Abstract
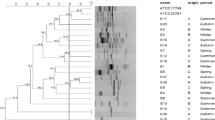
Using a 0.27 kb DNA probe specific for the heat-stable enterotoxin gene (nag-st) of Vibrio cholerae non-O1, 1109 strains representing 17 species of the genus Vibrio, isolated from clinical and environmental sources were examined. The nag-st gene was preponderantly associated with strains classified as V. mimicus; 16.8% of these strains hybridized. It was more frequent in the clinical isolates (22.6%) than in the environmental isolates (13.7%). The incidence of nag-st gene-positive strains of V. mimicus isolated from different countries was uniformly high and ranged between 8.7% (Bangladesh) and 57.1% (environmental strains from USA). The incidence of the nag-st gene was much lower among strains of V. cholerae non-O1 (3.6%). Probe-positive and-negative strains of V. mimicus and V. cholerae non-O1 were used to evaluate the performance of the conventional suckling mouse assay for detection of the NAG-ST enterotoxin. Of the 31 probe-positive strains, only five (16.1%) yielded a positive fluid accumulation ratio (FA ratio) when neat heated culture supernatant was used to perform the suckling mouse assay. All the 31 probe-positive strains gave a positive FA ratio when 20-fold concentrated and heated culture supernatants of the strains were used to perform the suckling mouse assay. The need to concentrate (by at least 20-fold) the culture supernatant of strains of V. mimicus and V. Cholerae non-O1 was identified as an important step to obtain consistent results when using the suckling mouse assay for detection of NAG-ST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arita, M., Honda, T., Miwatani, T., Takeda, T., Takao, T. & Shimonishi, Y. 1991 Purification and characterization of a heat-stable enterotoxin of Vibrio mimicus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 79, 105–110.
Arita, M., Takeda, T., Honda, T. & Miwatani, T. 1986 Purification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat stable enterotoxin. Infection and Immunity 52, 45–49.
Baumann, P. & Schubert, R.H.W. 1984 Family II. Vibrionaceae. In Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol. 1, eds Krieg, N.R. & Holt, J.G. pp. 516–550. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Burgess, M.N., Bywater, R.J., Cowley, C.M., Mullan, N.A. & Newsome, P.M. 1978 Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infection and Immunity 21, 526–531.
Hill, W.E., Payne, W.L., Zon, G. & Moseley, S.L. 1985 Synthetic oligonucleotide probes for detecting heat-stable enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 50, 1187–1191.
Hoge, C.W., Sethabutr, O., Bodhidatta, K.L., Echeverria, P., Robertson, D.C. & Morris, J.G.Jr 1990 Use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe to detect strains of non-serovar O1 Vibrio cholerae carrying the gene for the heat-stable enterotoxin (NAG-ST). Journal of Clinical Microbiology 28, 1473–1476.
Ichinose, Y., Yamamoto, K., Nakazone, N., Tanabe, M.J., Takeda, T., Miwatani, T. & Iwanaga, M. 1987 Enterotoxicity of El Tor-like hemolysin of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Infection and Immunity 55, 1090–1093.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. & Sambrook, J. 1982 Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Morris, J.G.Jr, Takeda, T., Tall, B.D., Losonsky, G.A., Bhattacharya, S.K., Forrest, B.D., Kay, B.A. & Nishibuchi, M. 1990 Experimental non-O group I Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in humans. Journal of Clinical Investigation 85, 697–705.
Nair, G.B., Bhattacharya, S.K. & Takeda, T. 1993 Detection of heat-stable enterotoxin producing strains of Yersinia enterocolitica and Vibrio cholerae non-O1 by a monoclonal antibody based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiology and Immunology 37, 181–189.
Nair, G.B., Oku, Y., Takeda, Y., Ghosh, A., Ghosh, R.K., Chattopadhyay, S., Pal, S.C., Kaper, J.B. & Takeda, T. 1988 Toxin profiles of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 from environmental sources in Calcutta, India. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54, 3180–3182.
Nishibuchi, M., Murakami, A., Arita, M., Jikuya, H., Takano, J., Honda, T. & Miwatani, T. 1989 Detection with synthetic oligonucleotide probes of nucleotide sequence variations in the genes encoding enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 27, 2272–2276.
Ogawa, A., Kato, J.I., Watanabe, H., Nair, G.B. & Takeda, T. 1990 Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin gene from Vibrio cholerae non-O1 isolated from a patient with traveller's diarrhoea. Infection and Immunity 58, 3325–3329.
Pal, A., Ramamurthy, T., Bhadra, R.K., Takeda, T., Shimada, T., Takeda, Y., Nair, G.B., Pal, S.C. & Chakrabarti, S. 1992 Reassessment of the prevalence of heat-stable enterotoxin (NAG-ST) among environmental Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strains isolated from Calcutta, India using a NAG-ST DNA probe. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58, 2485–2489.
Shimada, T., Sakazaki, R. & Kosako, Y. 1982 Occurrence and distribution of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and its enterotoxigenicity (six years study). Journal of Japanese Association of Infectious Diseases 56, 1017–1024.
Southern, E.M. 1975 Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. Journal of Molecular Biology 98, 503–517.
Takeda, T., Nair, G.B., Suzuki, K. & Shimonishi, Y. 1990 Production of a monoclonal antibody to Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) which is cross-reactive with Yersinia enterocolitica ST. Infection and Immunity 58, 2755–2759.
Takeda, T., Peina, Y., Ogawa, A., Dohi, S., Abe, H., Nair, G.B. & Pal, S.C. 1991 Detection of heat-stable enterotoxin in a cholera toxin gene-positive strains of Vibrio cholerae O1. FEMS Microbiology Letters 80, 23–28.
Yoshimura, S., Takao, T., Shimonishi, Y., Arita, M., Takeda, T., Imaishi, H., Honda, T. & Miwatani, T. 1986 A heat-stable enterotoxin of Vibrio cholerae non-O1: chemical synthesis, and biological and physicochemical properties. Biopolymers 25, 69–83.
Additional information
P. Yuan, A. Ogawa and T. Takeda are with the Department of Infectious Disease Research, National Children's Medical Research Center, 3-35-31 Taishido, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 154, Japan; P. Yuan is also with the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products, Beijing, China. T. Ramamurthy and G.B. Nair are with the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases, Calcutta, India. T. Shimada is with the National Institute of Health, Tokyo 141, Japan. S. Shinoda is with the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, P., Ogawa, A., Ramamurthy, T. et al. Vibrio mimicus are the reservoirs of the heat-stable enterotoxin gene (nag-st) among species of the genus Vibrio . World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 10, 59–63 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357565
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357565