Summary
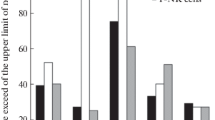
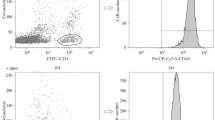
In patients with Hodkin's disease, the impaired immune reactivity, especially of the thymus dependent system, is well established. This decreased immune response of the lymphocytes from the peripheral blood contrasts to an increased lymphocytopoiesis in the lymphatic organs with a hyperplasia of these tissues. We studied the reactivity of peripheral T lymphocytes from 20 patients with Hodgkin's disease and 26 healthy control persons against autologous and allogeneic non T cells respectively in the mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC). Our experiments show an extremely depressed autologous mixed lymphocyte reactivity (MLR) of T lymphocytes from patients with Hodgkin's disease compared to those from normal donors. In the allogeneic MLC, the proliferation of the patients' T cells was stronger than in the autologous MLC, but significantly lower than the proliferation of normal T lymphocytes when stimulated by normal non T cells. Patients' non T cells stimulated T lymphocytes from healthy donors as well as non T lymphocytes from normals did. Finally, the autologous MLR of normal lymphocytes was significantly suppressed by 18 of 23 sera from Hodgkin's patients when these sera were substituted for normal AB serum in the cultures. These results demonstrate an impaired function of T lymphocytes from patients with Hodgkin's disease in the autologous MLC and the presence of one or more factors in their serum which inhibit the proliferation of normal lymphocytes in the autologous MLC. The role of suppressor cells and their factors will be discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Die gestörte Funktion des Immunsystems, besonders die der zellulären Immunabwehr ist bei Patienten mit Morbus Hodgkin seit langem bekannt. Dabei steht der verminderten Reaktivität der peripheren Blutlymphozyten eine gesteigerte Lymphozytopoese in lymphatischen Organen mit Hyperplasie dieser Gewebe gegenüber. Wir untersuchten die Reaktivität peripherer T-Lymphozyten von 20 Patienten mit Morbus Hodgkin und 26 gesunden Kontrollpersonen gegen autologe und allogene Nicht-T-Lymphozyten in der gemischten Lymphozytenkultur (MLC). Unsere Versuche hatten folgende Ergebnisse: (1) T-Lymphozyten von Morbus Hodgkin-Patienten werden nicht oder nur sehr schwach in der autologen MLC stimuliert. (2) In der allogenen MLC reagieren T-Zellen von Patienten deutlich stärker als in der autologen MLC, jedoch significant geringer als normale T-Lymphozyten gegen normale Nicht-T-Lymphozyten. Nicht-T-Zellen von Patienten stimulieren dagegen allogene T-Lymphozyten von Gesunden kaum weniger als normale Nicht-T-Zellen. (3) Wird eine autologe MLC mit Lymphozyten gesunder Spender, jedoch mit Serum von Patienten mit Morbus Hodgkin durchgeführt, zeigt sich eine signifikante, dosisabhängige Verminderung der Reaktivität gegenüber Kontrollen mit Serum von Normalpersonen. Diese Ergebnisse zeigen zusammengefaßt bei Patienten mit Morbus Hodgkin eine gestörte Funktion der T-Lymphozyten in der autologen MLC und die Existenz eines oder mehrerer Serumfaktoren, die die Proliferation von T-Lymphozyten gesunder Personen in der autologen MLC hemmen. Die Rolle von Suppressorzellen und derer Faktoren als Ursache für diese Befunde wird diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amlot PL, Slaney JM, Williams BD (1976) Circulating immune complexes and symptoms in Hodgkin's disease. Lancet 1:449
Bach FH, Voynow NK (1966) One-way stimulation in mixed lymphocyte culture. Science 153:545-
Begemann M, Claas G (1979) Suppression of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactivity by serum from patients with Hodgkin's disease. Immunobiol 156:264 (Abstract)
Begemann M, Claas G, Falke H (1980) Hemmung der autologen gemischten Lymphocytenkultur bei Morbus Hodgkin. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med 86:1055
Bieber MM, Fuks Z, Kaplan HS (1977) E-rosette inhibiting substance in Hodgkin's disease spleen extracts. Clin Exp Immunol 29:369
Böyum A (1968) Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 21: [Suppl 97]:77
Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff KJ, Smithers DW, Tubiana M (1971) Report of committee on Hodgkin's disease staging classification. Cancer Res 31:1860
Desforges JF, Rutherford CJ, Piro A (1979) Hodgkin's disease. N Engl. J Med 301:1212
de Hazo RD (1980) Indomethacin-responsive mononuclear cell dysfunction in Hodgkin's disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 17:66
