Abstract
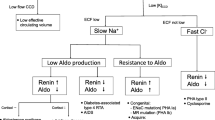
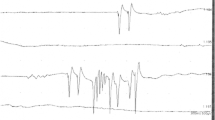
We report two cases of ascending muscular weakness progressing to areflexic quadriplegia caused by severe derangement of potassium homeostasis. The first patient presented with a 17-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency and severe hypokalemia. The second case had primary adrenocortical deficiency (Addison's disease) and extreme hyperkalemia. Complete recovery ensued after correction of the metabolic disorder in both cases. The role of potassium in the pathophysiology of neuromuscular excitation is discussed. We conclude that when neuromyopathy is present, metabolic causes should be considered and the serum potassium determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabow PA, Peterson LN (1980) Disorders of potassium metabolism. In: Schrier RW (ed) Renal and electrolyte disorders. Little-Brown, Boston, pp 183–221
Goldman DE (1943) Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes. J Gen Physiol 27:37
Hodgkin AL, Horowicz P (1959) Movements of sodium and potassium in single muscle fibers. J Physiol 146:405
Mohamed SD, Chapman RS, Crooks J (1966) Hypokalemia, flaccid quadraparesis and myoglobinuria with carbenoxolone. Br Med J 1:1581
Pollen RH, William RH (1960) Hyperkalemic neuromyopathy in Addison's disease. N Engl J Med 263:273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villabona, C., Rodriguez, P., Joven, J. et al. Potassium disturbances as a cause of metabolic neuromyopathy. Intensive Care Med 13, 208–210 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00254706
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00254706