Abstract
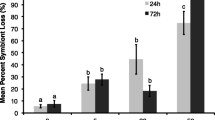
The loss of zooxanthellae during a short-term, experimentally simulated bleaching event resulted in significant changes to the secondary metabolite chemistry of the alcyonacean soft corals Sinularia flexibilis and Lobophytum compactum. The concentration of flexibilide, the most active cytotoxic secondary metabolite (with antimicrobial properties) in the tissues of Sinularia flexibilis increased by 126%, while that of its principal terpenoid algaecide, sinulariolide, simultaneously decreased to just 8% of that found in the controls. The changes were short lived, however, with concentrations of both compounds returning to control levels one month after bleaching; at the same time zooxanthellae levels were still only approximately 20% of the controls. Similarly, concentrations of isolobophytolide, the principal terpenoid secondary metabolite of Lobophytum compactum underwent a significant reduction for one month following bleaching. Like their nonbleached counterparts, both bleached individuals of Sinularia flexibilis and Lobophytum compactum experienced neither significant algal overgrowth nor predation following bleaching. Full recovery of zooxanthellae to baseline levels in all bleached corals occurred within four months. These results suggest that some soft corals are capable of surviving short-term bleaching events and the detrimental algal overgrowth that is often associated with bleaching, possibly by adjusting their secondary metabolite concentrations to suit specific needs. Support for the notion that resource allocation towards production of specific algaecides in bleached specimens translates also into higher protection was gained through analysis of naturally bleached soft corals. Bleached and overgrown individuals had significantly lower concentrations of species-specific algaecides than their bleached and unfouled and their unbleached counterparts.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aceret, T. L., Sammarco, P. W., and Coll, J. C. 1995. Toxic effects of alcyonacean diterpenes on scleractinian corals. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 188:63–78.
Barnes, D. J., and Chalker, B. E. 1990. Calcification and photosynthesis in reefbuilding corals and algae, pp. 109–131, in Z. Dubinsky (ed.). Ecosystems of the World: Coral Reefs, Vol. 25, Elsevier, New York.
Berkelmans, R., and Oliver, J. K. 1999. Large scale bleaching of corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 18:55–60.
Ciereszko, L. S. 1989. Sterol diterpenoid production by zooxanthellae in coral reefs: A review. Biol. Oceanogr. 6:363–374.
Coll, J. C. 1992. The chemistry and chemical ecology of octocorals. (Coelenterata, Anthozoa, Octocorallia). Chem. Rev. 92:613–631.
Coll, J. C., Tapiolas, D. M., Bowden, B. F., Webb, L., and Marsh, H. 1983. Transformation of soft coral (Coelenterata; Octocorallia) terpenes by Ovula ovum (Mollusca: Prosobranchia). Mar. Biol. 74:35–40.
Coll, J. C., Price, I. R., Koenig, G. M., and Bowden, B. F. 1987. Algal overgrowth of alcyonacean soft corals. Mar. Biol. 96:129–135.
Davies, P. S. 1991. Effect of daylight variations on the energy budgets of shallow-water corals. Mar. Biol. 108:137–144.
Davies, A. R., Targett, N. M., McConnell, O. J., and Young, C. M. 1989. Epibiosis of marine algae and benthic invertebrates: Natural products chemistry and other mechanisms inhibiting settlement and overgrowth, pp. 85–114, in P. J. Scheuer (ed.). Bioorganic Marine Chemistry, Vol. 3, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Drollet, J. H., Faucon, M., Maritorena, S., and Martin, P. M. V. 1994. A survey of environmental physico-chemical parameters during a minor coral mass bleaching event in Tahiti in 1993. Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 45:1149–1156.
Fabricius, K. 1998. Widespread bleaching of coral reefs in summer 1998. Aust. Coral Reef Soc. Newsl. June: 25–26.
Fabricius, K. 1999. Tissue loss and mortality in soft corals following mass bleaching. Coral Reefs 18:54.
Gershenzon, J. 1994. Metabolic costs of terpenoid accumulation in higher plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 20:1281–1328.
Gleason, D. F., and Wellington, G. M. 1993. Ultraviolet radiation and coral bleaching. Nature 365:836–838.
Glynn, P. W. 1993. Coral reef bleaching: Ecological perspectives. Coral Reefs 12:1–17.
Griffith, J. K. 1994. Predation on soft corals (Octocorallia: Alcyonacea) on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 45:1281–1284.
Hatcher, B. G., and Larkum, A. W. D. 1983. An experimental analysis of factors controlling the standing crop of epilithic algal community on a coral reef. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 69:61–84.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Salvat, B. 1995. Periodic mass-bleaching and elevated sea temperatures: Bleaching of outer reef slope communities in Moorea, French Polynesia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 121:181–190.
Jeffrey, S. W., and Humphrey, G. H. 1975. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c 1 and c 2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 167:191–194.
Jindal, A., Ritchie, K. B., Hayes, R. L., Goreau, T. J., and Smith, G. W. 1995. Bacterial ecology of selected corals following the 1994 South Central bleaching event, 27th Meeting Association of Marine Laboratories, Caribbean (abstract).
Jokiel, P. L., and York, R. H. 1982. Solar ultraviolet photobiology of the reef coral Pocillopora damnicornis and symbiotic zooxanthellae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 32:301–315.
Jones, R. J., Berkelmans, R., and Oliver, J. K. 1997. Recurrent bleaching of corals at Magnetic Island (Australia) relative to air and seawater temperature. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 158:289–292.
