Abstract
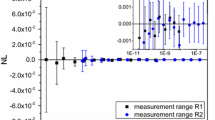
Radiance temperatures (at 658 and 898 nm) of niobium at its melting point were measured by a pulse-heating technique. A current pulse of subsecond duration was imparted to a niobium strip and the initial part of the melting plateau was measured by high-speed pyrometry. Experiments were performed with two techniques and the results do not indicate any dependence of radiance temperature (at the melting point) on initial surface or system operational conditions. The average radiance temperature at the melting point of niobium is 2420 K at 658 nm and 2288 K at 898 nm, with a standard deviation of 0.4 K at 658 nm and 0.3–0.6 K at 898 nm (depending on the technique used). The total uncertainty in radiance temperature is estimated to be not more than ±6 K. The results are in good agreement with earlier measurements at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (USA) and confirm that both radiance temperature and normal spectral emissivity (of niobium at its melting point) decrease with increasing wavelength in the region 500–900 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Cezairliyan,J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (U.S.) 77A:333 (1973).
A. Cezairliyan, A. P. Miiller, F. Righini, and A. Rosso, inTemperature. Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, Vol. 6, J. F. Schooley, ed. (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1992), pp. 377–382.
J. P. Hiernaut, F. Sakuma, and C. Ronchi,High Temp. High Press. 21:139 (1989).
F. Righini, G. C. Bussolino, A. Rosso, and J. Spišiak,Int. J. Thermophys. 14:485 (1993).
L. Coslovi, F. Righini, and A. Rosso,J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 12:216 (1979).
L. Coslovi, F. Righini, and A. Rosso,Alta Frequenza 44:592 (1975).
F. Righini, A. Rosso, and G. Ruffino,High Temp. High Press. 4:597 (1972).
F. Righini and A. Rosso, inTemperature. Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, Vol. 5, J. F. Schooley, ed. (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1982), pp. 433–438.
A. Cezairliyan and A. P. Miiller,Int. J. Thermophys. 13:39 (1992).
H. Preston-Thomas,Metrologia 27:3 (1990).
International Committee for Weights and Measures,Metrologia 5:35 (1969).
A. Cezairliyan, A. P. Miiller, F. Righini, and A. Rosso,High Temp. High Press. 23:325 (1991).
A. Cezairliyan,High Temp. High Press. 4:453 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Righini, F., Bussolino, G.C., Rosso, A. et al. Radiance temperatures (at 658 and 898 nm) of niobium at its melting point. Int J Thermophys 14, 495–510 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566048
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566048