Abstract
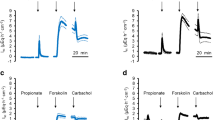
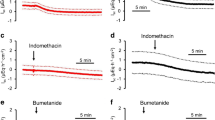
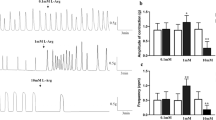
Effects of okadaic acid (OA) on mucosal damagewere examined in rat colon. OA was sprinkled on ratcolon mucosa under observation with anelectronic-endoscopic system, and OA was also applied tothe in vivo microscopic field. The OA-induced changesin transepithelialconductance (Gt) weremeasured by the Ussing voltage clamp technique. Byendoscopic observation, the luminal sprinkling of OA (60nmol/kg) evoked transient microthrombi in the submucosalvenule, which was followed by mucosal edema.Histological study after endoscopic observation showedsubmucosal fluid retention, suggesting an increase of vascular permeability. The microthrombi werealso detected by in vivo microscopy. Byelectrophysiological study after endoscopic observationwith and without OA addition, the basal Gtvalues were 54 ± 6.2 and 36.2 ± 4.2 mS/cm2,respectively (P < 0.01). Furthermore in control rats,the serosal addition of OA evoked an increase inGt in a concentration-dependent mannerwithout increasing lactate dehydrogenase release. 2,4,6-Triaminopyrimidinium inhibitedOA-induced Gt change by 60%. These resultsindicate that OA evokes an increase in paracellularpermeability of epithelium. We conclude that thedeveloped microthrombi are the first key event of OA-induced mucosaldamage, followed by an increase in permeability in thesubmucosal venule and in the paracellular pathway of theepithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tachibana K, Scheuer PJ, Tsukitani Y, Kikuchi H, van Eugen E, Clardy J, Gopichand Y, Schmitz FJ: Okadaic acid a cytotoxin polyether from two marinesponges of the genus Halichondria.J Am Chem Soc 103:2469 - 2471, 1981
Yasumoto T, Oshima Y, Yamaguchi M: Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 44:1249 - 1255, 1978
Yasumoto T, Murata M, Oshima Y, Matsumoto GK, Clardy J: Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. InAmerican Chemical Society 1984, pp 207- 214 ACS Symp Series No. 262. Seafood Toxins. EP Ragelis ed). Washington, DC.
Tripuraneni J, Koutsouris A, Pestic L, De Lanerolle P, Hecht G: The toxin of diarrheic shellfish poisoning, okadaic acid, increase s intestinal epithelial paracellular permeability. Gastroenterology 112:100 - 108, 1997
Terao K, Ito E, Yanagi T, Yasumoto T: Histopathological studies on experimental marine toxin poisoning. I. Ultrastructural changes in the small intestine and liver of suckling mice induced by dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-1. Toxicon 24:1141- 1151, 1986
Hecht GA, Pothoulakis C, Lamont J, Madara JL: Clostridium difficiletoxin A perturbs cytoskeletal structure and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolaye rs. J Clin Invest 82:1516 - 1524, 1988
Moldovan S, Livingston E, Zhang RS, Kleinman R, Guth P, Brunicardi FC: Glucose-induced islet hyperemia is mediated by nitric oxide. Am J Surg 171:16 - 20, 1996
Chen RY, Guth PH: Interaction of endogenous nitric oxide and CGRP in sensory neuron-induced gastric vasodilation. Am J Physiol 268:G791- G796, 1995
Chen RY, Chang CH, Guth PH: Gastric arteriolar and venular response s to nitrogenous and nonnitrogenous vasodilating agents in the rat. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp 14:197- 203, 1994
Karaki H, Mitsui M, Nagase H, Ozaki H, Shibata S, Uemura D: Inhibitory effect of a toxin okadaic acid, isolated from the black sponge on smooth muscle and platelets. Br J Pharmacol 98:590 - 596, 1989
Reuss L, Grady TP: Triaminopyrimidinium (TAP1 ) blocks luminal membrane K conductance in Necturusgallbladde r epithelium. J Membr Biol 48:285- 298, 1979
Kück-Biere U, von Engelhardt W: Factors affecting the potassium concentration at the mucosal surface of the proximal and the distal colon of guinea pig. Gut 31:64 - 69, 1990
Hall MC, Koch MO, Mcdougal WS: Mechanism of ammonium transport by intestinal segments following urinary diversion: Evidence for ionized NH4 + transport via K+ pathways. J Urol:453- 457, 1992
Hosokawa M, Tsukada H, Ueda S, Sakai M, Okuma M, Oda K, Takimoto M, Okada T, Urade Y: Regulation of ion transport by endothelins in rat colonic mucosa: Effects of an ETA antagonist (FR139317) and an ETB agonist (IRL1620). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:1313- 1322, 1995
Tominaga M, Tsukada H, Hosokawa M, Nakamura H, Taniguchi T, Ueda S, Sakai M, Okuma M: ONO-1078 antagonizes diarrhe a-causing change s in ion transport and smooth muscle contraction induced by peptidoleukotrienes in rat and human colon in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1058 - 1063, 1996
Edebo L, Lange S, Li XP, Allenmark S: Toxic mussels and okadaic acid induce rapid hyper secretion in the rat small intestine. Apmis 96:1029 - 1035, 1988
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosokawa, M., Tsukada, H., Saitou, T. et al. Effects of Okadaic Acid on Rat Colon. Dig Dis Sci 43, 2526–2535 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026658921369
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026658921369