Abstract
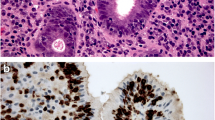
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is an important factor for maintaining the esophageal functional integrity. Goettingen minipigs were treated with either placebo or subcutaneous EGF (30 μg/kg/day) for four weeks. Wistar rats were treated with either placebo or subcutaneous EGF (150 μg/kg/day) for four weeks. At sacrifice, esophageal samples were obtained for histology, immunochemistry, and lectin characterization. In pigs, the thickness of the esophageal epithelium was almost doubled in the EGF-treated animals. Characterization with lectins revealed a normal pattern of differentiation. Subcutaneously administered EGF was visualized on cells located basally in the esophageal epithelium. In rats EGF-treatment increased the esophageal volume of the epithelium, the lamina propria of the mucosa, and the subnucosa. In conclusion, systemic EGF challenge induces growth of the esophageal epithelium with an unaltered pattern of differentiation. This supports previous studies demonstrating a beneficial effects of systemic EGF-treatment on sclerotherapyp-induced esophageal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prigent SA, Lemoine NR; The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res 4:1–24, 1992
Burgess AW: Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. Br Med Bull 45:401–424, 1989
Nexø E, Olsen PS, Poulsen K: Exocrine and endocrine secretion of renin and epidermal growth factor from the mouse submandibular glands. Regul Pept 8:327–334, 1984
Olsen PS, Poulsen SS, Kirkegaard, P, Nexø E: Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology 87:103–108, 1984
Sarosiek J, Hetzel DP, Yu Z, Piascik R, Li L, Rourk RM, McCallum RW: Evidence on secretion of epidermal growth factor by the esophageal mucosa in humans. Am J Gastroenterol 88: 1081–1087, 1993
Sakai Y, Nelson KG, Snedeker S, Bossert NL, Walker MP, McLachlan J, DiAugustine RP: Expression of epidermal growth factor in suprabasal cells of stratified squamous epithelia: Implications for a role in differentiation. Cell Growth Differ 5:527–535, 1994
Juhl CO, Jensen LS, Steiniche T, Moussa E: Recombinant human epidermal growth factor prevents sclerotherapyinduced esophageal ulcer and stricture formations in pigs. Dig Dis Sci 32:393–401, 1994
Juhl, CO, Vinter-Jensen L, Jensen LS, Nexø E, Djurhuus JC, Dajani EZ: Recombinant human epidermal growth factor accelerates healing of sclerotherapy-induced esophageal ulcers and prevents esophageal stricture formation in pigs. Dig Dis Sci 39:2671–2678, 1994
Juhl, CO, Vinter-Jensen L, Jensen LS, Dajani EZ: Preventive effects of recombinant human epidermal growth factor on the oesophageal epithelium in pigs subjected to sclerotherap. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:823–828, 1995
Gundersen HJG, Bendtsen TF, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Møller A, Nielsen K, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B, Sørensen FB, Vesterby A, West MJ: Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 996:379–394, 1988
Jensen LS, Kararupl N, Larsen JA, Nielsen TH: Effect of acute portal hypertension on hepatosplanchnic hemodynamics and liver function. Scand J Gastroenterol 22:463–470, 1986
Langkilde NC, Hastrup J, Olsen S, Wolf H, Ørntoft TF; Immunohistochemistry and cytochemistry of experimental rat bladder cancer: Binding of the lectins PNA and WGA and of a Ley mouse monoclonal antibody. Isolation and characterization of lectins fromVicia villosa. J Biol Chem 258:5165–5171, 1983
Lotan R, Skutelsky E, Danon E, Sharon N: The purification, composition and specificity of the anti-T lectin from peanuts (Arachis hypogeae). J biol Chem 250:8518–8523, 1975
Matsumoto I, Osawa T: Purification and characterization of an anti-H(O) phytohemagglutinin ofUlex europaeus. Biochim Biophys Acta 194:180–189, 1969
Nagata Y, Burger MM: Wheat germ agglutinin. Molecular characteristics and specificity for sugar binding. J Clin Invest 249:3116–3122, 1974
Etzler ME, Kabat EA: Purification and characterization of a lectin (plant agglutinin) with blood group A specificity fromDolchos biflorus. Biochemistry 9:869–877, 1970
Sternberger L.: Immunocytochemistry. New York, Wiley & Sons, 1974
Jaeger LA, Lamar CH: Immunolocalization of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF receptors in the porcine upper gastrointestinal tract. Am J Vet Res 53:1685–1692, 1992
Jørgensen PE, Poulsen SS, Nexø E: Distribution of i.v. administered epidermal growth factor in the rat. Regul Pept 23:161–169, 1988
Hwang DL, Lev Ran A: Infusion of epidermal growth factor in mice: Organ distribution and urinary excretion. Regul Rept 29:103–108, 1990
Kim DC, Sugiyama Y, Fuwa T, Sakamoto S, Iga T, Hanano M; Kinetic analysis of the elimination process of human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 38:241–249, 1989
Burwen SJ, Barker ME, Goldman IS, Hardek GT, Raper SE, Jones AL: Transport of epidermal growth factor by rat liver: Evidence for a nonlysosomal pathway. J Cell Biol 99:1259–1265, 1984
Matrisia LM, Planck SR, Magun BE: Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor. I. Acidification of125I-epidermal growth factor in intracellular organelles. J Biol Chem 259:3047–3052, 1984
Nexø E, Hansen HF: Binding of epidermal growth factor from man, rat and mouse to the human epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochim biophys Acta 843:101–106, 1985
Pascall JC, Jones DS, Doel SM, Clements JM, Hunter M, Fallon T, Edwards M, Brown KD: Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding pig epidermal growth factor. J Mol Endocrinol 6:63–70 (1991)
Jankowski J, Hopood D, Wormsley KG: Expression of epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha and their receptor in gastro-oesophageal diseases. Dig Dis 11:1–11, 1993
Itakura Y, Sasano H, Shiga C, Furukawa Y, Shiga, K, Mori S, Nagura H: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression in esophageal carcinoma. An immunohistochemical study correlated with clinicopathologic findings and DNA amplication. Cancer 74:795–804, 1994
Jankowski J, Hopwood D, Pringle R, Wormsley KG: Increased expression of epidermal growth factor receptors in Barrett's esophagus associated with alkaline reflux: A putative model for carcinogenesis. Am J Gastroenterol 88:402–408, 1993
Poller DN, Steele RJ, Morrell K.: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in Barrett's esophagus. Arch Pathol Lab Med 116:1226–1227, 1992
Neal DE, Charlton RG, Bennet MK: Histochemical study of lectin binding in neoplastic and non-neoplastic urothelium. Br J Urol 60:399–404, 1987
Yoshida Y, Okamura T, Shirakusa T: An immunohistochemical study of helix pomatia agglutinin binding on carcinomas of the esophagus. Surg Gynecol Obstet 177:299–302, 1993
Ørntoft TF: Carbohydrate changes in bladder carcinomas (review). APMIS 100(suppl 27):181–187, 1992
Mandel U.: Carbohydrates in oral epithelia and secretions. Variation with cellular differentiation. APMIS 100(suppl 27): 119–129, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported in part by the Danish Medical Research Council (12–1317) and by Gastrone Inc., Menlo Park, California.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orloff Juhl, C., Vinter-Jensen, L., Seier Poulsen, S. et al. Chronic treatment with epidermal growth factor causes esophageal epithelial hyperplasia in pigs and rats. Digest Dis Sci 40, 2717–2723 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220465
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220465