Abstract
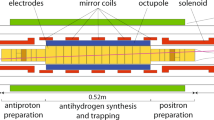
The possibility to produce, trap and study antihydrogen atoms rests upon the recent availability of extremely cold antiprotons in a Penning trap. Over the last five years, our TRAP Collaboration has slowed, cooled and stored antiprotons at energies 1010 lower than was previously possible. The storage time exceeds 3.4 months despite the extremely low energy, which corresponds to 4.2 K in temperature units. The first example of measurements which become possible with extremely cold antiprotons is a comparison of the antiproton inertial masses which shows they are the same to a fractional accuracy of 4×10−8. (This is 1000 times more accurate than previous comparisons and large additional increases in accuracy are anticipated.) To increase the number of trapped antiprotons available for antihydrogen production, we have demonstrated that we can accumulate or “stack” antiprotons cooled from successive pulsed injections into our trap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Gabrielse, X. Fei, K. Helmerson, S.L. Rolston, R. Tjoelker, T.A. Trainor, H. Kalinowsky, J. Haas and W. Kells, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 (1986) 2504.
G. Gabrielse, X. Fei, L.A. Orozco, S.L. Rolston, R. Tjoelker, T.A. Trainor, H. Kalinowsky, J. Haas and W. Kells, Phys. Rev. A40 (1989) 481.
G. Gabrielse, X. Fei, L.A. Orozco, R.L. Tjoelker, J. Haas, H. Kalinowsky, T. Trainor and W. Kells, Phys. Rev. Lett. 63 (1989) 1360.
G. Gabrielse, X. Fei, L.A. Orozco, R.L. Tjoelker, J. Haas, H. Kalinowsky, T.A. Trainor and W. Kells, Phys. Rev. Lett. 65 (1990) 1317.
G. Gabrielse, L. Haarsma and S.L. Rolston, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Proc. 88 (1989) 319; 93 (1989) 121.
A. Bamberger, U. Lynen, H. Piekarz, J. Piekarz, B. Povh, H.G. Ritter, G. Backenstoss, T. Bunaciu, J. Egger, W.D. Hamilton and H. Koch, Phys. Lett. 33B (1970) 233.
E. Hu, Y. Asano, M.Y. Chen, S.C. Cheng, G. Dugan, L. Lidofsky, W. Patton, C.S. Wu, V. Hughes and D. Lu, Nucl. Phys. A254 (1975) 403.
P. Roberson, T. King, R. Kunselman, J. Miller, R.J. Powers, P.D. Barnes, R.A. Eisenstein, R.B. Sutton, W.C. Lam, C.R. Cox, M. Eckhause, J.R. Kane, A.M. Rushton, W.F. Vulcan and R.E. Welsh, Phys. Rev. C16 (1977) 1945.
B.L. Roberts, Phys. Rev. D17 (1978) 358.
R.J. Hughes and M.H. Holzscheiter, Phys. Rev. Lett. 65 (1991) 854.
C. Tseng and G. Gabrielse, Hyp. Int., this volume.
W. Quint and G. Gabrielse, Wash. Meeting of the APS (postdeadline abstract, 1991); Hyp. Int., this volume.
M.H. Holzscheiter, R.E. Brown, J. Camp, T. Darling, P. Dyer, D.B. Holtkamp, N. Jarmie, N.S.P. King, M.M. Schauer, S. Cornford, K. Hosea, R.A. Kenefick, M. Midzor, D. Oakley, R. Ristinen and F.C. Witteborn, in:Atomic Physics, Vol. 12, ICAP XII, eds. J.C. Zorn and R.R. Lewis (AIP, New York, 1990) p. 573.
G. Gabrielse, in:Fundamental Symmetries, eds. P. Bloch, P. Pavlopoulos and R. Klapisch (Plenum Press, New York, 1987) p. 59.
G. Gabrielse, S.R. Rolston, L. Haarsma and W. Kells, Phys. Lett. A 129 (1988) 38.
T. Hänsch, Hyp. Int., this volume.
G. Gabrielse, Hyp. Int. 44 (1988) 349.
L. Gray and T.E. Kalogeropoulos, IEEE Trans. Nuc. Sci. NS-29 (1982) p. 1051.
L. Gray and T.E. Kalogeropoulos, Rad. Res. 97 (1984) 246.
T.E. Kalogeropoulos and R. Muratore, Nuc. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. 40/41 (1989) 1322.
G. Gabrielse and B.L. Brown, in:The Hydrogen Atom, eds. G.F. Bassani, M. Inguscio and T.W. Hänsch (Springer, Berlin, 1989) p. 196.
L. Haarsma, K. Abdullah and G. Gabrielse, Hyp. Int., this volume.
P.B. Schwinberg, R.S. Van Dyck Jr. and H.G. Dehmelt, Phys. Lett. 81A (1981) 119.
R.S. Van Dyck, private communication.
B.L. Brown and M. Leventhal, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 (1986) 1651.
C.M. Surko, M. Leventhal and A. Passner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 62 (1989) 901.
A. Vehanan, K.G. Lynn, P.J. Schultz and M. Eldrup, Appl. Phys. A32 (1983) 2572; A.P. Mills Jr., Appl. Phys. Lett. 37 (1980) 667; E.M. Gullikson, A.P. Mills Jr., W.S. Crane and B.L. Brown, Phys. Rev. B32 (1980) 5484.
R. Howell et al., in:Positron Scattering in Gases, eds. J.W. Humberston and M.R.C. McDowell (Plenum Press, New York, 1983) p. 126; K. Lynn et al., in:Positron Scattering in Gases, eds. J.W. Humberston and M.R.C. McDowell (Plenum Press, New York, 1993).
J.W. Humberston, M. Charlton, F.J. Jacobsen and B.I. Deutch, J. Phys. B20 (1987) L25.
M. Charlton, Phys. Lett. A 143 (1990) 143.
H. Herr, D. Hohl and A. Winnacker,Physics at LEAR with Low-Energy Cooled Antiprotons (Erice, 1982) p. 659; R. Neumann, H. Poth, A. Winnacker and A. Wolf, Z. Phys. A 313 (1983) 253.
A.L. Migdall, J.V. Prodan, W.D. Phillips, T.H. Bergeman and H.J. Metcalf, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54 (1985) 2596.
H.F. Hess, G.P. Kochanski, J.M. Doyle, N. Masuhara, D. Kleppner and T.J. Greytak, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59 (1987) 672.
T. Hänsch, R.G. Beausoleil, B. Couillaud, C. Foot, E.A. Hildum and D.H. McIntyre, in:Laser Spectroscopy, Vol. 8, eds. W. Persson and S. Svaberg (Springer, Berlin, 1987) p. 2.
T. Goldman, M.N. Nieto and R.J. Hughes, Phys. Lett. B 171 (1986) 217.
R. Hughes, Hyp. Int., this volume.
W. Quint, D. Hall and G. Gabrielse, Hyp. Int., this volume.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabrielse, G., Jhe, W., Phillips, D. et al. Extremely cold antiprotons for antihydrogen production. Hyperfine Interact 76, 81–93 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02316708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02316708