Abstract
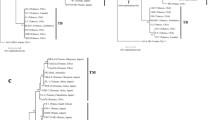
Binucleate Rhizoctonia anastomosis group (AG) D is the cause of rhizoctonia-patch and elephant-footprint diseases of zoysiagrass, and winter-patch disease of bentgrass. Rhizoctonia AG-D is also known as the causal pathogen of other diseases such as sharp-eye-spot of cereals, foot-rot of cereals and winter-stem-rot of mat rush. Isolates of AG-D have been divided into the two subgroups AG-D (I) and AG-D (II), based on the results of cultural characteristics and pathogenicity tests. Isolates obtained from zoysiagrass exhibiting symptoms of rhizoctonia-patch disease, from bentgrass with winter-patch disease, from wheat with foot-rot disease, and from mat rush with winter-stem-rot disease were reported to belong to subgroup AG-D (I). On the other hand, isolates obtained from zoysiagrass with elephant-footprint disease were assigned to subgroup AG-D (II). To confirm the existence of these two subgroups in AG-D, the genetic structure of AG-D isolates from turfgrass and other crops was compared. RFLP analysis of the ITS region from rDNA after digestion with the restriction enzymes EcoRI, HaeIII, HhaI, HinfI, and MboI separated AG-D isolates into two groups corresponding to AG-D (I) and AG-D (II). Furthermore, other AGs except AG-Q (AGs-A, Ba, Bb, C, E, F, G, I, K, L, O, P, and R. solani AG1-IC) did not have the same patterns that were seen for the two AG-D subgroups. AG-Q isolates from bentgrass showed the same patterns as AG-D (I). The results of the RAPD analysis also revealed the existence of two groups that corresponded to AG-D (I) and AG-D (II). These analyses revealed that Rhizoctonia AG-D isolates from turfgrass could be divided into two subgroups consistent with those based on cultural characteristics and pathogenicity. In addition, isolates of foot-rot disease of wheat and isolates of winter-stem-rot disease of mat rush whose cultural characteristics were the same as those of AG-D (I) also showed similar RFLP and RAPD patterns to those of AG-D (I) isolates from turfgrass.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balali GR, Whisson DL, Scott ES and Neate SM (1996) DNA fingerprinting probe specific to isolates of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3. Mycological Research 100: 467-470
Boerma GH and Verhoeven AA (1997) Checklist for scientific names of common parasitic fungi. Series 26: Fungi on field crops: Cereals and grasses. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology 83: 165-204
Boysen M, Borja M, del Moral C, Salazar O and Rubio V (1996) Identification oat strain level of Rhizoctonia solani AG4 isolates by direct sequence of asymmetric PCR products of the ITS regions. Current Genetics 29: 174-181
Bruns TD, White TJ and Taylor JW (1991) Fungi molecular systematics. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 22: 525-564
Burpee LL (1980) Rhizoctonia cerealis yellow patch of turfgrass. Plant Disease 64: 1114-1116
Burpee LL, Sanders PL, Cole H and Sherwood RT (1980) Anastomosis groups among isolates of Ceratobasidium cornigerum and related fungi. Mycologia 72: 689-701
Carling DE and Leiner RH (1987) Categorization of anastomosis interactions that occur between isolates of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 77: 1777
Cubeta MA, Echandi E, Abernethy T and Vilgalys R (1991) Characterization of anastomosis groups of binucleate Rhizoctonia species using restriction analysis of an amplified ribosomal RNA gene. Phytopathology 81: 1395-1400
Damaj M, Jabaji-Hare SH and Charest PM (1993) Isozyme variation and genetic relatedness in binucleate Rhizoctonia species. Phytopathology 83: 864-871
Duncan S, Barton JE and O'Brien PA (1993) Analysis of variation in isolates of Rhizoctonia solani by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Mycological Research 97: 1075-1082
Hyakumachi M and Sumino A (1984) New morphological type (IC) in Rhizoctonia solani AG1 isolated from sugar beet manufactory waste soils and of its characteristics. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan 50: 507-514
Ikata S and Yoshida M (1940) Studies on the disease of mat rush,1. Blight Special Bulletin, Okayama Agricultural Experiment Station 42: 1-47
Jabaji-Hare SH, Meller Y, Gill S and Charest PM (1990) Investigation of genetic relatedness among anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani using cloned DNA probes. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology 12: 393-404
Kataria HR and Hoffmann GM (1988) A critical review of plant pathogenic species of Ceratobasidium Rogers. Journal of Plant Disease and Protection 95: 81-107
Keijer J, Houterman PM, Dullemans AM and Korsman MG (1996) Heterogeneity in electrophoretic karyotype within and between anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani. Mycological Research 100: 789-797
