Summary
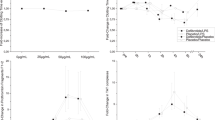
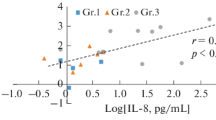
Fibrinolysis induced by the infusion of plasminogen activators into the circulation has been shown to cause coagulation disorders in ascites retransfusion. Dexamethasone is known to inhibit the synthesis of plasminogen activators by peritoneal macrophages. We therefore assessed its potential in preventing the occurrence of fibrinolysis by injecting 16 mg dexamethasone intraperitoneally in 10 patients 24 h before ascites retransfusion was performed. In addition, the effect of dexamethasone upon the activity or concentration of several proteases and antiproteases related to coagulation in plasma and ascites was analyzed on 15 occasions. An increase of the activity of plasminogen, α2-antiplasmin, and antithrombin III, and in the concentration of α1-protease inhibitor in ascites was induced by the dexamethasone injection. However, the reaction was not identical in all patients. Those patients having an increase of plasminogen activities of 0.6 CTA U/ml or more did not show signs of fibrinolysis during retransfusion. The results obtained indicate that intraperitoneal injection of dexamethasone decreases the concentration of plasminogen activators in ascites and thereby reduces the risk of coagulation disorders during retransfusion procedures. Since the effect is variable and not sustained, assessment of preoperative plasminogen concentrations is mandatory in order to prevent complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α2AP:
-
α2-Antiplasmin
- α1PI:
-
α1-Protease inhibitor
- AT III:
-
Antithrombin III
- CTA:
-
Committee on Thrombolytic Agents
- DIC:
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- EAR:
-
Extracorporeal ascites retransfusion
- FDP:
-
Fibrin(ogen) degradation products
- FM:
-
Fibrin monomers
- PVS:
-
Peritoneovenous shunt
References
Büller HR, Ten Cate JW (1983) Antithrombin III infusion in patients undergoing peritoneovenous shunt operation: failure in the prevention of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 49:128–131
Chapman HA, Vavrin Z, Hibbs JB (1982) Macrophage fibrinolytic activity: identification of two pathways of plasmin formation by intact cells and of the plasminogen activator inhibitor. Cell 28:653–662
Collen D (1976) Identification and some properties of a new fast reacting inhibitor in human plasma. Eur J Biochem 69:209–216
Epstein M (1982) Peritoneovenous shunt in the management of ascites and the hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology 82:790–799
Gibson PR, Dudley FJ, Jakobovits AW, Salem HH, McInnes IE (1981) Disseminated intravascular coagulation following peritoneovenous (LeVeen) shunt. Aust N Z J Med 11:8–12
Gordon S, Unkeless J, Cohn ZA (1974) Induction of macrophage plasminogen activator by endotoxin stimulation and phagocytosis. J Exp Med 140:995–1010
Hamilton JA (1981) Regulation of prostaglandin and plasminogen activator production by mouse peritoneal macrophage. J Reticuloendothelial Soc 30:115–128
Kumar R, Deykin D (1979) Pathogenesis and practical management of coagulopathy of liver disease. In: Davidson CS (ed) Problems in liver disease. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York, pp 66–78
Maier RV, Ulevtich RJ (1981) The induction of a unique procoagulant activity in rabbit hepatic macrophages by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol 127:1596–1600
Rivers RPA, Hathaway WE, Weston WL (1975) The endotoxin-induced coagulant activity of human monocytes. Br J Haematol 30:311–316
Schölmerich J, Volk BA, Köttgen E, Wilms H, Hasler C, Billmann P, Gerok W (1985) Ascites — neue Aspekte zur Pathophysiologie, Diagnostik and Therapie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 110:512–518
Schölmerich J, Diener W, Köttgen E, Maier KP, Costabel U, Gerok W (1986) Die extrakorporale Ascites-Reinfusion zur raschen Ascites-Elimination bei gastroenterologischen Notfallpatienten. Intensivmedizin 22:308–314
Schölmerich J, Zimmermann U, Köttgen E, Volk BA, Ehlers S, Gerok, W (1987) Proteases and antiproteases related to the coagulation system in plasma and ascites. I. An approach to differentiate between malignant and cirrhotic ascites. Klin Wochenschr 65:634–638
Schölmerich J, Zimmermann U, Köttgen E, Volk BA, Wilms H, Hasler C, Costabel U, Gerok W (1987) Proteases and antiproteases related to the coagulation system in plasma and ascites. Prediction of coagulopathy in ascites reinfusion. Clin Chim Acta, submitted for publication
Seifert SC, Gelehrter TD (1978) Mechanism of dexamethasone inhibition of plasminogen activator in rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 75:6130–6133
Tanner A, Keyhani A, Reiner R, Holdstock G, Wright R (1981) Proteolytic enzymes released by liver macrophages may promote hepatic injury in a rat model of hepatic damage. Gastroenterology 80:647–654
Tawes RL, Sydorak GR, Kennedy PA, Brown WH, Scribner RG, Beare JP, Harris EJ (1981) Coagulopathy associated with peritoneovenous shunting. Am J Surg 142:51–55
Vassalli JD, Hamilton J, Reich E (1976) Macrophage plasminogen activator: modulation of enzyme production by antiinflammatory steroids. Cell 8:171–181
Volk BA, Schölmerich J, Wilms H, Köttgen E, Witz G, Billmann P, Hoppe-Seyler P, Gerok W (1986) Peritoneovenöser Shunt in der Aszitestherapie: Komplikationen der Behandlung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 110:1685–1691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schölmerich, J., Zimmermann, U., Köttgen, E. et al. Proteases and antiproteases related to the coagulation system in plasma and ascites — Influence of dexamethasone. Klin Wochenschr 65, 639–642 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01875498
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01875498