Summary
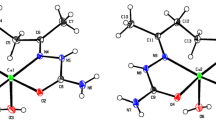
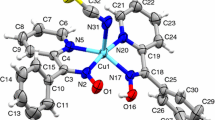
Some copper(II) complexes of the types: Cu(HPPK)-(PPK)X, Cu(HMPK)(MPK)X (where HPPK = syn-phenyl-2-pyridylketoxime, HMPK = syn-methyl-2-pyridylketoxime and X = Cl−, Br−, I−, NO3 −, SCN− or SeCN−) Cu(HPPK)2SO4 3 H2O and Cu(HMPK)2SO4 · 3 H2O were synthesized and characterized by analysis, magnetic susceptibility, e.s.r., reflectance and i.r. spectral measurements. The spectral data suggest that Cu(HPPK)(PPK)X and Cu(HMPK)(MPK)X containcis square-coplanar [Cu(HPPK)(PPK)]+ and [Cu(HMPK)(MPK)]+ units respectively, linked by weakly coordinated anions, giving infinite polymeric highly distorted octahedral chain structures, whereas Cu(HPPK)2SO4 · 3H2O and Cu(HMPK)2SO4 · 3 H2O have acis distorted octahedral structure containing two ligand molecules of ketoxime and a bidentate sulphate group. The polycrystalline e.s.r. spectra suggest a distorted octahedral stereochemistry for the CuII ion involving a\(d_{x^2 - y^2 } \) ground-state. By using e.s.r. and reflectance spectral data, the orbital reduction parameters, k11 and k1 were calculated and interpreted in terms of molecular orbital coefficients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. F. Lindoy and S. E. Livingstone,Coord. Chem. Rev., 2, 173 (1967); W. R. McWhinnie and J. D. Miller,Advan. Inorg. Chem. Radiochem., 12, 135 (1969); E. D. McKenzie,Coord. Chem. Rev., 6, 187 (1971).
A. Chakravorthy,Coord. Chem. Rev., 13, 1 (1974).
F. Holmes, G. Lees and A. E. Underhill,J. Cltem. Soc. A, 999 (1971); M. Mohan, H. C. Khera, S. G. Mittal and A. K. Sirivastava,Acta Chim. Hung.,91, 417 (1976).
R. S. Drago and E. I. Baucom,Inorg. Chem., 11, 2064 (1972).
A. I. Vogel,A Text Book of Quantitatlve Inorganic Analysis, Longmans, London, 1961.
B. N. Figgis and R. S. Nyholm,J. Chem. Soc., 4190 (1958).
F. E. Mabbs and D. J. Machin,Magnetism and Transition Metal Complexes, Chapman and Hall, London, 1973, p. 5.
B. N. Figgis,Introduction to Ligand-Field Theory, Interscience, New York, 1969, p. 278.
A. Earnshaw,Introduction to Magneto-Chemistry, Academic Press, New York, 1968.
B. J. Hathaway,Essays Chem., 2, 61 (1971).
B. J. Hathaway and A. A. G. Tomlinson,Coord. Chem. Rev., 5, 1 (1970).
K. W. H. Stevens,Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 219, 542 (1953); A. H. Maki and B. R. McGarvery,J. Chem. Phys., 29, 31 (1955); D. Kivelson and R. Neiman,J. Chem. Phys., 35, 149 (1961).
B. J. Hathaway, D. E. Billing, P. Nicholls and I. M. Procter,J. Chem. Soc. A, 319 (1969).
A. Earnshaw, L. F. Larkworthy and K. C. Patel,J. Chem. Soc. A, 1339 (1969); A. B. P. Lever and E. Mantovani,Inorg. Chem.,10, 817 (1971), B. J. Hathaway.Struct. Bonding,14, 49 (1973).
I. M. Procter, B. J. Hathaway and P. Nicholls,J. Chem. Soc. A, 1678 (1968); A. A. G. Tomlinson. B. J. Hathaway, D. E. Billing and P. Nicholls,J. Chem. Soc. A, 65 (1969).
A. Palm and H. Werbin,Canad. J. Chem., 31, 1004 (1953); R. A. Krause. N. S. Colthup and D. H. Busch,J. Phys. Chem., 65, 2216 (1961); E. J. Poziomek and L. G. Vaughan,J. Pharm. Sci, 54, 811 (1965); L. G. Ward, T. L. Meek and G. E. Cheney,Inorg. Chem. Acta., 4, 43 (1970).
B. Sen and D. Malone,J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 34, 3509 (1972).
N. S. Gill, R. H. Nuttall, D. E. Scaife and D. W. A. Sharp,J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 18, 79 (1961); P. E. Figgins and D. H. Busch,J. Phys. Chem., 65, 2236 (1961); G. Zerhi, J. Overend and B. Crawford,J. Chem. Phys., 38, 122 (1963); J. H. S. Green, W. Kynaston and H. M. Paisley,Spectrochim Acta., 19, 549 (1963); S. P. Sinha,Spectrochim Acta, 20, 879 (1964): N. S. Gill and H. J. Kingdon,Aust. J. Chem., 19, 2197 (1966).
N. F. Curtis and Y. M. Curtis,Inorg. Chem., 4, 804 (1965); Y. Komiyama and E. C. Lingafelter,Acta. Cryst., 17, 1145 (1964).
J. L. Burmeister,Coord. Chem. Rev., 1, 205 (1966);3, 225 (1968); M. E. Farago and J. M. James,Inorg. Chem., 4, 1706 (1965); R. Barbucci, G. Cialdi. G. Ponticelli and P. Paoletti,J. Chem. Soc. A, 1775 (1969).
K. Nakamoto, J. Fujita, S. Tanaka and M. Kobayashi,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 79, 4904 (1957); A. Hezel and S. D. Ross,Spectrochim. Acta, 24A, 985 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, M., Paramhans, B.D. Transition metal chemistry of oxime-containing ligands, part XI. Copper(II) complexes of syn-phenyl-2-pyridylketoxime and syn-methyl-2-pyridylketoxime. Transition Met Chem 5, 113–117 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01396885
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01396885