Lipps PE and Herr LJ (1982) Etiology of Rhizoctonia cerealis in sharp eyespot of wheat. Mycological Research 100: 789-797
Liu ZL and Sinclair JB (1992) Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 2. Phytopathology 82: 778-787
Liu ZL and Sinclair JB (1993) Differentiation of intraspecific groups within anastomosis group 1 of Rhizoctonia solani using ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer and isozyme comparisons. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology 15: 272-280
Liu ZL, Domier LL and Sinclair JB (1993) ISG-specific ribosomal DNA polymorphism of the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Mycologia 85: 795-800
Liu ZL, Domier LL and Sinclair JB (1995) Polymorphism of genes coding for nuclear 18S rDNA indicates genetic distinctiveness of anastomosis group 10 from other groups in the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61: 2659-2664
Matsuoka M. (1959) On the winter sheath blight of rush plants. Kyushu Agricultural Research 21: 158
Mazzola M, Wong TO and Cook RJ (1996) Virulence of Rhizoctonia oryzae and R. solani AG-8 on wheat and detection of R. oryzae in plant tissue by PCR. Phytopathology 86: 354-360
Ogoshi A, Oniki M, Araki T and Ui T (1983) Anastomosis groups of binucleate Rhizoctonia in Japan and North America and their perfect stages. Transactions of the Mycological Society of Japan 24: 79-87
Ogoshi A, Oniki M, Sakai R and Ui T (1979) Anastomosis grouping among isolates of binucleate Rhizoctonia. Transactions of the Mycological Society of Japan 20: 33-39
Ogoshi A (1976) Studies on the grouping of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn with hyphal anastomosis and on the perfect stages of groups. Bulletin of National Institute of Agricultural Science Series C 30: 1-63
Oniki M, Kobayashi K, Araki T and Ogoshi A (1986a) A new disease of turf-grass caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-Q. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan 52: 850-953
Oniki M, Ogoshi A and Araki T (1986b) Ceratobasidium strarie, C. cornigeum, and C. gramineum, the teleomorph of the pathogenic binucleate Rhizoctonia fungi from gramineous plants. Transactions of Mycological Society of Japan 27: 147-158
Schneider JHM, Salazar O, Rubio V and Keijer J (1997) Identification of Rhizoctonia solani associated with field-grown tulips using ITS rDNA polymorphism and pectic zymograms. European Journal of Plant Pathology 103: 607-622
Sneath PA and Sokal RR (1973) Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco
Swofford DL (1993) PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 3.1.1. Computer program distributed by the Illinois Natural History Survey. Campaingn, IL
Takamatsu S (1989) A new snow mold of wheat and barley caused by the foot rot fungus, Ceratobasidium gramineum. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan 55: 233-237
Tanaka A, Kitabayashi H, Tani T and Ogoshi A (1994) A pathogen causing patch so-called ‘elephant footprint’ on zoysia grasses. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan (Abstr. and Japanese) 60: 344
Tani T (1989) Soil diseases of turfgrass. Noyaku Graph (Japanese) 109: 2-5
Tanpo H, Kudo J, Tani T and Ogoshi A (1990) The Rhizoctonia disease of bentgrass turf occurred in winter season in Japan. Journal Japanese Society of Turfgrass Science 19: 31-38
Uchino H, Kanazawa K and Ogoshi A (1983) Anastomosis group of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolated from diseased sugar beet seedlings. Memoirs of the Faculty of Agriculture Hokkaido University 13: 494-499
Vilgalys R and Gonzalez D (1990) Ribosomal DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 80: 151-158
White TJ, Burns T, Lee S and Taylor J (1990) Amplification of PCR Products: A Guide to Methods and Applications. In: Innis MA, Gelfland DH, Sninsky JJ and White TJ (eds) (pp 315-321). Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA
Yang J and Kharbanda PD (1996) Characterization, virulence and genetic variation of Rhizoctonia solani AG-9 in Alberta. Plant Disease 80: 513-518
Yap IV and Nilson RJ (1996) Winboot: A program for performing boot strap analysis of binary data to determine the confidence limits of UPGMA-based dendrograms. IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 14. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philipinnes. 22 pp
Yoder OC (1988) Cochliobolus heterostrophus cause of southern corn leaf blight. In: Sidhu GS (ed) Advances in Plant Pathology, Vol 6 (pp 93-122). Genetics of Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Academic Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toda, T., Hyakumachi, M., Suga, H. et al. Differentiation of Rhizoctonia AG-D Isolates from Turfgrass into Subgroups I and II Based on rDNA and RAPD Analyses. European Journal of Plant Pathology 105, 835–846 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008736404263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008736404263