Abstract
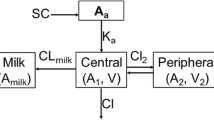
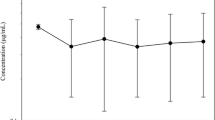
Some pharmacokinetic parameters of eprinomectin were determined in goats following topical application at a dose rate of 0.5 mg/kg. The plasma concentration versus time data for the drug were analysed using a one-compartment model. The maximum plasma concentration of 5.60±1.01 ng/ml occurred 2.55 days after administration. The area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) was 72.31±11.15 ng day/ml and the mean residence time (MRT) was 9.42±0.43 days. Thus, the systemic availability of eprinomectin to goats was significantly lower than that for cows. The low concentration of eprinomectin in the plasma of goats suggests that the pour-on dose of 0.5 mg/kg would be less effective in this species than in cows. Further relevant information about the optimal dosage and residues in the milk of dairy goats is needed before eprinomectin should be used in this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Alvinerie, M., Sutra, J.F. and Galtier, P., 1993. Ivermectin in goat plasma and milk after subcutaneous injections. Annales de Recherches Vétérinaires, 24, 417–421
Alvinerie,M., Sutra, J.F., Galtier, P. and Mage, C., 1999. Pharmacokinetics of eprinomectin in plasma and milk following topical administration to lactating dairy cattle. Research in Veterinary Science, 66, (in press)
Asato, D. and France, D.J., 1990. To American Cyanamid, US Patent 4916, 154–158
Bogan, J., Benoit, E. and Delatour, P., 1987. Pharmacokinetics of oxfendazole in goats: a comparison with sheep. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 10, 305–309
Campbell, W.C. and Benz, G.W., 1984. Ivermectin: a review of efficacy and safety. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 7, 1–16
Chartier, C. and Hoste, H., 1997. La therapeutique anthelminthique chez les caprins. Le Point Vétérinaire, 28, 125–132
Chartier, C., Etter, E., Pors, I. and Alvinerie, M., 1999. Activity of eprinomectin in goats against experimental infections with Haemonchus contortus, Teladorsagia circumcinta and Trichostrongylus colubriformis.Veterinary Record, 144, 99–100
Galtier, P., Escoula, L., Camguilhem, R. and Alvinerie, M., 1981. Comparative bioavailability of levamisole in non lactating ewes and goats. Annales de Recherche Vétérinaires, 12, 109–114
Gayrard,V., Alvinerie,M. and Toutain, P.L., 1999. Comparison of pharmacokinetic profiles of doramectin and ivermectin pour-on formulations in cattle.Veterinary Parasitology, 81, 47–55
Goudie, A., Evans, N., Gration, K., Bishop, B., Holdom, K., Kaye, B., Wicks, S., Lewis, D., Weatherley, A.C., Herbert, A. and Seymour, D., 1993. Doramectin – a potent novel endectocide. Veterinary Parasitology, 49, 5–15
Jackson, F., Jackson, E. and Coop, R.L., 1992. Multiple anthelmintic resistant nematodes in goats. Research in Veterinary Science, 53, 371–373
Leathwick, D.M., 1995. A case of moxidectin failing to control ivermectin resistant Oestertagia species in goats.Veterinary Record, 136, 443–445
Perrier, D. and Mayershon, M., 1982. Non-compartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 71, 372–373
Shoop,W.L., Ergeton, J.R., Eary, C.H., Haines, H.W., Michael, B.F., Mrozik, H., Eskola, P., Fisher,M.H., Slayton, L., Ostlin, D.A., Skelly, B.J., Fulton, R.K., Barth, D., Costa, S., Gregory, L.M., Campbell, W.C., Seward, R.L. and Turner, M.J., 1996. Eprinomectin: a novel avermectin for use as topical endectocide for cattle. International Journal for Parasitology, 26, 1227–1235
Sutra, J.F., Chartier, C., Galtier, P. and Alvinerie, M., 1998. Determination of eprinomectin in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with automated solid phase extraction and fluorescence detection. Analyst, 123, 1525–1527
Takiguchi, Y., Mishima, H., Okuda, M., Terao, M., Aoki, A. and Fukuda, R., 1980. Milbemycins a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation isolation and physico-chemical properties. Journal of Antibiotics, 33, 1120–1126
Watson, T.G., Hosking, B.C., Leathwick, D.M. and McKee, P.F., 1996. Ivermectin-moxidectin side resistance by Ostertagia species isolated from goats and passaged to sheep. Veterinary Record, 38, 472–474
Yamaoka, K., Tanigawara, K., Nakacawa, T. and Uno, T., 1981. A pharmacokinetic analysis program (MULTI) for microcomputer. Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics, 4, 879–885
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvinerie, M., Lacoste, E., Sutra, J. et al. Some Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Eprinomectin in Goats following Pour-on Administration. Vet Res Commun 23, 449–455 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006373609314
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006373609314