Abstract
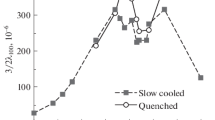
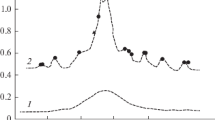
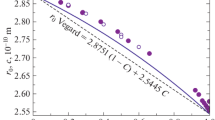
TheCuAuFe system has been studied by room temperature Mössbauer spectroscopy in order to examine the influence of varying both iron (Cu94−yAu6Fey; y=0.2–1.0 at%) and gold (Cu99−xAuxFe1; x=6–50.7 at%) concentrations on the clustering of iron atoms. Samples were examined in different metallurgical states, as rolled, fast quenched and melt spun with similar degrees of clustering being observed. The isomer shift is found to vary inversely with atomic volume for the Cu99−xAuxFe1 alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Window, Phil.Mag. 26 (1972) 681.
S.J. Campbell and P.E. Clark, J.Phys.F. 4 (1974) 1073.
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, “Constitution of Binary Alloys”, McGraw-Hill, New York (1958).
D.K-H. Finkler, A.E. Maurer, S.J. Campbell, T. Heck and U. Gonser, Physica B 1987 (in press)
T.J. Panek and J. Kansy, J.Phys.F. 12 (1982) 269.
B. Window, Phys.Rev.B 6 (1972) 2013.
R. Ingalls, F. Van der Woude and G.A. Sawatzky in “Mössbauer Isomer Shifts”, eds G.K. Shenoy and F.E. Wagner, North Holland, Amsterdam (1978), p361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finkler, D.KH., Heck, T., Maurer, A.E. et al. Segregation of iron inCuAuFe alloys. Hyperfine Interact 41, 571–574 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02400455
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02400455