de Vita VT (1973) Lymphocyte reactivity in Hodgkin's disease: a lymphocyte civil war. N Engl J Med 289:801
Engleman EG, Benike C, Hoppe RT, Kaplan HS (1979) Suppressor cells of the mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Transplant Proc XI:1827
Engleman EG, Benike CJ, Hoppe RT, Kaplan HS (1980) Autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Evidence for a T cell defect. J Clin Invest 66:149
Fuks Z, Strober S, Kaplan HS (1976) Interaction between serum factors and T lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease. Use as a diagnostic test. N Engl J Med 295:1273
Glöckel U, Stasing C, Koch B, Leitner O, Kalden JR (1980) Autologous MLC reactivity (AMLC) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Immunobiol 157:221 (Abstract)
Goodwin JS, Bankhurst AD, Messner RP (1977) Suppression of human T cell mitogenesis by prostaglandin. Existence of a prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. J Exp Med 146:1719
Goodwin JS, Messner RP, Bankhurst AD, Peake GT, Saiki JH, Williams RC (1977) Prostaglandin-producing suppressor cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med 297:963
Goodwin JS, Webb DR (1980) Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 15:106
Grifoni V, del Giaco GS, Manconi PE, Tognella S (1972) Surface immunoglobulins on lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease. Lancet 1:848
Haakenstadt AO, Mannik M (1977) The biology of immune complexes. In: N Talal (ed) Automimmunity. Academic Press, New York, p 277
Hillinger SM, Herzig GP (1978) Impaired cell-mediated immunity in Hodgkin's disease mediated by suppressor lymphocytes and monocytes. J Clin Invest 61:1620
James SP, Elson CO, Waggoner JG, Jones EA, Strober W (1980) Deficiency of the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Invest 66:1305
Kabelitz D, Fink U, Flad HD, Rastetter J (1977) Lack of autologous MLC reaction in chronic lymphatic leukemia. Z Immun-Forsch 153:313 (Abstract)
Kaplan HS (1976) Hodgkin's disease and other human malignant lymphomas: advances and prospects — G.H.A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res 36:3863
Kaplan HS (1980) Hodgkin's Disease: Unfolding concepts concerning its nature, management and prognosis. Cancer 45:2439
Kaplan HS, Smithers DW (1959) Autoimmunity in man and homologous disease in mice in relation to malignant lymphomas. Lancet 2:1
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1957) Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J Am Statist Assoc 47:583
Kuntz MM, Innes JB, Weksler ME (1976) Impaired immune surveillance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Res 24:448 A (Abstract)
Kuntz MM, Innes JB, Weksler ME (1976) Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. IV. Human T lymphocyte proliferation induced by by autologous or allogeneic non T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 143:1042
Kuntz MM, Innes JB, Weksler ME (1979) The cellular basis of the impaired autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 63:151
Long JC (1979) The immunopathology of Hodgkin's disease. Clin Haematol 8:531
Lukes RJ, Craver LF, Hall TC, Rappaport H, Rubin P (1966) Part 1. Report of the nomenclature committee. Cancer Res 26:1311
Miller RA, Kaplan HS (1978) Generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes in the autologous mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol 121:2165
Miyasaka N, Sauvezie B, Pierce DA, Daniels TE, Talal N (1980) Decreased autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest 66:928
Moody CE, Casazza BA, Christenson WN, Weksler ME (1979) Lymphocyte transformation by autologous cells. VIII. Impaired autologous mixed lymphocyte reactivity in patients with acute infectious mononucleosis. J Exp Med 150:1448
Moretta L, Mingari MC, Moretta A (1979) Human T cell subpopulations in normal and pathologic conditions. Immunol Rev 45:163
Moretta L, Webb SR, Grossi CE, Lydyard PM, Cooper MD (1977) Functional analysis of two human T cell subpopulations: Help and suppression of B cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM (TM) or IgG (TG). J Exp Med 146:184
Offner H, Clausen J (1974) Inhibition of lymphocyte response to stimulants induced by unsatured fatty acids and prostaglandins. Lancet 2:400
Opelz G, Kiuchi M, Takasugi M, Terasaki PI (1975) Autologous stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulations. J Exp Med 142:1327
