at the end of the purification cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anson ML (1938) Estimation of pepsin, papain and cathepsin with hemoglobin. J. Gen. Physiol. 22: 79-89.
Batt BC, Yabannavar VM and Singh V (1995) Expanded bed adsorption process for protein recovery from whole mammalian cell culture broth. Bioseparation 5: 41-52.
Belter PA, Cunningham FL and Chen JW (1973) Development of a recovery process for novobiocin. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 15(3): 533-549.
Biely P (1993) Biochemical aspects of the production of microbial hemicellulases. In: Coughlan MP and Hazlewood GP (eds.) Hemicellulose and Hemicellulases (pp. 29-51). Portland Press, London.
Breccia JD, Castro GR, Baigorí MD and Siñeriz F (1995) Screening of xylanolytic bacteria using a colour plate method. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 78: 469-472.
Breccia JD, Siñeriz F, Baigorí MD, Castro GR and Hatti-Kaul R (1998) Purification and characterization of a thermostable xylanase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. EnymeMicrob. Technol. 22: 42-49.
Chang Q and Chen J (1996) Liquid-liquid reversed micellar extraction for isolating enzymes: Studies on the purification of α-amylase. Process Biochem. 31: 371-375.
Chase HA (1994) Purification of proteins by adsorption chromatography in expanded beds. Trends Biotechnol. 12: 296-303.
Chu IM, Lee C and Tsu-Shun L (1992) Production and degradation of alkaline protease in batch cultures of Bacillus subtilisATCC 14416. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 14: 755-761.
Coughlan MP and Hazlewood GP (1993) Beta-1,4-D-xylan-degrading enzyme systems: biochemistry, molecular biology and applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 17: 259-289.
Frej AKB, Hjorth R and Hammarström Å (1994) Pilot scale recovery of recombinant Annexin V from unclarified Escherichia colihomogenate using expanded bed adsorption. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44: 922-929.
Hansson M, Ståhl S, Hjorth R, Uhlén M and Moks T (1994) Singlestep recovery of a secreted recombinant protein by expanded bed adsorption. Biotechnol. 12: 285-288.
Hermanson GT, Krishna Mallia A and Smith PK (1992) In: Immobilized Affinity Ligand Techniques (pp. 294-313). Academic Press, San Diego.
Hjorth R, Kämpe S and Carlsson M (1995) Analysis of some operating parameters of novel adsorbents for recovery of proteins in expanded beds. Bioseparation 5: 217-223.
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680-685.
Lochmüller CH, Ronsick CS and Wigman LS (1988) Fluidized-bed separators reviewed: A low pressure drop approach to column chromatography: Prep Chromat 1: 93-108.
Meyer HP and Fiechter A (1985) Production of cloned human leukocyte interferon by Bacillus subtilis: Optimal production is connected with restrained growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50: 503-507.
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal. Chem. 31: 426-428.
Oakley RB, Kirsch DR and Morris NR (1980) A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 105: 361-363.
Priest FG (1977) Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol. Rev. 41: 711-753.
Smith PK, Krohn RI and Hermanson EK (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 150: 76-85.
Thömmes J, Halfar M, Lenz S and Kula M-R (1995) Purification of monoclonal antibodies from whole hybridoma fermentation broth by fluidized bed adsorption. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 45: 205-211.
Wells CM, Lyddiatt A and Patel K (1987) Liquid fluidized bed adsorption in biochemical recovery from biological suspensions. In: Verrall MS and Hudson MJ (eds.) Separations for Biotechnology (pp. 217-224). Ellis-Horwood, Chichester.
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J and Linko M (1994) Xylanases in bleaching: From an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 13: 335-350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breccia, J.D., Hatti-Kaul, R., Castro, G.R. et al. Isolation of β-Xylanase from whole broth of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by adsorption on a matrix in fluidized bed with low degree of expansion. Bioseparation 8, 273–280 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008174513826
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008174513826