Jones, R. J., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Larkum, A. D. W., and Schreiber, U. 1998. Temperatureinduced bleaching of corals begins with impairment of dark metabolism in zooxanthellae. Plant, Cell Environ. 21:1219–1230.
KÜhl, M., Cohen, Y., Dalsgaard, T., Jorgensen, B. B., and Revsbech, N. P. 1995. Microenvironment and photosynthesis of zooxanthellae in scleractinian corals studied with microsensors for O2, pH and light. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 117:159–172.
Kushmaro, A., Rosenberg, E., Fine, M., and Loya, Y. 1997. Bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica by Vibrio AK-1. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 147:159–165.
Leone, P., Bowden, B. F., Carroll, A. R., and Coll, J. C. 1995. Chemical consequences of relocation of the soft coral Lobophytum compactum and its placement in contact with the red alga Plocamium hamatum. Mar. Biol. 122:675–679.
Lesser, M. P. 1997. Oxidative stress causes coral bleaching during exposure elevated temperatures. Coral Reefs 16:187–192.
Lesser, M. P., Stochaj, W. R., Tapley, D. W., and Shick, J. M. 1990. Bleaching in coral reef anthozoans: Effects of irridiance, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature on the activities of protective enzymes against active oxygen. Coral Reefs 8:225–232.
Maida, M., Carroll, A. R., and Coll, J. C. 1993. Variability of terpene content in the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia), and its ecological implications. J. Chem. Ecol. 19:2285–2296.
Maida, M., Sammarco, P. W., and Coll, J. C. 1995. Effects of soft corals on scleractinian coral recruitment. I. Directional allelopathy and inhibition of settlement. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 121:191–202.
Michalek, K., and Bowden, B. F. 1997. A natural algacide from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alcyonacea). J. Chem. Ecol. 23:259–273.
Miller, D. J., and Yellowlees, D. Y. 1989. Inorganic nitrogen uptake by symbiotic marine cnidarians: A critical review. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 237:109–125.
Muscatine, L., Falkowski, P. G., Porter, J. W., and Dubinsky, Z. 1984. Fate of photosynthetic fixed carbon in light-and shade adapted colonies of the symbiotic coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 222:181–202.
Nair, S., and Simidu, U. 1987. Distribution and significance of heterotrophic marine bacteria with antibacterial activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53(12):2957–2962.
Papastephanou, C., and Anderson, D. G. 1982. Crassin acetate biosynthesis in a cell-free homogenate of zooxanthellae from Pseudoplexaura porosa (Houttyun); implication to the symbiotic process. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 73B(3):617–624.
Paul, V. J., and Fenical, W. 1986. Chemical defense in tropical green algae, order Caulerpales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 34:255–264.
Paul, V. J., and Van Alstyne, K. L. 1988. Chemical defense and chemical variation in some tropical Pacific species of Halimeda (Halimedaceae: Chlorophyta). Coral Reefs 6:263–270.
Paul, V. J., and Van Alstyne, K. L. 1992. Activation of chemical defenses in tropical green algae Halimeda spp. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 160:191–203.
Ritchie, K. B., Dennis, J. H., McGrawth, T., and Smith, G. W. 1993. Bacteria associated with bleached and nonbleached areas of Montastrea annularis, pp. 75–80, in L. Kass (ed.). 5th Symposium on Natural History of Bahamas, San Salvador, Bahamas.
Salih, A., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Cox, G. 1998. Bleaching responses of symbiotic dinoflagellates in corals: The effects of light and elevated temperature on their morphology and physiology, pp. 199–215, in J. G. Greenwood, N. G. Hall (eds.), Australian Coral Reef Society 7th Anniversary Conference, Heron Island.
Sammarco, P. W. 1996. Comments on coral reef regeneration, bioerosion, biogeography, and chemical ecology: Future directions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 200:135–168.
Sammarco, P. W., and Coll, J. C. 1990. Lack of predictability in terpenoid function. Multiple roles and integration with related adaptations in soft corals. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:273–289.
Suharsono, Pipe, R. K., and Brown, B. E. 1993. Cellular and ultrastructural changes in the endoderm of the temperate sea anemone Anemonia viridis as a result of increased temperature. Mar. Biol. 116:311–318.
Sutton, D. C., and Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 1990. Host-zooxanthellae interactions in four temperate marine invertebrate symbioses: Assessment of effect of host extracts on symbionts. Biol. Bull. 178:175–186.
Toren, A., Landau, L., Kushmaro, A., Loya, Y., and Rosenberg, E. 1998. Effect of temperature on the adhesion of Vibrio AK-1 to Oculina patagonica and coral bleaching. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:1379–1384.
Wang, J.-T., and Douglas, A. E. 1998. Nitrogen recycling or nitrogen conservation in an algainvertebrate symbiosis? J. Exp. Biol. 201:2445–2453.
Williams, D. H., Stone, M. J., Hauck, P. R., and Rahman, S. K. 1989. Why are secondary metabolites (natural products) biosynthesized? J. Nat. Prod. 52:1189–1208.
WIlliams, E. J., and Bunkley-Williams, L. 1990. The world-wide coral reef bleaching cycle and related sources of coral mortality. Atoll Res. Bull. 335:1–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michalek-Wagner, K., Bowden, B.F. Effects of Bleaching on Secondary Metabolite Chemistry of Alcyonacean Soft Corals. J Chem Ecol 26, 1543–1562 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005525110045
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005525110045