Abstract
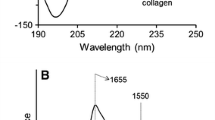
The thermal stability of acid-soluble collagens was studied by circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Adult bovine dermal collagen (BDC), rat-tail tendon collagen (RTC), and calf skin collagen (CSC) were compared. Despite some variability in amino acid composition and apparent molecular weight, the CD spectra for helical and unordered collagen structures were essentially the same for all the sources. The melting of these collagens occurs as a two-stage process characterized by a pretransition (T p) followed by complete denaturation (T d). The characteristic temperatures vary with the source of the collagen; for mature collagens (BDC, RTC) T p = 30°C and T d = 36deg;C, and for CSC T p = 34°C and T d = 40°C. Neutral salts, NaCl or KCl, at low concentrations (0.02–0.2 M) appear to bind to the collagens and shift the thermal transitions of these collagens to lower temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bailey, A. J. (1992). J. Soc. Leather Tech. Chem. 76, 111–127.
Brown, E. M. (1999). J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 94, 59–67.
Brown, E. M., Dudley, R. L., and Elsetinow A. R. (1997). J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 92, 225–233.
Chen, J. M., Kung, C. E., Feairheller, S. H., and Brown, E. M. (1991). J. Protein Chem. 10, 535–552.
Danby, J. P., and Shillito, J. F. (1959). J. Soc. Leather Trades' Chem. 43, 3–17.
Danielsen, C. C. (1982). Collage, Rel. Res. 2, 143–150.
Friess, W., and Lee, G. (1996). Biomaterials 17, 2289–2294.
Gekko, K., and Koga, S. (1983). J. Biochem. 94, 199–205.
Holmgren, S. K., Taylor, K. M., Bretscher, L. E., and Raines, R. T. (1998). Nature 392, 666–667.
Horgan, D. J., King, N. L., Kurth, L. B., and Kuyper, R. (1990). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 281, 21–26.
Hulmes, D. A, Miller, J. S., Parry, D. A. D., Piez, K. A., and Woodhead-Galloway, J. (1973). J. Mol. Biol. 79, 137–148.
Kadler, K. (1994). Protein Profiles 1, 519–638.
King, G., Brown, E. M., and Chen, J. M. (1996). Protein Eng. 9, 43–49.
Komsa-Penkova, R., Koynova, R., Kostov, G., and Tenchov, B. G. (1996). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1297, 171–181.
Lee, J. C., and Timasheff, S. N. (1981). J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7193–7201.
Miller, E. J. (1988). In Collagen (Nimni, M. E., ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, Vol. 1, Chapter 5, pp. 139–156.
Na, G. C. (1986). Biochemistry 25, 967–973.
Na, G. C. (1988). Collagen Rel. Res. 8, 315–330.
Na, G. C. (1989). Biochemistry 28, 7161–7167.
Na, G. C., Phillips, L. J., and Freire, E. I. (1989). Biochemistry 28, 7153–7161.
Noda H. (1972). J. Biochem. 71, 699–703.
Notbohm, H., Mosler, S., Bodo, M., Yang, C., Lehmann, H., Barge, B., and Muller, P. K. (1992). J. Protein Chem. 11, 635–643.
Piez, K. A. (1984). In Extracelluar Matrix Biochemistry (Piez, K. A., and Reddi, A. H., eds.), Elsevier, New York, pp. 1–39.
Rose, P. I. (1992). In Advances in Meat Research: Inedible Meat By-Products (Pearson, A. M., and Dutson, T. R., eds.), Elsevier, New York, pp. 217–263.
Rusling, J. F., and Kumosinski, T. F. (1996). In Nonlinear Computer Modeling of Chemical and Biochemical Data, Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Russell, A. E. (1973). Biochem. J. 131, 335–342.
Schachman, H. K. (1959). In Ultracentrifugation in Biochemistry, Academic Press, New York, pp. 201–214.
Sinanoglu, O. (1968). In Molecular Associations in Biology (Pullman, B., ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 427–445.
van der Rest, M., and Garrone, R. (1991). FASEB J. 5, 2814–2823.
Williams, B. R., Gelman, R. A., Poppke, D. C., and Piez, K. A. (1978). J. Biol. Chem. 253, 6578–6585.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, E.M., Farrell, H.M. & Wildermuth, R.J. Influence of Neutral Salts on the Hydrothermal Stability of Acid-Soluble Collagen. J Protein Chem 19, 85–92 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007074314686
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007074314686