Abstract
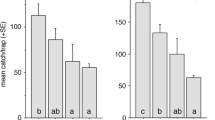
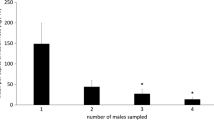
exo-Brevicomin (E), frontalin (F), and myrcene (M) were released at two rates 10-fold apart with verbenone at four rates 10-fold apart, and without verbenone in plots with one trap on a vertical cylinder at the pheromone source and one trap on each of four cylinders 5 m away. Catch of the western pine beetleDendroctonus brevicomis decreased with increasing levels of verbenone at both release rates of EFM, but not all differences in catch were statistically significant. Significantly more beetles were caught at the high rate of EFM than at the low rate, combining all rates of verbenone. The percent of total beetles caught at the center trap tended to decrease with increasing rates of verbenone, but the only statistically significant differences were at the low rate of EFM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedard, W.D., Tilden, P.E., Wood, D.L., Silverstein, R.M., Brownlee, R.G., andRodin, J.O. 1969. Western pine beetle: Field response to its sex pheromone and a synergistic host terpene, myrcene.Science 164:1284–1285.
Bedard, W.D., Wood, D.L., Tilden, P.E., Lindahl, K.Q., Jr., Silverstein, R.M., andRodin, J.O. 1980a. Field responses of the western pine beetle and one of its predators to host- and beetle-produced compounds.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:625–641.
Bedard, W.D., Tilden, P.E., Lindahl, K.Q., Jr., andRauch, P.A. 1980b. Effects of verbenone andtrans-verbenol on the response ofDendroctonus brevicomis to natural and synthetic attractant in the field.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:997–1013.
Browne, L.E., Wood, D.L., Bedard, W.D., Silverstein, R.M., andWest, J.R. 1979. Quantitative estimates of the western pine beetle attractive pheromone components,exo-brevicomin, frontalin, and myrcene in nature.J. Chem. Ecol. 5:397–414.
Byers, J.A., andWood, D.L. 1980. Interspecific inhibition of the response of the bark beetles,Dendroctonus brevicomis andIps paraconfusus, to their pheromones in the field.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:149–164.
Byers, J.A., andWood, D.L. 1981. Interspecific effects of pheromones on the attraction of the bark beetlesDendroctonus brevicomis andIps paraconfusus in the laboratory.J. Chem. Ecol. 7:9–18.
Byers, J.A., Wood, D.L., Craig, J. andHendry, L.B. 1984. Attractive and inhibitory pheromones produced in the bark beetle,Dendroctonus brevicomis, during host colonization: Regulation of inter- and intraspecific competition.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:861–877.
Furniss, M.M.,Clausen, R.W.,Markin, G.P.,Mcgreoor, M.D., andLivingston, R.L. 1981. Effectiveness of Douglas-fir beetle antiaggregative pheromone applied by helicopter. U.S. Dep. Agric. For. Serv. Intermt. For. Range Exp. Stn. Gen. Tech. Rep. INT-101, 6 pp.
Kinzer, G.W., Fentiman, A.F., Jr., Page, T.F., Jr., Foltz, R.L., Vité, J.P., andPitman, G.B. 1969. Bark beetle attractants: identification, synthesis and field bioassay of a new compound isolated fromDendroctonus.Nature 221:477–478.
Livingston, W.H., Bedard, W.D., Mangini, A.C., andKinzer, H.G. 1983. Verbenone interrupts attraction of roundheaded pine beetle,Dendroctonus adjunctus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), to sources of its natural attractant.J. Econ. Entomol. 76:1041–1043.
McGregor, M.D., Furniss, M.M., Oaks, R.D., Gibson, K.E., andMeyer, H.E. 1984. MCH pheromone for preventing Douglas-fir beetle infestation in windthrown trees.J. For. 82:613–616.
Renwick, J.A.A. 1967. Identification of two oxygenated terpenes from the bark beetlesDendroctonus frontalis andDendroctonus brevicomis.Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst. Plant Res. 23:355–360.
Renwick, J.A.A., andVité, J.P. 1970. Systems of chemical communication inDendroctonus.Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst. Plant Res. 24:283–292.
Richerson, J.V., andPayne, T.L. 1979. Effects of bark beetle inhibitors on landing and attack behavior of the southern pine beetle and beetle associates.Environ. Entomol. 8:360–364.
Rudinsky, J.A., Furniss, M.M., Kline, L.N., andSchmitz, R.F. 1972. Attraction and repression ofDendroctonus pseudotsugae (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) by three synthetic pheromones in traps in Oregon and Idaho.Can. Entomol. 104:815–822.
Silverstein, R.M., Brownlee, R.G., Bellas, T.E., Wood, D.L., andBrowne, L.E. 1968. Brevicomin: principal sex attractant in the frass of the female western pine beetle.Science 159:889–891.
Tilden, P.E., andBedard, W.D. 1985. Field response ofDendroctonus brevicomis to exo-brsvicomin, frontalin, and myrcene released at two proportions and three levels.J. Chem. Ecol. 11:757–766.
Tilden, P.E., Bedard, W.D., Lindahl, K.Q., Jr., andWood, D.L. 1983. TrappingDendroctonus brevicomis: Changes in attractant release rate, dispersion of attractant, and silhouette.J. Chem. Ecol. 9:311–321.
Watterson, G.P., Payne, T.L., andRicherson, J.V. 1982. The effects of verbenone and brevicomin on the within-tree populations ofDendroctonus frontalis.J. Ga. Entomol. Soc. 17:118–126.
Winer, B.J. 1962. Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. McGraw-Hill, New York. 672 pp.
Wood, D.L. 1972. Selection and colonization of ponderosa pine by bark beetles, pp. 101–117,in H.F. van Emden (ed.). Insect/Plant Relationships. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Wood, D.L. 1982. The role of pheromones, kairomones, and allomones in the host selection and colonization behavior of bark beetles.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 27:411–446.
Wood, D.L., andBedard, W.D. 1977. The role of pheromones in the population dynamics of the western pine beetle, pp. 643–652,in D. White (ed.). Proceedings of the XV International Congress of Entomology, Washington, D.C., August 19–27, 1976. Entomological Society of America, College Park, Maryland.
Wood, D.L., Browne, L.E., Ewing, B., Lindahl, K., Bedard, W.D., Tilden, P.E., Mori, K., Pitman, G.B., andHughes, P.R. 1976. Western pine beetle: Specificity among enantiomers of male and female components of an attractant pheromone.Science 192:896–898.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Coleoptera: Scolytidae.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tilden, P.E., Bedard, W.D. Effect of verbenone on response ofDendroctonus brevicomis toexo-Brevicomin, frontalin, and myrcene. J Chem Ecol 14, 113–122 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01022535
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01022535