Summary
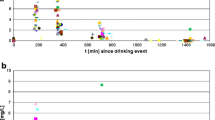
Demethylation of aminopyrine was measured in 25 healthy controls and 19 epileptics on long-term treatment with anticonvulsants by the14C-aminopyrine breath test. Compared to controls epileptics exhibited increased cumulative14CO2-exhalation rates (88.7% at 30 min, 62.6% at 2 h and 24.8% at 8 h) following ingestion of 2 µCi14C-aminopyrine.
The results suggest that long-term treatment with antiepileptic drugs results in increased demethylating function of the liver which can be easily detected by a simple breath analysis technique like decreased demethylation in chronic liver disease.
Zusammenfassung
Die Demethylierung von Aminophenazon wurde bei 25 Lebergesunden ohne Medikamenteneinnahme und 19 Epileptikern unter antikonvulsiver Langzeitbehandlung mittels des14C-Aminophenazon-Atemtestes untersucht. Im Vergleich zur Kontrollgruppe bestand bei Epileptikern unter antikonvulsiver Langzeitbehandlung eine gesteigerte Demethylierung für14C-Aminophenazon (kumulative14CO2-Exhalation: nach 1/2 h 88,7%, nach 2 h 62,6% und nach 8 h nur noch 24,8%). Der14C-Aminophenazon-Exhalationstest läßt sich nicht nur zur Erkennung einer verminderten Demethylierung der Leber bei chronischen Lebererkrankungen, sondern auch zur Erfassung einer gesteigerten Demethylierungsfunktion bei Patienten unter induzierenden Pharmaka verwenden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Andreasen, P.B., Ranek, L., Statland, B.E.: Clearance of antipyrine-dependence of quantitative liver function. Europ. J. clin. Invest.4, 129–134 (1974)
Branch, R.A., Herbert, C.M., Read, A.E.: Determinants of serum antipyrine half-lives in patients with liver disease. Gut14, 569–573 (1973)
Brodie, B.B., Axelrod, J.: The fate of aminopyrine (Pyramidone) in man and methods for the estimation of aminopyrine and its metabolites in biological material. J. Pharmacol Exptl. Therap.99, 171–184 (1950)
Caspary, W.F., Hesch, R.D., Matte, R.:, Effect of vitamin D and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on intestinal calcium absorption in epileptics under anticonvulsant therapy. Horm. Metabol. Res.7 271–273 (1975)
Caspary, W.F., Reimold, W.V.: Klinische Bedeutung des14C-Glykocholat-Atemtestes in der gastroenterologischen Diagnostik bei Erkrankungen mit gesteigerter Dekonjugation von Gallensäuren. Deutsche Med. Wschr.101, 353–360 (1976)
Caspary, W.F., Schäffer, J., Brunner, G.:14C-Aminopyrin-(Pyramidon®)-Atemtest — neuer quantitativer Leberfunktionstest. 82. Tagung der Deutschen Ges. für Innere Medizin, Wiesbaden, April 1976
Conney, A.H., Davidson, C., Gastel, R.: Adaptive increases in drug metabolizing enzymes induced by phenobarbital and other drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exptl. Ther.130, 1–8, (1960)
Conney, A.H.: Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol. Rev.19, 317–366 (1967)
Fromm, H., Hofmann, A.F.: Breath-test for altered bile-acid metabolism. Lancet2, 621–625 (1971)
Hepner, G.W., Vesell, E.S.: Assessment of aminopyrine metabolism in man by breath analysis after oral administration of14C-aminopyrine. New Engl. J. Med.291, 1384–1388 (1974)
Gelehrter, T.D.: Enzyme induction. New Engl. J. Med.294, 589–595 (1976)
Remmer, H.: The role of the liver in drug metabolism. Amer. J. Med.49, 617–629 (1970)
Silver, J., Neale, G., Thompson, G.R.: Effect of phenobarbitone treatment on vitamin D metabolism in mammals. Clin. Science Mol. Med.46, 433–448 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Wesentliche Teile der Arbeit wurden von J. Schäffer im Rahmen einer Inaugural-Dissertation der Medizinischen Fakultät der Universität Göttingen durchgeführt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caspary, W.F., Schäffer, J. Gesteigerte Demethylierung von Aminophenazon unter antikonvulsiver Langzeitbehandlung. Klin Wochenschr 56, 677–679 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01477022
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01477022
Key words
- Demethylation
- Aminopyrine
- Drugs metabolism
- Antiepileptic drugs
- Calcium absorption
- Diphenylhydantoin
- Microsomal enzyme system