Abstract
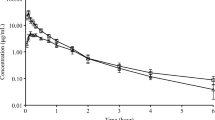
The disposition kinetics and urinary excretion of pefloxacin after a single intravenous administration of 5 mg/kg were investigated in crossbred calves and an appropriate dosage regimen was calculated. At 1 min after injection, the concentration of pefloxacin in the plasma was 18.95±0.892 μg/ml, which declined to 0.13±0.02 μg/ml at 10 h. The pefloxacin was rapidly distributed from the blood to the tissue compartment as shown by the high values for the initial distribution coefficient, α (12.1±1.21 h–1) and the constant for the rate of transfer of drug from the central to the peripheral compartment, K 12 (8.49±0.99 h–1). The elimination half-life and volume of distribution were 2.21±0.111 h and 1.44±0.084 L/kg, respectively. The total body clearance (ClB) and the ratio of the drug present in the peripheral to that in the central compartment (P/C ratio) were 0.454±0.026 L/kg h) and 5.52±0.519, respectively. On the basis of the pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in the present study, an appropriate intravenous dosage regimen for pefloxacin in cattle for most of the bacteria sensitive to it would be 6.4 mg/kg repeated at 12 h intervals.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arret, B., Johnson, D.P. and Krishbaum, A., 1971. Outline of details for microbiological assay of antibiotics: second revision. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 60, 1689-1694
Barragry, T.B., 1994. Tetracyclines, chloramphenicol and quinolones. In: C. Cann, S. Hunsberger and R. Lukens (eds), Veterinary Drug Therapy, (Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia), 282-291
Gibaldi, M. and Perrier, D., 1982. Methods of residuals. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd edn. (Marcel Dekker, New York), 433-444
Hong, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, N., Zhang, H. and Liang, D., 1995. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin injection in healthy volunteers. Hua Hsi I Ko Ta Hsueh Hsueh Pao, 26, 315-318
Hooper, D.C., 1995. Quinolones. In: G.L. Mandell, J.E. Bennett and R. Dolin (eds), Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 4th edn, (Churchill Livingstone, New York), 364-375
Hooper, D.C. and Wolfson, J.S., 1991. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. New England Journal of Medicine, 324, 384-394
Kaartinen, L., Panu, S. and Pyorala, S., 1997. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in horses after single intravenous and intramuscular administration. Equine Veterinary Journal, 29, 378-381
Leysen, D.C., Haemers, A. and Pattyn, S.R., 1989. Mycobacteria and the new quinolones. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 33, 1-5
Mandell, G.L. and Petri, W.A., 1996. Sulfonamides, trimethoprim–suflamethoxazole, quinolones, and agents for urinary tract infections. In: J.G. Hardman, L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon and A.G. Gilman (eds), Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 9th edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York), 1057-1072
Mengozzi, G., Intorre, L., Bertini, S. and Soldani, G., 1996. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin after intravenous and intramuscular administration in sheep. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 57, 1040-1043
Moutafchieva, R. and Djouvinov, D., 1997. Pharmacokinetics of pefloxacin in sheep. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 20, 405-407
Nawaz, M., Khan, H. and Rahman, Z., 1980. Pharmacokinetics of sulfadimidine in ruminants. Proceedings of the First International Congress of Veterinary Pharmacology, Cambridge, UK, 57-63
Norris, S. and Mandell, G.L., 1988. The quinolones: history and overview. In: V.T. Andirole (ed.), The Quinolones (Academic Press, New York), 1-22
Patil, R.V., Gatne, M.M., Somkuwar, A.P. and Ranade, V.V., 1996. Pharmacokinetics and milk concentration of pefloxacin injection (Pelwin) in lactating cows. Indian Veterinary Journal, 73, 1130-1132
Walker, R.D., Stein, G.E., Hauptman, J.G. and MacDonald, K.H., 1992. Pharmacokinetics evaluation of enrofloxacin administered orally to healthy dogs. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 53, 2315-2319
Zeng, Z.L. and Feng, Q.M., 1996. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of enrofloxacin in pigs. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 16, 606-612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, A., Dumka, V. & Deol, S. Disposition Kinetics and Urinary Excretion of Pefloxacin after Intravenous Injection in Crossbred Calves. Vet Res Commun 24, 189–196 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006408415431
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006408415431