Order SE, Hellmann S (1972) Pathogenesis of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet 1:571
Reed DM (1902) On the pathological changes in Hodgkin's disease, with especial reference to its relation to tuberculosis. John Hopkins Hosp Rep 10:133
Romagnani S, Maggi E, Biagiotti R, Giudizi MG, Amadori A, Ricci M (1978) Altered proportion of Tμ and Tγ-cell subpopulations in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Scand J Immunol 7:511
Sachs L (1968) Statistische Auswertungsmethoden. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sakane T, Green JI (1979) Specificity and suppressor function of human T cells responsive to autologous non T cells. J Immunol 123:584
Sakane T, Steinberg AD, Green I (1978) Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction between T and non T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3464
Schechter GP, Soehnlen F (1978) Monocyte-mediated inhibition of lymphocyte blastogenesis in Hodgkin's disease. Blood 52:261
Scheurlen PG, Schneider W, Pappas A (1971) Inhibition of transformation of normal lymphocytes by plasma factor from patients with Hodgkin's disease and cancer. Lancet 2:1265
Scheurlen PG, Schneider W, Pappas A (1972) Identifizierung eines Lymphocytenhemmfaktors im Serum von Patienten mit malignen Tumoren. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med 78:129
Seiler FR, Sedlacek HH, Kanzy EJ, Lang W (1972) Über die Brauchbarkeit immunologischer Nachweismethoden zur Differenzierung funktionell verschiedener Lymphozyten: Spontanrosetten, Komplementreceptor-Rosetten, und Immunglobulinrezeptoren. Behring Inst Mitt 52:26
Sibbitt WL, Bankhurst AD, Williams RC (1978) Studies of cell subpopulations mediating mitogen hyporesponsiveness in patients with Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest 61:55
Sinkovics JG, Shullenberger CC (1975) Hodgkin's disease (Letter). Lancet 2:506
Smith JB, Knowlton RP (1979) Activation of suppressor T lymphocytes in human autologous mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol 123:419
Smith JB, Knowlton RP, Koons LS (1977) Immunologic studies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: defective stimulation of T cell proliferation in autologous mixed lymphocyte culture. J Natl Cancer Inst 58:579
Stockman GD, Mumford DM (1974) The effect of prostaglandins on the in vitro blastogenic response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Exp Haematol 2:65
Sugden PJ, Lilleyman JS (1980) Impairment of lymphocyte transformation by plasma from patients with advanced Hodgkin's disease. Cancer 45:899
Tomonari K (1980) Cytotoxic T cells generated in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. I. Primary autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol 124:1111
Trepel F, Schick P (1977) Morbus Hodgkin — eine atypische Immunreaktion. Med Klin 72:1003
Twomey JJ, Laughter AH, Farrow S, Douglass CC (1975) Hodgkin's disease. An immunodepleting and immunosuppressive disorders. J Clin Invest 56:467
Van de Stouwe RA, Kunkel HG, Halper JP, Weksler ME (1977) Autologous mixed lymphocyte culture reactions and generation of cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med 146:1809
Webb DR, Jamieson AT (1976) Control of mitogen-induced transformation: Characterisation of a splenic suppressor cell and its mode of action. Cell Immunol 24:45
Webb DR, Nowowiejski I (1978) Mitogen-induced changes in lymphocyte prostaglandin levels: A signal for the induction of suppressor cell activity. Cell Immunol 41:72
Webb DR, Osheroff PL (1976) Antigen stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis and control of immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1300
Weir DM (ed) (1978) Handbook of experimental immunology, 3d edn. Blackwell, Oxford London Edinburgh Melbourne
Weksler ME, Kozak R (1977) Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. V. Generation of immunologic memory and specificity during the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Exp Med 146:1833
Yam LT, Li CY, Crosby WH (1971) Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol 55:183-
Zorini CO, Neri A, Comis M, Manella E, Paciucci PA (1974) Influence of Hodgkin's serum on PHA stimulation of normal lymphocytes. Lancet 1:745
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Begemann, M., Claas, G. & Falke, H. Impaired autologous mixed lymphocyte reactivity in Hodgkin's disease. Klin Wochenschr 60, 19–26 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01721583
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01721583