Abstract
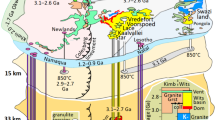
The vein graphite deposits of Sri Lanka are located in a Precambrian high grade metamorphic terrain dominated by granulite facies rocks. The vein graphite has been interpreted as being of solid phase lateral secretion origin, derived by hydrothermal solutions or of biogenic origin. Based on what is known on the composition of the fluids under granulite facies conditions and the role of these fluids in their transport through the crust, the origin of the graphite is proposed to be the direct consequence of granulite facies metamorphism in the presence of a CO2 rich fluid under low fO2 conditions. This CO2 rich fluid could promote hydraulic fracturing and precipitation of vein graphite. Textures and structures of the vein graphite indicate syntectonic deposition by a crack-seal process under granulite facies metamorphic conditions. This model is supported by temperature estimates on graphite based on XRD data and stable carbon isotopes of graphite that suggest a deep-seated crustal origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger, A.R., Jayasinghe, N.R.: Precambrian structure and chronology in the Highland Series of Sri Lanka. Prec. Res. 3:559–576 (1976)
Cameron, E.N.: Graphite in Industrial Minerals and Rocks. J.L. Gilson (Ed), AIME, New York, 455–468 (1960)
Cooray, P.G.: Geology of the country around Rangala, Geol. Surv. Dept., Ceylon, Mem. 2:138 p. (1961)
Cooray, P.G.: Geology of the country around Alutgama, Geol. Surv. Dept., Ceylon, Mem. 3:111 p. (1965)
Cooray, P.G.: An introduction to the geology of Ceylon. Nat'l Museums of Ceylon, Colombo, 324 p. (1967)
Cooray, P.G.: Hornblende-garnet granulites from Hatton, Ceylon. Geol. Mag. 109:37–44 (1972)
Dahanayake, K., Jayasena, H.A.H.: General geology and petrology of some Precambrian crystalline rocks from the Vijayan complex of Sri Lanka. Prec. Res. 19:301–315 (1983)
Diessel, C.F.K., Offler, R.: Change in physical properties of coalified and graphitised phytoclasts with grade of metamorphism. Neus. Jahr. Min. Mon. 1:11–26 (1975)
Dissanayake, C.B.: The origin of graphite of Sri Lanka. Org. Geoch. 3:1–7 (1981)
Dobner, A., Graf, W., Hahn-Weinheimer, P., Hirner, A.: Stable carbon isotopes of graphite from Bogala Mine, Sri Lanka. Lithos 11:251–255 (1978)
Douthitt, C.B.: Precambrian coal or anthraxolite: A Source for Graphite in high-grade schists and gneisses — A discussion. Ec. Geol. 77:1247–1249 (1982)
Douthitt, C.B.: Boron in graphite: content, speciation and significance. Chem. Geol. 53:129–133 (1985)
Erdosh, G.: Geology of the Bogala Mine, Ceylon and the origin of vein type graphite. Min. Dep. 5:375–382 (1970)
Ferry, J.M.: Petrology of the graphitic sulfide-rich schists from south-central Maine: an example of desulfudation during prograde regional metamorphism. Am. Mineral. 66:908–930 (1981)
Fyfe, W.S., Price, N.J., Thompson, A.B.: Fluids in the Earth's Crust. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 383 pp. (1978)
Garson, M.S., Goossens, P.J.: Comparative Gondwana metallogeny and structures in southwestern India, Sri Lanka and Madagascar, Abstr., 26th IGC, Paris, 934 (1980)
Glassley, W.: Fluid evolution and graphite genesis in the deep continental crust. Nature 295:229–231 (1982)
Glassley, W.: Deep crustal carbonates as CO2 fluid sources: evidence from metasomatic reaction zones. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 84:15–24 (1983)
Goossens, P.J.: Graphite deposits of the Precambrian and their mining development. In UN DTCD, The Development Potential of Precambrian Mineral Deposits, 123–155 (1981)
Hamilton, L.H., Ramsden, A.R., Stephens, J.F.: Fossiliferous graphite from Undercliff, NSW. Jour. Geol. Soc. Australia 17:31–37 (1970)
Hansen, E.C., Newton, R.C., Janardhan, A.S.: Fluid inclusions in rocks from the amphibolite facies gneiss to charnockite progression in Southern Karnataka, India: direct evidence concerning the fluids of granulite metamorphism. J. Met. Geol. 2:249–264 (1984)
Hoefs, J.: Stable Isotope Geochemistry. 208 p. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer, 1980
Katz, M.B.: The Precambrian metamorphic rocks of Ceylon. Geol. Rund. 60:1523–1549 (1971)
Katz, M.B.: Facies series of the high grade metamorphic rocks of the Ceylon Precambrian. 24th IGC, Montreal, Sec. 2:43–51 (1972)
Katz, M.B.: Lineament analysis of LANDSAT imagery applied to mineral exploration. AGID Rept. 7:157–166 (1982)
Kumar, G.R.R., Srikantappa, C., Hansen, E.: Charnockite formation at Ponmudi in Southern India. Nature 313:207–209 (1985)
Lamb, W., Valley, J.W.: Metamorphism of reduced granulites in low CO2 vapour free environment. Nature 312:56–58 (1984)
Landis, C.A.: Graphitization of dispersed carbonaceous material in metamorphic rocks. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 30:34–45 (1971)
Perera., L.R.K.: Co-existing cordierite-almandine — A key to the metamorphic history of Sri Lanka. Prec. Res. 25:349–364 (1984)
Ramsay, J.G., Huber, M.I.: The Techniques of Modern Structural Geology, Vol. 1. Strain Analysis, Academic Press, London, 307 p. (1983)
Shengelia, D.M., Akhulediani, R.A., Ketskhoveli, D.N.: The graphite geothermometer. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSR 235:132–134 (1979)
Silva, K.K.M.W.: Tectonic control of graphite mineralization in Sri Lanka. Geol. Mag. 111:307–312 (1974)
Sturt, B.A.: Exsolution during metamorphism with particular reference to feldspar solid solution. Min. Mag. 37:815–832 (1970)
Wadia, D.N.: A brief account of the mineralogy of the graphite deposits of Ceylon; a note on the origin of graphite. Ceylon Dept. Mineral Rec., Prof. Pap. 1:15–24 (1945)
Weis, P.L., Friedman, I., Gleason, J.P.: The origin of epigenetic graphite: evidence from isotopes. Geoch. Cosmoch. Acta 45:2325–2332 (1981)
Wijayananada, N.P., Jayawardena, D.E.S.: Some aspects of the geology of graphite mineralisation in Sri Lanka, with particular reference to Kahatagaha-Kolongaha area. Trans. Instn. Min. Metall. B 92:93–98 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, M.B. Graphite deposits of Sri Lanka: a consequence of granulite facies metamorphism. Mineral. Deposita 22, 18–25 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204238
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204238