Summary
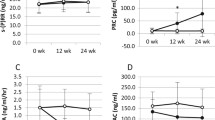
The effects of orally administered glandular kallikrein on urinary kallikrein, aldosterone and prostaglandin E (PGE) excretion, plasma renin activity (PRA), immunoreactive 6-keto PGF1α and thromboxane B2 concentrations and platelet aggregation were studied in 12 patients with essential hypertension (EH). After a 2-week control period, each patient was given orally 450 KU/day of hog glandular kallikrein for 8 weeks. Urinary kallikrein, aldosterone and PGE excretion, and plasma 6-keto PGF1α and thromboxane B2 concentrations were measured by radio-immunoassay. Platelet aggregation was measured by the addition of ADP, collagen or ristocetin with an aggregometer. Urinary kallikrein excretion and plasma 6-keto PGF1α concentration were significantly decreased in patients with EH. There were no significant differences in PRA, urinary aldosterone excretion and plasma thromboxane B2 concentrations between control subjects and patients with EH. There was a significant decrease in blood pressure in patients with EH coinciding with significant increases of urinary kallikrein and PGE excretion and plasma immunoreactive 6-keto PGF1α concentration after administration of glandular kallikrein. There was also a significant inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by collagen in these patients. Thus, a suppression of the kallikrein-kinin-prostaglandin system in patients with EH was found, and a decrease in blood pressure with an increment of urinary kallikrein, PGE excretion, plasma immunoreactive 6-keto PGF1α and inhibition of platelet aggregation in vivo by the administration of glandular kallikrein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BK:
-
bradikinin
- EH:
-
essential hypertension
- KU:
-
kallikrein unit
- PG:
-
prostaglandin
- PRA:
-
plasma renin activity
- PRP:
-
platelet rich plasma
- TX:
-
thromboxane
References
Abe K, Seino M, Otsuka Y, Yoshinaga K (1976) Urinary kallikrein excretion and sodium metabolism in human hypertension. In: Pisano JJ, Austen KF (eds) Chemistry and biology of the kallikrein-kinin system in health and disease. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington. Forgarty Center Proceedings No. 27, 411
Born GV (1962) Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature 194:927–929
Carretero OA, Scicli AG (1978) The renal kallikrein-kinin system in human and in experimental hypertension. Klin Wochenschr 56 (suppl 1):113–125
Chen LS, Ito T, Ogawa K, Shikano M, Satake T (1984) Plasma concentrations of 6-keto prostaglandin F1α, thromboxane B2 and platelet aggregation in patients with essential hypertension. Jpn Heart J 25:1001–1009
Elliot AH, Nuzum FR (1934) The urinary excretion of a depressor substance (kallikrein of Frey and Kart) in arterial hypertension. Endocrinology 18:462–474
Fink E, Dietl T, Seifert J, Fritz H (1979) Studies on the biological function of glandular kallikrein. Adv Exp Med Biol 120B, 261–273
FitzGerald GA, Pedersen AK, Patrono C (1983) Analysis of prostacyclin and thromboxane biosynthesis in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 67:1174–1177
Granström E, Samuelsson B (1978) Quantitative measurement of prostaglandins and thromboxanes: General considerations. Frölich (ed) Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res Vol 5. Raven Press, New York, pp 119–210
Grose JH, Lebel M, Gbeassor FM (1980) Diminished urinary prostacyclin metabolites in essential hypertension. Clin Sci (suppl 6):1215–1235
Haber E, Koerner T, Page LB, Kliman B, Purnode A (1967) Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurement of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol 29:1349–1355
Jaffe BM (1974) Radioimmunoassay in clinical medicine. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield Ill
Margolius HS, Geller RG, Pisano JJ, Sjoerdsma A (1971) Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet II 1063–1065
Margolius HS, Geller KF, de Jong W, Pisano JJ, Sjoerdsma A (1972) Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertension. Circ Res 31 (suppl II):125–131
Morita I, Kanayasu T, Murota S (1984) Kallikrein stimulates prostacyclin in bovine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Acta 792:304–309
Nasjletti A, Malik KU (1981) Relationships between the kallikrein-kinin and prostaglandin systems. Life Sci 25:99–109
Overlack A, Stumpe KO, Ressel C, Kolloch R, Zywzok W, Krück F (1980) Decreased urinary kallikrein activity and elevated blood pressure normalized by orally applied kallikrein in essential hypertension. Klin Wochenschr 58:37–42
Overlack A, Stumpe KO, Ressel C, Krück F (1979) Low urinary kallikrein excretion and elevated blood pressure normalized by orally applied kallikrein in essential hypertension. Clin Sci 57:263–265
Shimamoto K, Chano J, Margolius HS (1980) The radioimmunoassay of human urinary kallikrein and comparisons with kallikrein activity measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 51:840–848
Smith MC, Dunn MJ (1981) Renal kallikrein, kinins and prostaglandins in hypertension. In: Hypertension, Vol 8: Contemporary Issues in Nephrology. Brenner BM, Stein JH (eds). Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 168–202
Uehara Y, Ishii T, Ikeda T, Atarashi K, Takeda T, Murao S (1983) Plasma levels of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α in normotensive subjects and patients with essential hypertension. Prostaglandin, Leukotoriens and Med 11:95–104
Werle E, Korsten H (1938) Der Kallikreingehalt des Herzens, des Speichels und des Blutes bei Gesunden und Kranken. Z Ges Exp Med 103:153–162
Yanaihara T, Okaru Y, Yanaihara N, Kojima A, Sato M, Inoue S, Suzuki K (1981) Intestinal absorption of glandular kallikrein in rabbits. Tan To Sui 2:263–370 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogawa, K., Ito, T., Ban, M. et al. Effects of orally administered glandular kallikrein on urinary kallikrein and prostaglandin excretion, plasma immunoreactive prostanoids and platelet aggregation in essential hypertension. Klin Wochenschr 63, 332–336 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731977
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731977