Abstract
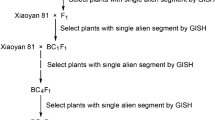
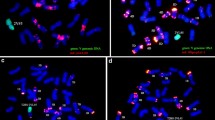
Several Triticum aestivum L.-Haynaldia villosa disomic 6VS/6AL translocation lines with powdery mildew resistance were developed from the hybridization between common wheat cultivar Yangmai 5 and alien substitution line 6V(6A). Mitotic and meiotic C-banding analysis, aneuploid analysis with double ditelosomic stocks, in situ hybridization, as well as the phenotypic assessment of powdery mildew resistance, were used to characterize these lines. The same translocated chromosome, with breakpoints near the centromere, appears to be present in all the lines, despite variation among the lines in their morphology and agronomic characteristics. The resistance gene, conferred by H. villosa and designated as Pm21, is a new and promising source of powdery mildew resistance in wheat breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen PD, Liu DJ (1982) Cytogenetic studies of hybrid progenies between Triticum aestivum and Haynaldia villosa. J Nanjing Agric Univ 4:1–16
Chen PD, Liu DJ (1986) Identification of Haynaldia villosa chromosomes in alien wheat additions. In: Li ZS (ed) Proc 1st Int Symp on Chromosome Engineering in Plants, Xian, China, pp 31–33
Friebe B, Hatchett JH, Gill BS, Mukai Y, Sebeta EF (1991a) Transfer of Hessian fly resistance from rye to wheat via radiation-induced terminal and intercalary chromosome translocations. Theor Appl Genet 83:33–40
Friebe B, Mukai Y, Dhaliwal HS, Martin TJ, Gill BS (1991b) Identification of alien chromatin specifying resistance to wheat streak mosaic and greenbug in wheat germplasm by C-banding and in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 81:381–389
Friebe B, Jiang J, Gill BS, Dyck PL (1993) Radiation-reduced non-homoeologous wheat-Agropyron intermedium chromosomal translocations conferring resistance to leaf rust. Theor Appl Genet 86:141–149
Gill BS, Friebe B, Endo TR (1991) Standard karyotype and nomenclature system for description of chromosome bands and structural aberrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 34:830–839
Hueros G, Gonzales JM, Sanz JC, Ferrer E (1991) Gliadin gene location and C-banding identification of Aegilops longissima chromosomes added to wheat. Genome 34:236–240
Jiang JM, Gill BS (1993) A “zebra” chromosome arising from multiple translocations involving non-homoeologous chromosomes. Chromosoma 102:612–617
Jiang JM, Chen PD, Friebe B, Raupp WJ, Gill BS (1993) Alloplasmic wheat-Elymus ciliaris chromosome addition lines. Genome 36:327–333
Jiang JM, Morris KLD, Gill BS (1994) Introgression of Elymus trachycaulus chromatin into common wheat. Chromosome Res, 2:3–13
Lapitan NLV, Sears RG, Gill BS (1984) Translocation and other karyotypic structural changes in wheat x rye hybrids regenerated from tissue culture. Theor Appl Genet 68:547–554
Le HT, Armstrong KC, Miki B (1989) Detection of rye DNA in wheat-rye hybrids and wheat translocation stocks using total genomic DNA as a probe. Plant Mol Biol Rep 7:150–158
Liu DJ, Chen PD, Pei GZ, Wang YN, Qiu BX, Wang SL (1988) Transfer of Haynaldia villosa chromosomes into Triticum aestivum. In: Miller TE, Koebner RMD (eds) Proc 7th Int Wheat Genet Symp, Cambridge, UK, pp 355–361
Liu DJ, Chen PD, Raupp JW (1993) Determination of homoeologous groups of Haynaldia villosa chromosomes. In: Proc 8th Int Wheat Genet Symp, Beijing, China, pp 181–185
Li WL, Chen PD, Qi LL, Liu DJ (1995) Cloning of repeated DNA sequences specific to Haynaldia villosa for detecting its chromatin in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 90:526–533
McIntosh RA (1983) A catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proc 6th Int Wheat Genet Symp, Kyoto, Japan, pp 1218–1225
Mukai Y, Gill BS (1991) Detection of barley chromatin added to wheat by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 34:448–452
Pei GZ, Chen PD, Liu DJ (1986) A cytogenetic analysis of some powdery mildew-resistant strains of hybrid progeny between wheat and Haynaldia villosa. J Nanjing Agric Univ 1:1–9
Qi LL, Chen PD, Liu DJ (1995) The gene Pm21-a new source of resistance to wheat powdery mildew. Acta Agron Sin 21(3): 257–260
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KA, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Schafer JF (1987) Wheat disease — rusts, smuts and powdery mildew. In: Heyne EG (ed) Wheat and wheat improvement (2nd edn.). Amer Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 542–584
Wu ZS (1990) Breeding for disease resistance. In Wu ZS (ed) Wheat breeding. Agric Pub Press of China, Beijing, pp 267–270
Xiong EW, Cao Y, Bo YJ, Xia QP, Yang XY, Wu ZF (1983) Identification and analysis of powdery mildew resistance in common wheat cultivars. Plant Protection of China 3:5–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. E. Hart
This research was supported by grants from the National High-Tech R and D Program and the National Science and Technology Commission
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P.D., Qi, L.L., Zhou, B. et al. Development and molecular cytogenetic analysis of wheat-Haynaldia villosa 6VS/6AL translocation lines specifying resistance to powdery mildew. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 91, 1125–1128 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223930
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223930